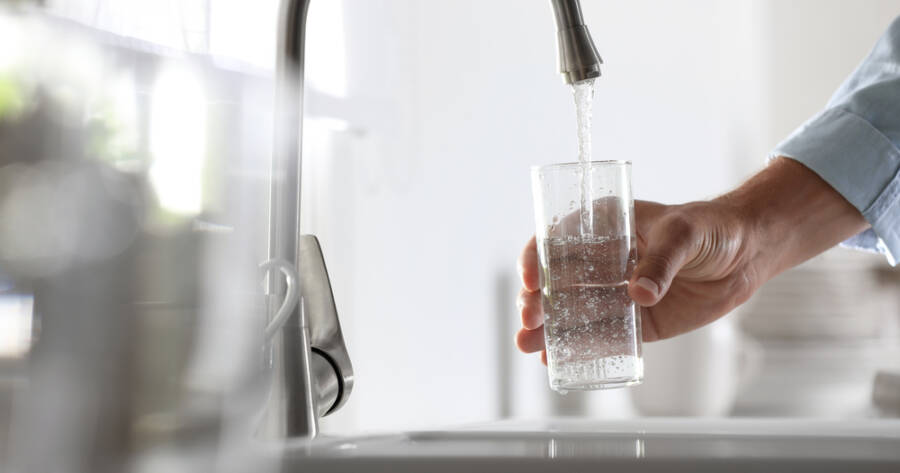
Some homes in the U.S. (especially those built before 1986) still contain lead service pipes, and lead can end up in drinking water when the lead pipes corrode. A person can have short-term effects from very high levels (lead poisoning), or display symptoms of long-term lead exposure at lower levels.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has set the maximum contaminant level goal for lead in drinking water “at zero because lead is a toxic metal that can be harmful to human health even at low exposure levels”. The EPA also notes “there is no known safe level of lead in a child’s blood.” With that being said, here are seven possible health outcomes of lead exposure from water (and other sources)…
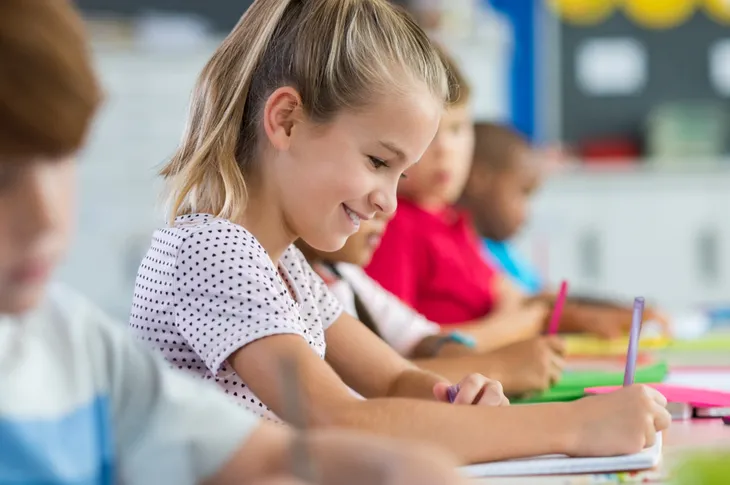
Lowered IQ in Children
The World Health Organization (WHO) notes that although low doses of lead were once thought to be safe for children, “lead is now known to produce a spectrum of injury across multiple body systems”. In particular, lead can affect the development of a young child’s brain, resulting in a lower intelligence quotient (IQ), notes the source.
This exposure can also negatively affect a child’s attention span, as well as their educational attainment (number of grades completed), adds the source. Even the lowest lead concentrations of 5 micrograms per deciliter (once considered safe for children) can affect the intelligence and behavior of children, notes WHO.
