Type 2 diabetes is one of the biggest health risks we face today. Anyone can develop type 2 diabetes, and it’s a chronic health condition that you have to manage in order to prevent potential complications. Because of how serious the complications of type 2 diabetes can be, it’s important to understand what diabetes can look like and how its symptoms first appear.
Since diabetes is a chronic condition, you should know how it’s treated and managed over time. Type 2 diabetes can be treated in several ways. Many of which you can discover by searching online.
If you’re wondering what diabetes looks like and how it can be managed, here’s what you need to know.
Want diabetes content delivered straight to your inbox? Sign up for our Diabetes newsletter and receive exclusive news and articles written from our team of diabetes experts.
What Causes Type 2 Diabetes?
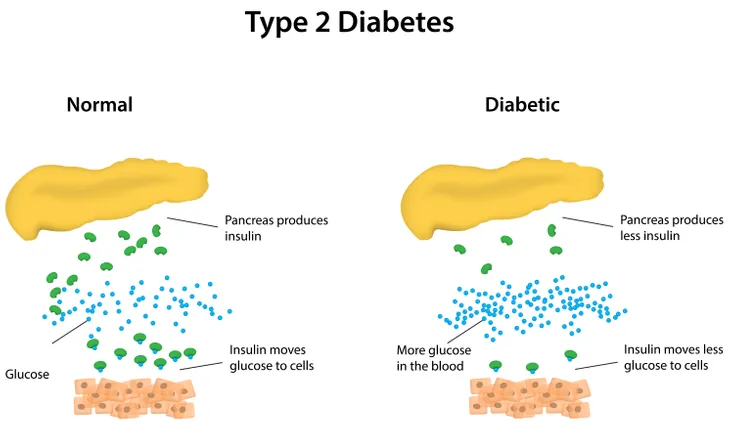
Type 2 diabetes occurs when your body’s cells don’t respond normally to the hormone that regulates the amount of glucose in the blood. Essentially, you develop a resistance to this hormone. As your cells become increasingly resistant to action of this hormone, it prevents the entry of glucose into the cell, causing levels to rise in the blood sugar. These high blood sugar levels can lead to other serious health issues.
Type 2 diabetes can be caused by several different factors or health considerations, including:
- Genes (i.e., having a first-degree relative [parent or sibling(s)] with the disease)
- Being overweight or obese;
- Having metabolic syndrome
- Too much glucose created by the liver
- Bad communication between cells
- Broken beta cells, the cells that produce the hormone that regulates glucose in the blood.
Additionally, if you have certain risk factors in your health history or background, you may be at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes. The more risk factors you have, the more likely you may be to become diabetic. These risk factors include:
- Being > 45 years of age
- Having an immediate family member (i.e., parents, brother, or sister) with diabetes
- Being of a certain ethnicity, such as African American, Hispanic American, Native American, or Pacific Islander, or Alaska Native
- Having high blood pressure (or hypertension)
- Low high-density lipoprotein (HDL) or “good” cholesterol
- Prediabetes
- High triglyceride levels
- Sedentary lifestyle (i.e., being physically active < 3 times per week)
- Having had gestational diabetes (i.e., diabetes during pregnancy) or having given birth to a baby weighing > 9-pounds
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
If you’re at risk for type 2 diabetes, it’s important to talk with your doctor. Make sure to discuss your potential risk level and ways that you may be able to mitigate that risk.
Signs and Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
When people develop type 2 diabetes, it isn’t always immediately obvious. In fact, the symptoms of this condition can be very mild or subtle. This means you can live with type 2 diabetes without even realizing it. In fact, 7.3 million people who currently have type 2 diabetes don’t know it yet.
Considering the large number of diabetics that go undiagnosed, it’s so important to know what type 2 diabetes looks like in terms of symptoms. To prevent diabetes, you will need to be able to spot even small changes to your health.
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes can include:
- Being very thirsty (known clinically as polydipsia)
- Urinating frequently (known clinically as polyuria)
- Irritability
- Fatigue
- Experiencing blurry vision
- Tingling or numbness in your hands or feet
- Wounds that take a long time to heal or don’t heal
- Recurring yeast infections
- Unexplained weight loss
Other changes to your health and well-being may also be a sign of type 2 diabetes. Make sure to talk with your doctor if you’re concerned about any changes that you notice.
How Type 2 Diabetes is Treated
If you are diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, your doctor will create a plan for treating and managing your condition. With proper care, it’s possible to effectively manage type 2 diabetes.
One of the biggest components of type 2 diabetes management is checking your blood glucose levels. Your doctor will let you know how often this should be done. Doing so will help you and your doctor understand where your type 2 diabetes and overall health stand.
Type 2 diabetes can also be treated and managed with lifestyle changes, medication, and regular check-ins with your doctor. Treatment regimens can include a combination of different approaches to keep your health on a positive track and prevent possible complications.
Medication
Medication may be necessary to keep your type 2 diabetes under control. Typically, the following medications are prescribed to help manage the condition:
- Metformin: Lowers blood glucose levels and helps the body’s response to the hormone that regulates glucose in the blood.
- Sulfonylureas: Helps the body make more of the hormone that regulates glucose in the blood.
- Meglitinides: Fast-acting medication that stimulates production of the hormone that regulates glucose in the blood.
- Thiazolidinediones: Makes the body more sensitive to the hormone that regulates glucose in the blood.
- Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors: Helps lower blood glucose levels.
Other medications may be used in conjunction with these listed. However, it will depend on what your doctor determines is needed for your health.
Lifestyle Changes
Managing type 2 diabetes often includes changing your diet, exercising regularly, and other habits. Adjusting your lifestyle can help you control your blood sugar levels and adopt a healthier way of living.
Lifestyle changes for diabetes typically include:
- Eating a diet that’s rich in fiber and healthy carbohydrates, with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Limiting your consumption of refined carbohydrates, sweets, and animal fats
- Eating only until you’re full
- Controlling your weight, and
- Getting half an hour of aerobic activity each day
With your doctor’s help, you’ll learn how to recognize high and low blood sugar as well as what you can do to keep your levels in a good place.
Be on Top of Your Condition
The good news about type 2 diabetes is that the condition can be managed by you and your doctor. Therefore, it’s important to follow your doctor’s advice, stick to a healthy diet, and be on top of your blood sugar levels.
Also, be sure to keep an eye on your overall health in order to prevent or delay possible complications.