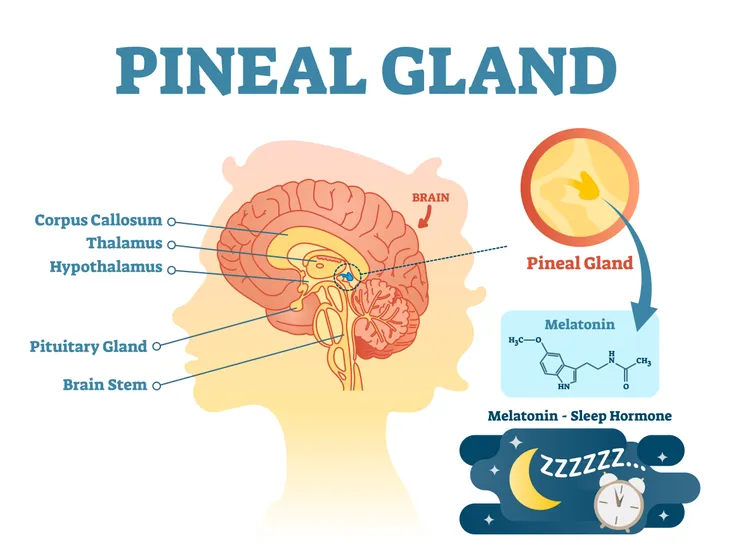
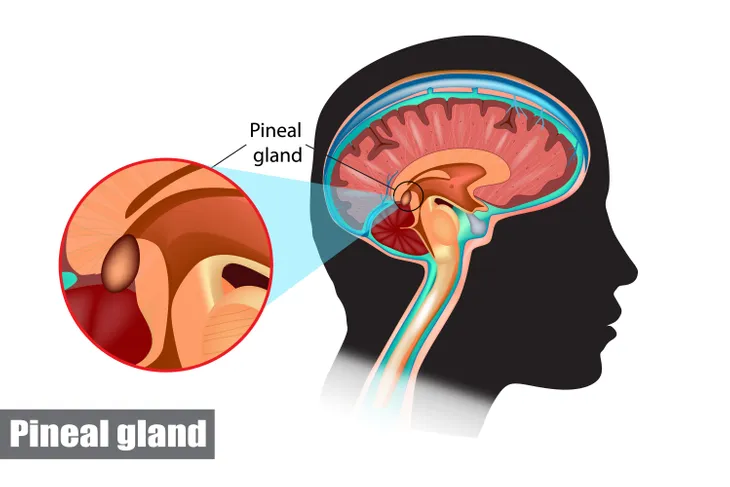
The small, pear-shaped gland known as the pineal gland is located in the brain. It was once referred to as the “third eye” due to its location, deep in the center of the brain, says Medical News Today. Back then, French philosopher Rene Descartes thought it contained a persons soul. While we now know that not to be true, it’s true function remains a mystery to researchers. However, they do know that it produces and regulates hormones, such as melatonin.
To learn more about this mysterious organ, follow along as we dive into what the pineal gland is, particularly the role it plays in the human body.
What is the Pineal Gland?
According to Medical News Today, the pineal gland can be found in the middle of the brain and is comprised of two distinct hemispheres, which are connected by fibers. It “contains mainly pinealocytes, which are cells that produce the hormone melatonin; and glial cells, which are a particular type of brain cells that support neurons (the cells that transmit information to other cells),” writes the source.
Pineal Gland Function
Produces Melatonin
Researchers aren’t entirely sure what the true function of the pineal gland is. However, they do know that it is responsible for secreting a single hormone — melatonin. “This simple hormone is special because its secretion is dictated by light,” writes Endocrine Web.
