Some of the first health issues we experience impact the ears, with many children suffering from ear infections during their first months, even years, of life. This is largely because children’s ears, and their immune systems are still developing.
But what other types of ear problems can we experience? And what kinds of hearing problems affecting people older than newborns and toddlers? Here, we’ll take a closer look at some fairly prevalent ear issues that can cause pain and discomfort prior to an individual receiving appropriate treatment from their doctor.
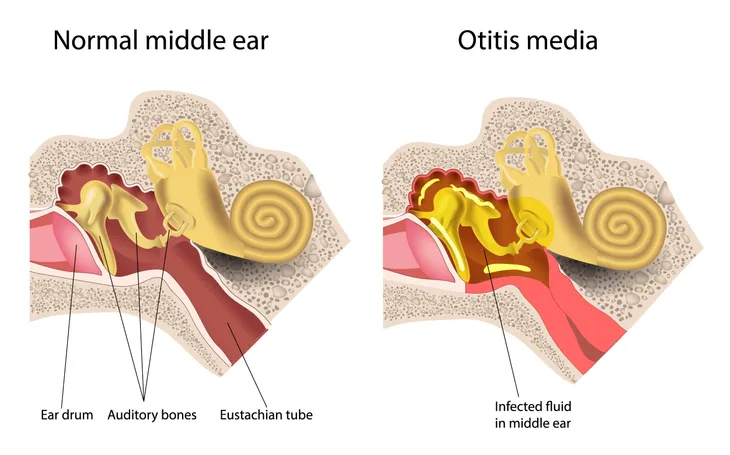
Otitis Media
The name may be rather unfamiliar, even strange, but otitis media is a fairly straightforward ear problem. In simple terms, it primarily involves the inflammation of the middle section of the ear, with this problem resulting in the steady build-up of fluid that in some cases leads to a bacterial infection.
Parents of young children are likely to become familiar with this issue prior to their children reaching age 7 or so. Children experiencing otitis media are likely to complain of discomfort affecting the ear and may actually pull at their ear in an effort to find relief. Other symptoms are more general and include crying, mild fever, and irritability.
Otitis Media with Effusion
Unlike the standard version of otitis media, otitis media with effusion may not cause significant pain and discomfort. However, it does result from a buildup of fluid and is most often found in young children whose ears are still in the development stage. Because otitis media with effusion doesn’t cause the pain associated with otitis media, it is best diagnosed by a doctor, usually after examining the ear with special equipment.
The danger of otitis media with effusion is that, without the patient being particularly bothered by any symptoms, it can fly under the radar until the fluid builds up enough to cause a serious ear infection or even damage to the eardrum. This makes identifying and treating the problem tricky, particularly as antibiotics are rarely effective. It’s worth noting that individuals with seasonal allergies are more likely to experience otitis media with effusion.
Glue Ear
Glue ear gets its name from the thick, often sticky excessive residue that builds up in the middle section of the ear, causing discomfort and even hearing loss. This build-up of fluid can make it feel like a foreign object has been inserted directly into the ear and pushed in just out of reach.
The biggest problem with glue ear is that, in some cases, it may not go away on its own, and because it often affects children, whose ear development is still under way, it can be very challenging to diagnose, as few toddlers have the vocabulary to fully outline their discomfort. Should the problem persist and intensify, it can make communication and even learning more difficult for young children.
Excessive Ear Wax
While glue ear, also outlined on this list, is prominent among children, adults are more likely to experience irritation associated with the excessive buildup of earwax. As with glue ear, this can feel like something has been placed in the ear just out of reach.
Excessive ear wax is a common problem among adults and rarely leads to significant health concerns. However, it may require an individual use special ear drops designed to thin out ear wax and eliminate the associated discomfort. People who frequently experience this problem may need to explore more effective methods for cleaning their ears, such as using a syringe to remove built-up earwax.
Otitis Externa (“Swimmer’s Ear”)
Otitis externa (“swimmer’s ear”), unlike otitis media, impacts the outer rather than middle section of the ear canal causing the inner part of the ear to swell and become irritated. It’s often caused by exposure to some kind of pollutant, such as water high in bacteria. However, while the name implies that the problem is caused by immersion in water, an individual can actually experience swimmer’s ear without going anywhere near a beach, pond or pool.
