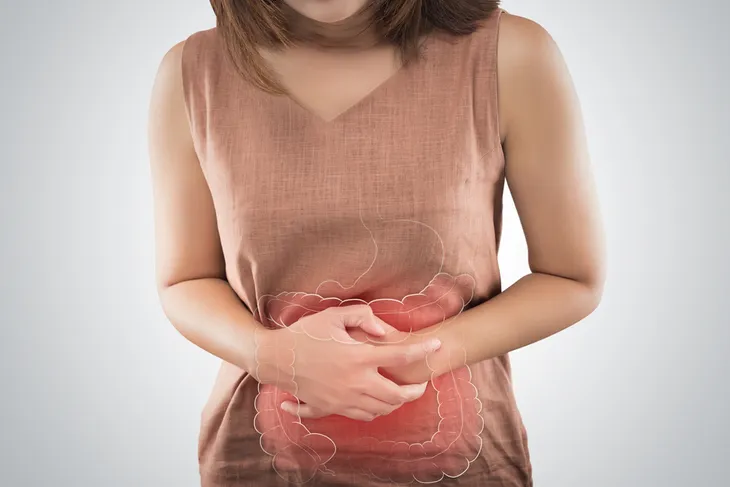
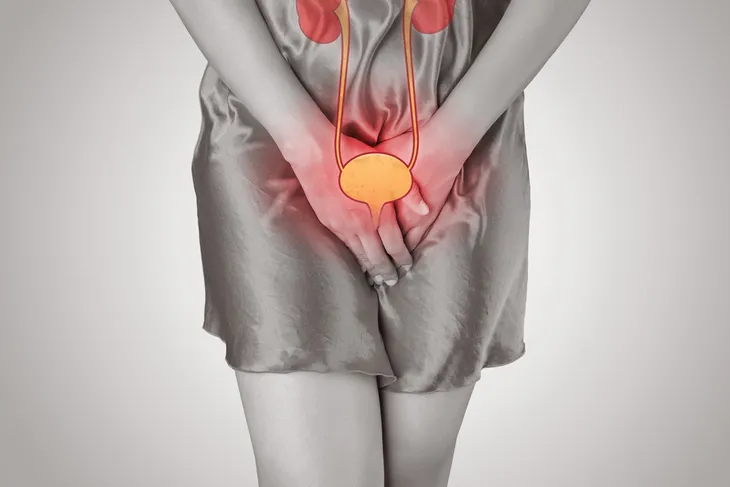
Ovarian cancer is known as the “silent killer” because symptoms are often so subtle, they just seem like routine or common annoyances. However, the difference is that they will occur almost every day and not go away. The trouble is that, by the time symptoms are considered an issue, the cancer has spread and progressed too far to treat effectively.
Only 20-percent of ovarian cancer cases are found early enough to treat the disease. We’re doing our part to make known the 15 early warning signs of this silent killer of women…
Abdominal Pain
Pain in the pelvic area or belly (abdomen) that feels very different from normal indigestion or menstrual problems (i.e., cramps) may be indicative of ovarian cancer. Most patients complain of abdominal pain that persists for longer than 2-weeks, which isn’t associated with their menstrual period, diarrhea, or the stomach flu.
Indigestion
Persistent indigestion, gas, nausea, or other gastrointestinal issues, such as heartburn, are quite common and persistent in ovarian cancer.
Loss of Appetite
Ovarian cancer is known to cause an abrupt loss of appetite that’s normally out of character for the person affected. This is because the cancer impacts metabolism, or the breakdown of food into energy that fuels the body.
Bloating
Frequent bloating or gas pain in your abdomen or pelvis that doesn’t go away is another symptom of ovarian cancer. For instance, if your abdomen bloats so much that your clothes fit tighter around your waist suddenly without diet or changes in activity, this may be cause for a doctor’s visit.
