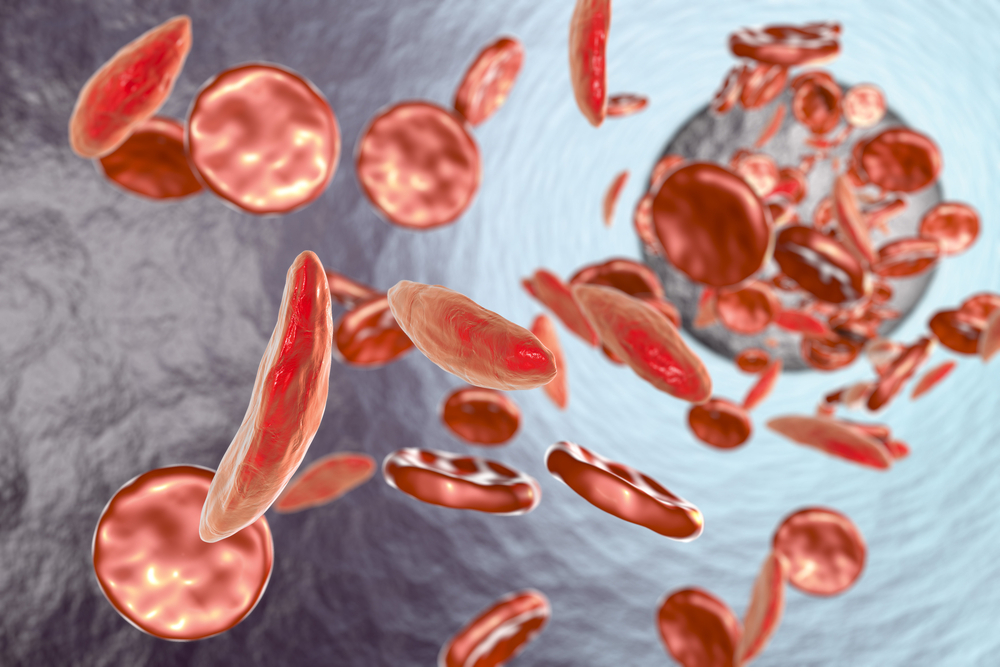
You may have heard of sickle cell anemia before. It’s a serious illness that’s caused by the development of an irregular form of hemoglobin (a protein found inside our red blood cells that is capable of carrying oxygen through the body) known as hemoglobin S. When hemoglobin S emerges, it has a dramatic effect on the way our red blood cells function. Specifically, it can drastically weaken those cells, making them so fragile that, under a microscope, they appear in the shape of sickles (or scythes), hence the name.
Aside from affecting a red blood cell’s shape, hemoglobin S can also reduce the body’s ability to transport oxygen through the body, meaning our major organs and tissues can be negatively impacted. Unfortunately, if both parents have sickle cell anemia, a child is generally guaranteed to inherit it. The key is recognizing the symptoms of this disease and taking action when it begins to appear.
Pain Crises
People with sickle cell anemia are very familiar with the term “crisis,” because patients with sickle cell anemia tend to go through bouts of intense pain and discomfort, known as pain crises, that can spread throughout the body, from the chest down through the back and into the leg muscles and joints. These crises can be so intense that they can make doing everyday activities, such as walking to work or looking after the kids, monumentally difficult tasks.
It’s worth noting that crises may not occur often; in fact, some people don’t experience them for years at a time. It’s also rare for crises to appear in young children, although it can be difficult to identify them when a child’s language skills are still developing. Generally speaking, pain crises appear a few times per year and can be so intense that they may require a patient with sickle cell anemia to spend a few days in the hospital.
Fever
“Crises,” or episodes of pain and discomfort that can last for days are the most visible symptom of sickle cell anemia. However, these difficult episodes are hardly the only sign of the illness. A generally less serious symptom is fever, which may be the first sign that trouble, including a crisis, is on the way.
Anyone with sickle cell anemia should keep a thermometer nearby, so they can carefully monitor their temperature and take action if a fever starts to emerge. Many patients will find that a fever reaching a certain temperature can mark the starting point of more serious symptoms, such as intense joint pain.
