Are you tired of dealing with unsightly and uncomfortable toenail fungus? These revolutionary treatments offer a lasting solution to restore your toe health. Say goodbye to embarrassment and discomfort, and say hello to healthy, fungus-free toes. Find more info about these new treatment options below to revitalize your toenails.
About Toenail Fungus
Toenail fungus is a common infection that can be challenging to get rid of. Around 20-percent of people in the United States develop a fungal toenail infection; a stat that rises to 75-percent of people aged 60 or over. Toenail fungus rarely causes pain or complications, but it can be unsightly and annoying to deal with.
Fortunately, there are various effective ways to prevent and treat fungal toenail infections at home. Your doctor can also prescribe stronger medication if your toenail fungus doesn’t respond to home remedies. Knowing how to spot the symptoms of a fungal toenail infection can help you treat the problem quickly and stop it from spreading.
Symptoms
A mild case of toenail fungus isn’t usually painful. It often causes the affected nail to turn whitish or yellowish, although it can appear dark brown if there’s a lot of debris underneath. Over time, your infected toenail may become thickened, and you might notice that it crumbles or breaks easily.
More severe toenail fungus can smell mildly unpleasant, and your toenail might change shape. Toenail distortion caused by a fungal infection can cause pain.
Causes
Toenail fungus occurs when fungal microorganisms get under the nail. Many types of fungi can cause a nail infection, but the most common are dermatophytes. The fungus feeds off keratin, a substance in your toenails that makes them hard.
Most people develop toenail fungus after walking barefoot on damp surfaces where fungi tend to flourish, such as swimming pool decks and locker rooms. Sometimes, a fungal foot infection called athlete’s foot can spread to the toenails and cause a fungal toenail infection.
Risk Factors
Older adults have a higher risk of developing toenail fungus. Toenails tend to become more brittle with age, forming cracks that allow the fungus to get underneath the nail. Reduced blood flow related to age can also make a fungal toenail infection more likely.
You’re also more likely to experience toenail fungus if you have poor circulation, a compromised immune system, or a preexisting health condition, such as diabetes. Skin conditions and injured toenails also increase the risk of developing toenail fungus.
Complications
Complications from a fungal toenail infection are relatively rare, but a severe infection can cause lasting toenail damage. Occasionally, a fungal toenail infection can lead to a bacterial infection in your foot that could spread throughout your body, such as cellulitis.
People with diabetes and compromised immunity are at a significantly greater risk of bacterial infection. Therefore, if you have these conditions, consult your healthcare provider if you develop a fungal toenail infection or injure your feet.
Diagnosis
Sometimes, skin conditions, such as psoriasis, can cause similar symptoms to toenail fungus. Therefore, your doctor may ask about preexisting conditions before diagnosing toenail fungus.
Often, a healthcare professional can diagnose a fungal toenail infection by examining your toenails. They may take a sample of toenail clippings or scrape some of the material from under your toenail to send for lab testing. Testing these samples can help them identify the fungus causing the infection and prescribe the correct treatment. It can also help detect and rule out an alternative cause, such as bacteria or yeast.
Home Remedies
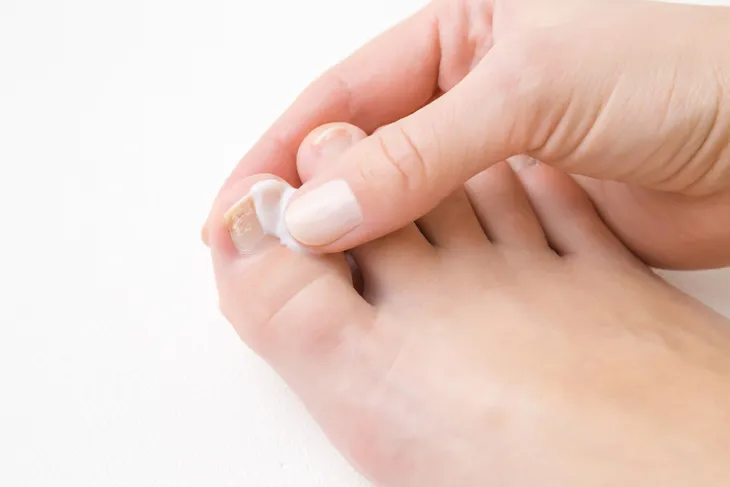
If you don’t have a health condition that puts you at a higher risk of infection, you can often treat a fungal nail infection at home. You can purchase over-the-counter antifungal creams, ointments, and nail polishes to treat toenail fungus. Soaking your toenails in water before applying the treatment can make it more effective.
If you have thickened toenails, you may benefit from trimming your toenails and thinning them with a nail file first. Trimming and filing can help the treatment permeate the toenail more effectively and reduce pain and pressure.
Oral Medications
If your fungal toenail infection is severe or you’re at risk of complications, your doctor may prescribe a course of oral antifungal medication. These medications can treat the infection more quickly than topical treatments. They also encourage the toenail to grow, replacing the infected area with a healthy nail.
Most people need to take oral medications for 6- to 12-weeks to see results. It’s worth noting, these medications can cause various side effects, including liver damage. Therefore, they may not be suitable if you have certain health conditions, and your doctor may request blood tests to check how your body responds.
Surgery
Most people with a fungal nail infection won’t need surgery. However, your doctor may recommend surgery if your symptoms are particularly severe or less invasive treatment options haven’t worked.
Sometimes, doctors remove the infected toenail temporarily to allow them to apply a topical antifungal medication directly to the infection site. The toenail can then regrow once the infection improves. However, you might choose to have your toenail removed permanently if your fungal nail infection doesn’t improve with medication or causes you severe discomfort.
Can You Catch Toenail Fungus?
Toenail fungus can spread from person to person through direct physical contact, and it’s relatively contagious. People with a fungal toenail infection or athlete’s foot can also leave fungus on surfaces if they walk barefoot, especially in dark, damp areas. Anyone who walks on these surfaces can then develop athlete’s foot or a fungal toenail infection themselves.
If you have a fungal toenail infection, you can avoid spreading it to other people by wearing shoes or slippers. Washing your hands after touching your feet can also prevent transferring the fungus to surfaces.
Can Toenail Fungus Spread?
Generally, toenail fungus is unlikely to spread to other parts of the body. However, you can infect other areas if you touch the affected toe and don’t wash your hands before touching your skin.
Dermatophyte fungus can infect the skin and cause a condition known as ringworm. It can also infect the groin, scalp, or other toenails. Occasionally, toenail fungus can spread to the skin between the toes and cause foot fungus, known as athlete’s foot.
Prevention
Practicing good hygiene can help prevent fungal toenail infections. Washing your hands and feet regularly and keeping your toenails short can reduce the risk of fungi getting underneath your toenails, and you should disinfect your nail scissors each time you use them.
Preventing athlete’s foot can also reduce the risk of a fungal infection spreading to your toenails. Dry your feet thoroughly after washing, and wear clean, breathable socks and shoes. You can also purchase antifungal powders to stop fungus from growing in older shoes.
Pedicures and Toenail Fungus
If you get a salon pedicure, there’s a risk of picking up a fungal toenail infection from the instruments or foot baths. Therefore, it’s essential to check that your salon sterilizes the instruments between clients. Also, avoid putting your feet in a footbath if you have a toenail injury or any cuts or sores on your feet.
Sometimes, the filing techniques used by salon technicians can damage your toenails and increase the chances of getting toenail fungus. Consider asking them not to use metal files on your toenails, and tell them if you feel pain during your pedicure.