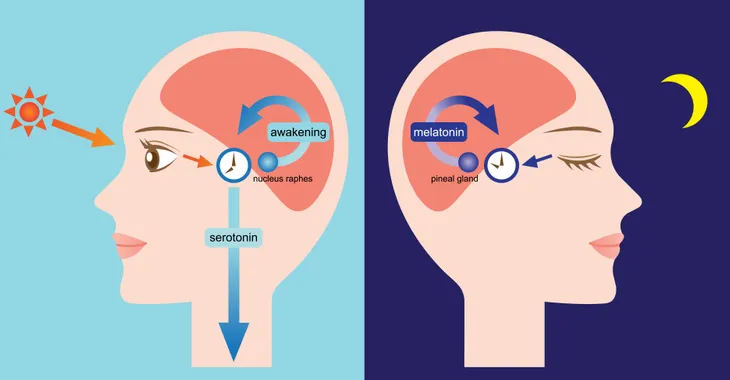
You’ve likely heard of melatonin before, because it’s a natural hormone produced by our body to regulate sleep patterns. These sleep patterns are known as circadian rhythms. What we know for sure is that the pineal gland affects our circadian (biological) rhythm. It also regulates certain reproductive hormones, adds the source.
Controls the Body’s Internal Clock
The body’s internal clock is known as its circadian rhythm. It’s a 24-hour biological cycle that is characterized by our sleeping patterns. For most people, daylight and darkness helps to dictate our circadian rhythm. “Light exposure stops the release of melatonin, and in turn, this helps control your circadian rhythms,” explains Endocrine Web. As a result, the body releases a small amount of melatonin during the day and more during the night. This has “some influence over your reaction to a photoperiod (the length of day versus night).”
Since the pineal gland is responsible for secreting melatonin, it’s thought that people with sleep disorders may have a dysfunctional pineal gland. To help control melatonin in the body, many people use melatonin supplements. These help in making you feel tired, assisting in regulating sleep patterns. You might use them while traveling and battling jet leg or after working a night shift. They can also assist in helping someone fall asleep faster, says Healthline.
These supplements are safe for most people when taken in a low dose for both short and long-term use. “Typically, dosages range from 0.2-mg to 20-mg, but the right dose varies between people,” writes Healthline. You should always talk to a doctor before taking melatonin.
Promotes Heart Health
Some research has shown a connection between melatonin and cardiovascular health. A review published in 2016 found that the melatonin produced in the pineal gland can actually have a positive impact on a person’s heart health and their blood pressure. These findings may show that melatonin may be able to treat cardiovascular disease, says Healthline. However, more research is necessary.
Effects Menstrual Cycle
A study published in the Biological Research for Nursing back in 2007 found that light exposure and melatonin levels may affect a woman’s menstrual cycle, says Healthline. Any woman who is experiencing irregular menstrual cycles may have low levels of melatonin. Similar to the research on melatonin and heart health, more studies are needed.
Effects Mental Health
Unlike the other functions on this list that are largely driven by melatonin, this one is linked to the size of the pineal gland. According to Healthline, there may be a correlation between certain mood disorders and the size of the pineal gland.
A 2015 study published in the official journal of the Danubian Psychiatric Association found that lower pineal gland volume may increase a person’s chance of developing schizophrenia, as well as other mood disorders. Again, more research is necessary to draw a more accurate conclusion.
Due to the fact that the pineal gland can affect a person’s sleep schedule and potentially cause sleep deprivation, it also impacts mental health or can worsen some mental health conditions, says Medical News Today. Some of these disorders have been linked to access to light and melatonin secretion. “Seasonal affective disorder, for instance, is a form of depression that affects a person’s mood and tends to occur when light levels are low,” writes the source. However, a 2017 review found no evidence linking melatonin to mood disorders.
May Impact Risk Factors for Cancer
There is some research suggesting a link between the pineal gland, particularly a dysfunctional one, and a person’s risk of developing cancer. Healthline refers to a study performed on rats which found that “lowering pineal function through overexposure to light led to cellular damage and increased risk for colon cancer.”
On the other hand, another study found that melatonin can be used to possibly improve the outcome of cancer in some people. This is particularly true in people with advanced tumors, says the source. “More research is needed to determine how melatonin affects the production and blocking of tumors,” adds Healthline. “It’s also unclear what dosage may be appropriate as a complementary treatment.”
Pineal Gland and Reproduction
In addition to affecting a woman’s menstrual cycle, the pineal gland can also impact reproduction. This is due to the fact that melatonin blocks the secretion of gonadotropins.
These are “luteinizing hormone and follicle stimulating hormone,” which are necessary for ovulation. Gonadotropins are “from the anterior pituitary gland,” and are necessary for the proper function of both the ovaries and testes.