Urinary Frequency
Urinary problems, such as being overwhelmed by a sudden urge to urinate as well as peeing more often than usual, may be signs of ovarian cancer. This can include bouts of incontinence (complete loss of bladder control before you can get to a bathroom) that will gradually worsen over a few weeks.
Feeling Full Quickly
In the more advanced stages of ovarian cancer, the cancer tumor itself can sit on the surface of the stomach, on the omentum (the fold in the abdominal cavity that connects the stomach to other organs), or on the intestines, causing a patient to feel full very quickly (a condition known as “early satiety”) when they eat.
Alternating Constipation and Diarrhea
Changes in bowel habits, such as constipation and diarrhea, will often go hand in hand with ovarian cancer. This occurs when an ovarian tumor swells and puts pressure on the stomach, bowel, and bladder.
Lower Back Pain
A persistent, achy, dull pain in the lower back is a common sign of ovarian cancer. Many women equate the feeling with labor pain.
Sudden Weight Loss
Shedding 10 or more pounds without the help of dieting or exercising is a common warning sign in women with ovarian cancer. Even though someone might consider it to be a welcome occurrence, this rapid and unexplained weight loss should be reported to your doctor immediately.
Vaginal Bleeding
A lesser known early warning sign, one that has only been noted in approximately one quarter of women with ovarian cancer, is spotting or irregular vaginal bleeding outside of the regular menstrual cycle. Other vaginal abnormalities may include the sudden development of sores or blisters in the vaginal area, changes in skin color, or thick discharge.
Shortness of Breath
Women with ovarian cancer may also experience difficulty breathing, otherwise known as shortness of breath. Unfortunately, this symptom only tends to occur in the late stages of the disease, after it has spread (metastasized). As the tumors increase in size, they can press against the lungs, making it difficult to breathe.
Cancer can also cause a build up of fluid, known as ascites. This fluid accumulates in the abdomen, putting pressure on the surrounding organs and muscles, including the diaphragm (the muscle that pulls open the lungs, allowing air to be drawn in), thus resulting in difficulty breathing.
Pain During Intercourse
Another early indication of ovarian cancer is pain during intercourse, medically referred to as dyspareunia. VeryWell Health indicates, “This pain is often felt on one side more than the other but can be generalized.”
The source adds that the pain may be similar to that experienced with menstrual cramps, and may “begin with intercourse and continue for some time afterward.” Dyspareunia is a symptom that can occur with other conditions as well, however, so it’s important to get checked out by a doctor to determine the exact cause.
Fatigue
Because fatigue can be the result of a wide array of factors, from overwork to excessive stress, it is an easily dismissed warning sign of ovarian cancer. But if you’ve tried getting more rest and still can’t seem to shake the feeling, it’s important to let your doctor know about it.
Such fatigue doesn’t tend to occur on its own, however. So be mindful if your tiredness or lack of energy occurs alongside other symptoms mentioned on this list, such as persistent abdominal pain, indigestion, and bloating.
Menstrual Irregularities
Vaginal bleeding outside of the regular menstrual cycle isn’t the only type of menstrual irregularity that can occur in women with ovarian cancer. For example, the Cancer Treatment Centers of America says, “[You may experience] pain shortly before or after the start of your period.”
Tumors in the ovaries may also cause you to miss your period entirely, sometimes for several months at a time. But, as with fatigue, missed periods on their own aren’t necessarily indicative of ovarian cancer. However, if you’re experiencing irregular menstrual cycles along with other symptoms listed here, however, be sure to make an appointment with your doctor.
Dermatomyositis
Although less common, women with ovarian cancer may develop dermatomyositis, a rare inflammatory disease. There are two distinctive symptoms of dermatomyositis, the first of which is changes in the skin, specifically a violet or red-colored rash that appears “most commonly on your face and eyelids and on knuckles, elbows, knees, chest and back,” according to the Mayo Clinic.
The second symptom is muscle weakness in areas such as the hips, shoulders, and neck that tends to worsen over time. Although dermatomyositis tends to precede an ovarian cancer diagnosis, the source indicates that in some cases it may develop after.