- Diverticulitis can be a serious condition, so catching and treating it early is important to avoid complications.
- Lifestyle changes can help lower the risk of developing or reduce symptoms of diverticular disease, including maintaining a healthy weight, stopping smoking and following a healthy diet.
- Diverticulosis is more common in older people.
- Diverticulosis does not always progress to diverticulitis.
Diverticulitis is a serious condition that affects men and women of all ages, although it is more common in older people. Untreated diverticulitis can be a very serious health issue. It’s important to know that a healthy, well-rounded diet can reduce the risk of developing diverticular diseases. Around 200,000 people are hospitalized for diverticulitis each year in the United States alone. It’s important to manage diverticular disease carefully. Careful application of some home remedies, coupled with a few lifestyle changes, can help alleviate the condition and stop it from reaching the stage where it requires surgical intervention.
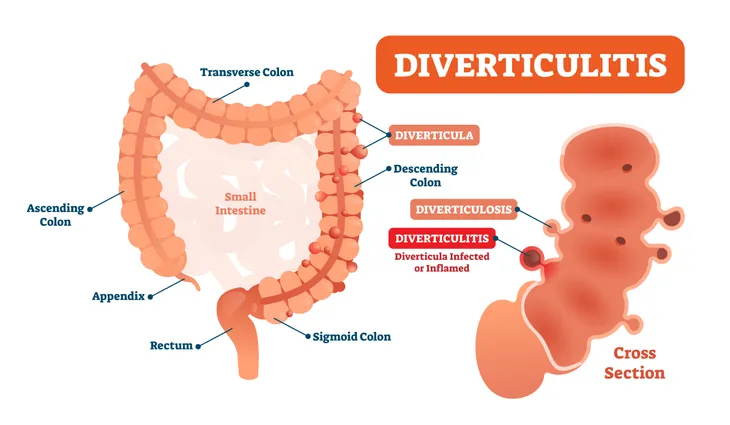
Diverticulosis vs. Diverticulitis: What’s the Difference?
Diverticulosis and diverticulitis are two conditions that occur in your large intestine (also called your colon), says the Cleveland Clinic. Even though they sound similar and both occur in the large intestine, there are some key differences you should know.
Diverticulosis refers to the presence of bulges in the wall of the colon, known as diverticula. Diverticulosis is common and it does not usually cause symptoms or need treatment. In contrast, diverticulitis refers to the inflammation and/or infection of the diverticula. Mild cases of diverticulitis can be treated using antibiotics. More serious cases may require surgical intervention.
Causes and Risk Factors of Diverticulitis
It’s not fully known what causes this condition, but it’s thought that people are at greater risk of developing diverticulosis if they don’t eat enough fiber. Low fiber diets can lead to constipation, which puts strain on the tissues of the colon. Over time, the increased pressure causes diverticula to form, and these may then become infected due to the presence of bacteria in the stools.
A low-fiber diet isn’t the only risk factor for diverticulitis. The Mayo Clinic says, being obese, leading a sedentary lifestyle, and consuming a diet high in animal fat can also increase your risk. Smoking and taking certain medications can also be contributing factors to the development of diverticulitis.
What Are the Symptoms of Diverticulitis?
Diverticulosis is often asymptomatic; however, some people do experience minor symptoms such as:
- Bloating
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Cramping or abdominal pain
The above symptoms may be chronic (persistent).
Diverticulitis can cause acute symptoms, which appear suddenly but do not last for a long time. Symptoms of diverticulitis can include:
- Pain in the lower-left area of the abdomen
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Fevers and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
Most people with diverticulitis experience pain that comes on suddenly and is quite severe. However, the pain can be mild at first and worsen gradually over time in some cases.
Can Diverticulitis Be Treated?
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases notes that diverticulitis can be treated using antibiotics. In some cases, doctors may also prescribe pain relief in the form of acetaminophen. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatories are not recommended for people with diverticulitis because they may increase the risk of complications.
Another common treatment for diverticulitis is to go on a liquid diet for a while to rest the colon. If this is recommended, then the diet will gradually re-introduce solid foods as the patient’s symptoms improve. If the symptoms do not improve with the above treatments, then surgery may be required to remove parts of the colon.
Managing Diverticular Disease at Home
Diverticular disease affects people of all ages, but it’s more common in older adults. You can reduce your risk of developing diverticular disease by maintaining a healthy weight, stopping smoking, and eating a high-fiber diet.
People who use aspirin or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory painkillers on a regular basis are at an increased risk of developing diverticula. Seek professional medical advice if you have been prescribed such painkillers for a long-term condition and are concerned about diverticulosis.