Swelling
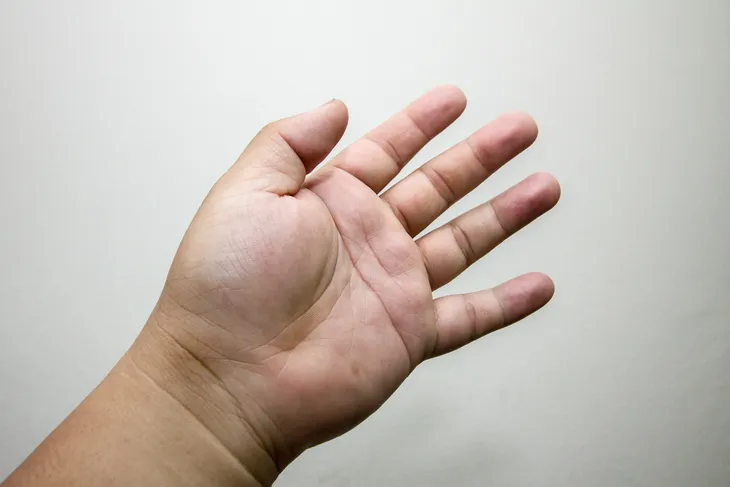
Because sickle cell anemia results in the production of hemoglobin S, which can rob red blood cells of their oxygen as they pass through the body, the end result is often inflammation. This can be most apparent in the extremities, including the hands and feet.
Inflammation of the hands and feet may not be the first symptom that appears when a sickle cell anemia crisis begins to emerge. Additionally, it can be difficult to discern when swelling has actually occurred by simply looking at the hands or feet. Instead, most patients will recognize this symptom when it’s accompanied by pain and general discomfort that can make walking or grasping objects uncomfortable.
Generalized body pain
One thing that sets sickle cell anemia apart from other illnesses is its tendency to cause pain in many different parts of the body. That’s because the core cause of this issue emerges in the body’s red blood cells, which pass from one part of the human anatomy to the other rather frequently.
The result of this widespread movement of affected red blood cells can lead to feelings of pain and discomfort in the chest, abdomen, limbs, and joints. In fact, it’s conceivable that sickle cell anemia could leave one with serious chest pain while feeling joint pain in the knees and uncomfortable swelling in the hands and feet. It is a total body experience, in the worst way.
Lung infections
Sickle cell anemia is caused when hemoglobin S reduces the amount of oxygen available in red blood cells. This oxygen makes its way into red blood cells in the lungs and spreads throughout the body from there. As patients of this disease are aware, this lack of oxygen can make red blood cells weak and effectively spread this fragility to other parts of the body.
It makes sense that people suffering from sickle cell anemia will often experience lung infections because the great number of red blood cells coursing through the lungs have significantly less oxygen than they would in a healthy person. This can make it seem like someone with sickle cell anemia is constantly short of breath, which can make it difficult to be even moderately physically active.
Fatigue
One of the most common symptoms of sickle cell anemia is a general and pervasive feeling of extreme exhaustion, primarily because, at its core, sickle cell anemia involves the robbing of oxygen from red blood cells by the tyrannical hemoglobin S. In the end, this theft of oxygen from the body’s red blood cells prevents adequate oxygen from reaching all parts of the body, making fatigue virtually inevitable.
This pervasive feeling of fatigue can make it difficult for patients with sickle cell anemia to perform even basic daily activities, from getting the kids up for school to getting through the typical workday. It may also mean they struggle to participate in physically demanding activities, such as sports, and can instead leave them feeling like retiring to the bedroom for naps.
Irritable mood
What kind of mood are you in when you feel completely exhausted and in constant discomfort or pain? For those of us who have experienced a really bad cold or illness, we know these feelings, even those that are temporary, can leave us feeling irritable and generally anti-social. In short, few people who feel tired and in pain want to venture out into public to spend time with other people.
Patients with sickle cell anemia can experience this problem on an almost constant basis. Because their illness makes pain and exhaustion frequent issues, it can be difficult for them to leave the home to socialize with others. In some cases, it can make just going to work or leaving the house to get groceries seem almost impossible.