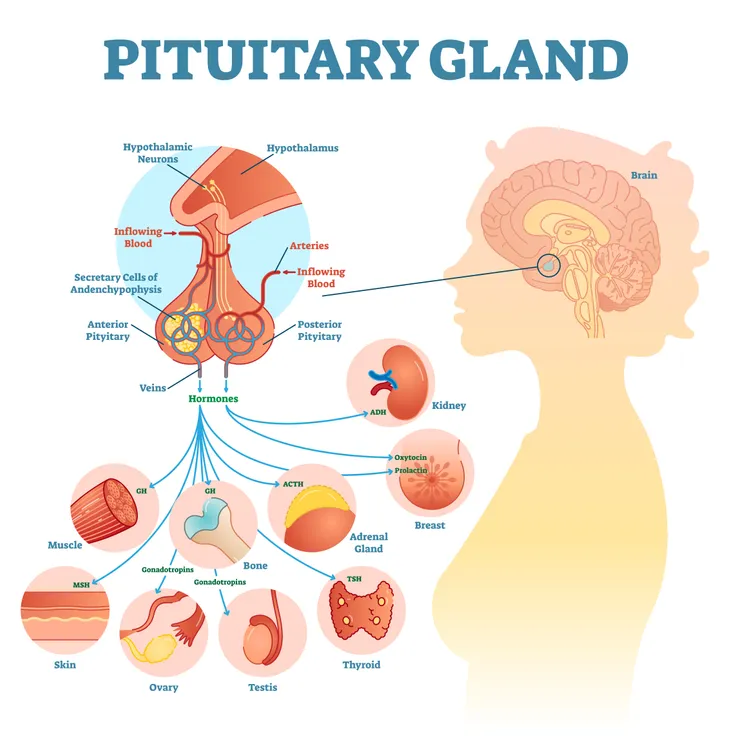
May Impact Pituitary Gland Function
The pituitary gland is another gland located in the brain. It protrudes from the hypothalamus, which is responsible for a number of hormonal functions (such as growth and thyroid function), says Medical News Today.
So, what does this have to do with the pineal gland? According to the source, there has been research linking the pineal gland to the behavior of the pituitary gland. “Melatonin may block the pituitary gland from secreting hormones that play essential roles in the development of the ovaries and testes and regulate functions such as the menstrual cycle,” writes the source.
It’s Function Declines with Age
Similar to the human body in general, the function of the pineal gland declines with age. In particular, the amount of melatonin it secretes. According to Medical News Today, it’s unlikely the decrease in melatonin is the sole culprit for any age-related changes in the body, but lower levels of this hormone could help explain the aging process. In fact, as people age, they tend to sleep less or have trouble falling asleep. There could be some correlation to the pineal gland. (To help, check out this article on Sleeping Tips for Seniors).
Another study on mice found that changes to the pineal gland may affect bone metabolism. This is more evidence that the function of the pineal gland declines with age, as more postmenopausal women are vulnerable to osteoporosis.
Impacts Sense of Direction
A 1985 study published in the British Medical Journal found that people with damage to their pineal gland also had a decreased sense of direction. This suggests that the pineal gland may affect our (or at least some people’s) innate sense of direction or spatial navigation.
Result of a Dysfunctional Pineal Gland
There are two major problems that can occur with the pineal gland, causing it to malfunction. The first is a large accumulation of calcium deposits. “These deposits are normal in healthy individuals, but excessive calcification can prevent the pineal gland from functioning properly,” writes Medical News Today.
The second is, due to its association with the hypothalamus, the pineal gland can encounter problems such as cancer, tumors, or hormonal issues. While tumors on the pineal gland are extremely rare, they can alter the function of this pear-shaped organ.
How would someone know if their pineal gland is dysfunctional? The source goes on to explain that the most common symptom of a dysfunction pineal gland is a change in circadian rhythms. This could be either sleeping too much or too little. You might feel active and restless in the night or struggle to stay awake during the day. Other symptoms include “headache, nausea, vomiting, tremor, difficulty with sense of direction, fertility issues (including changes to menstrual cycle or ovulation), osteoporosis,” explains the source, as well as mental health issues.