In reality, swimmer’s ear can be caused by the build-up of moisture in the ear for any reason, including exposure to humid, hot weather or a climate that features lots of rain or fog. Additionally, swimmer’s ear can develop slowly over time, rather than resulting from a single episode, and is often worsened by attempts to remove moisture through the use of cotton swabs. In the most extreme cases, pus may leak out of the ear, an alarming symptom for anyone but particularly children. The good news is that otitis externa is usually easy to treat. Antibiotics have been shown to be effective in its treatment and some individuals may see symptoms go away on their own.
Damaged Eardrum
Damage to the eardrum can result in significant pain and discomfort and, unfortunately, is surprisingly easy to do. This is because the eardrum is only a very thin membrane separating the middle and inner sections of the ear. Given that the preeminent manner of cleaning the ear remains using cotton swabs, it’s not surprising that many people visit their doctors seeking treatment for a damaged eardrum each year.
The good news is that a damaged eardrum usually heals on its own without special treatment. However, this healing depends in large part on the state of the ear, including the level of moisture (the more dry, the better) and sanitation. Even in ideal conditions, a damaged eardrum can take a few weeks to fully heal.
Congenital Hearing Loss
When we think of hearing loss, we typically imagine older adults who may have been exposed to loud machinery, music, or other noise hazards. But congenital hearing loss starts at birth, meaning it affects children and continues to impact them throughout their lives.
Individuals with a family history of hearing problems are far more likely to experience congenital hearing loss than others. Some genetic syndromes that can be involved include Usher, Treacher Collins, and Down syndromes. Complications during labor can also result in hearing issues. Additionally, if a mother has a significant health problem, such as maternal diabetes or an infection (such as toxoplasmosis, rubella, herpes, cytomegalovirus, or German measles), their child could experience congenital hearing loss.
Acquired Hearing Loss
The type of hearing loss we most often imagine, resulting from exposure to severe exposure to noise, is known as acquired hearing loss. A lifetime of listening to loud noise, such as wearing headphones or operating loud machinery in a confined space, can result in acquired hearing loss.
But there are other causes of this type of hearing loss, including chronic or untreated infections of the ear, mumps, meningitis, whooping cough, measles, chicken pox, damaged ear drum, and even influenza. Still, anyone who’s concerned an infection is causing hearing loss should talk to their doctor about the problem as soon as possible.
Objects in the Ear
It’s pretty rare that an adult will get an object lodged so deep in their ear that it causes serious hearing problems, although it can happen, particularly if one works in a dangerous job. But more often than not when objects become lodged in the ear and cause hearing loss, it’s a problem affecting a child rather than an adult.
This is because many children learn by experimenting with objects. It’s why so many children put objects in their mouths, leading to choking concerns. But, they may also place them in their nose or ears, problems that can cause significant tissue damage and may require surgery to resolve. If your child is complaining about hearing loss and you believe an object may be the culprit, talk to your doctor right away and avoid trying to remove the object yourself.
Complications Due to Medication
You’ve probably seen advertisements for medications that include a long list of possible side effects. One of these side effects can be acquired hearing loss, which sometimes emerges when an individual has a surprise reaction to a medication.
While this problem would seem rare, there are actually many types of medication that can lead to hearing loss. This list includes antibiotics, cancer treatment drugs, erectile dysfunction treatments, malaria drugs, diuretics, and even aspirin. If you’re taking a new medication and notice it affects your hearing in any way, talk to your doctor immediately.
Blood Supply Issues Causing Hearing Loss
Restrict blood flow to any part of the body and you can expect that anatomical area to experience difficulties functioning properly. This rule most certainly applies to the ears and, although you wouldn’t necessarily expect it, some major health problems that can cause blood flow issues may actually impact our hearing.
These major health problems include heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure. Otosclerosis, a bone disease of the middle ear, can also present problems. All of these issues can result in restricted blood flow to the ears and, in doing so, can cause hearing loss. If you’ve experienced any of these health problems and have noticed your hearing is affected, talk to your doctor right away.