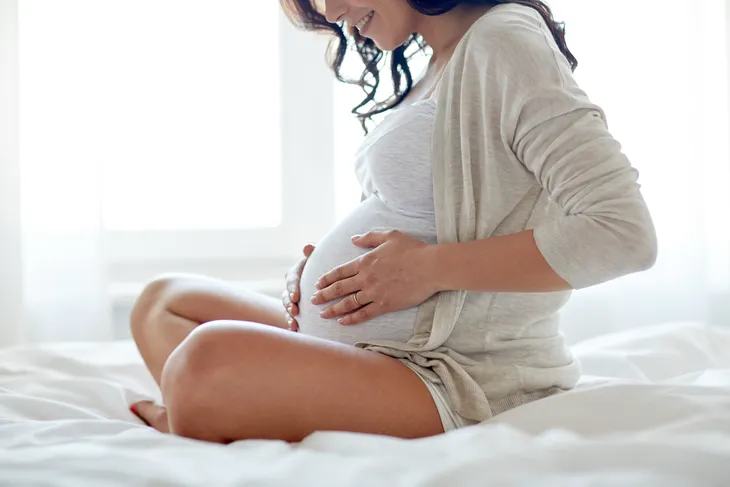
Prenatal Effects
Low levels of lead can affect a fetus and the mother. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) explains, “Lead readily crosses the placenta by passive diffusion and has been detected in the fetal brain as early as the end of the first trimester.”
These adverse health effects during pregnancy from lead exposure include gestational hypertension, spontaneous abortion (miscarriage), low birth weight, and premature birth. Pregnant women are advised against drinking tap water from lead pipes, or to drink filtered water and bottled water (ensure they’re BPA-free bottles). Fertility of both men and women can be affected by lead exposure – meaning conception will be difficult to begin with.
Pica
This is a condition that compels people to eat things that aren’t meant to be edible. For example, a symptom of lead poisoning in children is eating paint chips, according to the Mayo Clinic. Other examples are people eating dirt or even harmful objects.
Meanwhile, water isn’t the only source of lead. The EPA explains that homes in the U.S. built before 1978 likely have lead-based paint (it was banned that year), which along with lead-contaminated dust “is one of the most common causes of lead poisoning”. Basically, lead exposure can cause a child to eat something like a paint chip, which itself may contain lead.
Trigger of Autoimmune Diseases?
EvenBetterHealth.com explains that studies have been completed showing heavy metals including lead have been associated with the development of the autoimmune diseases including lupus, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, chronic fatigue syndrome, fibromyalgia, and even type 1 diabetes. Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system attacks healthy cells.
Meanwhile, The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) notes that adults with occupational exposure to lead report more colds and influenza, and also exhibit suppressed levels of immunoglobulin A, an important antibody found in respiratory and digestive tracts.
Mood Disorders
Both children and adults can have negative mental health impacts from being exposed to lead. Children may become more irritable, lashing out more or having temper tantrums, while adults could suffer conditions such as anxiety or depression.
In fact, those same symptoms in adults can be experienced by children exposed to low levels of lead, according to an article from NPR.org. The article cites a study in China, which tracked the health of 1,341 preschool children with an average blood-lead concentration of 6.5 micrograms per deciliter. By the end of preschool, the children were tested again, and “the children who had more lead in their blood were more likely to have emotional problems, anxiety, and pervasive developmental problems.”
Loss of Appetite
The Mayo Clinic notes that lead poisoning (in children in particular) can be a reason why they’re not eating. Loss of appetite and weight loss are both listed as signs and symptoms of lead exposure.
Along with those symptoms are abdominal pain (also present in adults with lead poisoning), vomiting, and tiredness and fatigue. However, these kinds of health problems could be associated with a number of conditions, so it’s probably best to consult a doctor.
Death
WHO explains that high levels of lead can even lead to death, especially in children who are more prone to it. In some children, it can cause convulsions or a coma. “Children who survive severe lead poisoning may be left with mental retardation and behavioral disorders,” explains the organization.
WHO notes that The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) estimates more than 850,000 people died around the world from lead exposure, mostly in middle or low-income countries. The organization strives to spread knowledge about the dangers of lead in water and other sources, such as contaminated soil. “Lead poisoning is entirely preventable,” it notes.
 Gorodenkoff / Shutterstock
Gorodenkoff / Shutterstock