Some home remedies may help alleviate the symptoms of diverticulitis such as making changes to your diet, taking over-the-counter pain relief, and engaging in gentle exercises. Let’s take a closer look at these next.
 novak.elcic / Shutterstock
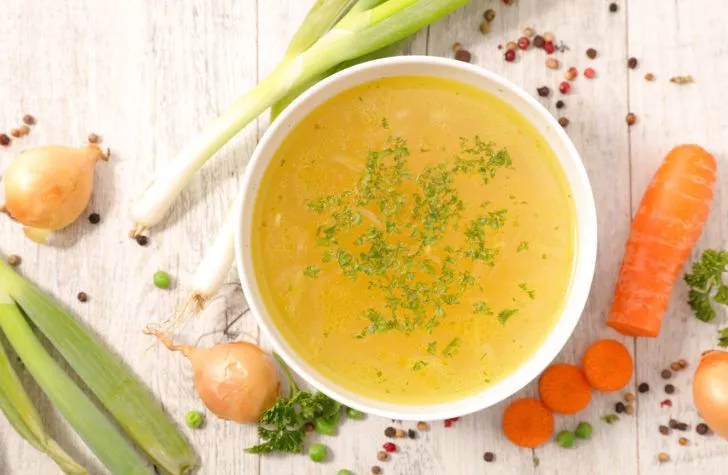
novak.elcic / Shutterstock1. Changing to a Liquid Diet
Doctors often recommend a liquid diet for people who have diverticulitis. Switching to a diet of broth, gelatin, pulp-free fruits, ice chips, and water for a couple of days could help reduce diverticulitis symptoms. Gradually reintroduce solid foods after a couple of days.
It’s worth noting, you should not stay on a liquid diet for more than a couple of days without seeking advice from a doctor. A liquid diet doesn’t provide your body with all the nutrients it needs and staying on this diet for too long may lead to weakness and other complications.
As you start to feel better, your doctor may recommend that you start adding low-fiber foods (such as eggs, fish, poultry, fruit, and veggies with no pulp, and rice) slowly to your diet. That said, it’s important that you follow their directions closely.
2. Over-the-Counter Pain Relief and Dietary Supplements
Acetaminophen (also known as Tylenol) can help reduce the pain associated with diverticulitis. Avoid non-steroidal anti-inflammatories because they could cause further irritation to the colon. If you’re not sure whether a specific painkiller is suitable for your symptoms, seek advice from your doctor.
Some dietary supplements might help, too. Fiber supplements such as psyllium or methylcellulose may reduce the symptoms of constipation or diarrhea. These supplements bulk up your stools, making them easier to pass. Some people experience bloating or excess gas when they start taking these supplements. Always talk to a doctor before adding fiber supplements to your daily routine.
3. Probiotics
Probiotics are microorganisms that are often found in fermented food products. Adding probiotics to your diet could help to improve gut health but it could also benefit your symptoms of diverticulitis too. In fact, the probiotic Lactobacillus casei is thought to be effective at reducing the symptoms of diverticulitis.
So how can you make sure you’re getting enough probiotics? The most common ways of taking in probiotics are through “live” yogurts and milk drinks. They’re also found in other fermented foods (such as pickles, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi) and can be taken in pill or powdered form, many of which are available at a regular grocery store.
4. Green Tea and Aloe Juice
Aloe vera juice can ease the symptoms of cramping and pain associated with diverticulitis. It can also help to reduce constipation. Aloe vera juice is inexpensive and widely available in health food stores. You don’t need to drink a lot of it to experience beneficial effects — just one or two ounces per day should be enough to provide relief.
Green tea is known for its anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and anti-viral properties. It’s a refreshing, relaxing drink that can help alleviate the symptoms of diverticulitis and reduce your risk of infection. In addition, someone who switches from drinking caffeine-rich, calorie-dense, or sugar-laden beverages to consuming green tea instead may find they experience secondary benefits such as better sleep and more stable energy levels.
5. Vitamin D
The body can make its own vitamin D, assuming a person gets sufficient exposure to sunlight on a day-to-day basis. However, people who live in parts of the world that see shorter days during the winter months often struggle to get enough sunlight. The same can apply to those who work from home or spend most of their days in an office.
Research suggests that individuals who are deficient in vitamin D may be at greater risk of developing diverticulitis. Some foods, including oily fish, cheese, eggs, and beef liver contain vitamin D. Many packaged foods such as cereals and margarine are fortified with Vitamin D today, too.
6. Gentle Exercise
Exercise is an important part of living a healthy lifestyle but it turns out exercise helps the body release endorphins, which act as painkillers. Gentle physical activity could help to alleviate some of the pain caused by diverticulitis.
It’s important to seek medical advice before starting any new exercise plan, especially if you’ve been sedentary for a long time. Listen to your body and don’t exercise if the movement causes more pain.
Some examples of gentle exercises include walking, swimming, and slow cycling. Even getting out and doing some gardening can be enough to improve cardiovascular health and help relieve mild pain.
Don’t Ignore Sudden or Long-Lasting Pain
While it is possible to manage mild pain at home, diverticulitis can be a serious medical condition. Infections that do not respond to home treatment or antibiotics may need surgical intervention. Severe diverticulitis can lead to complications such as a blockage in the intestine, perforations of the colon, or the formation of fistulas.
For this reason, it’s important to seek advice about any new or unexplained abdominal pain before trying home remedies and to follow up with a medical professional if the home remedy does not produce relief quickly or the symptoms get worse.