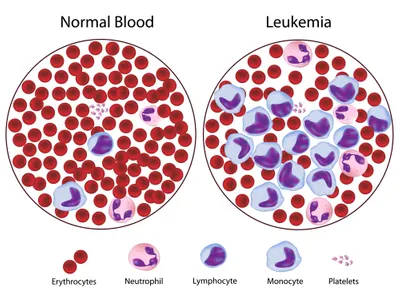
When you receive a cancer diagnosis, it’s very natural to question what contributed your leukemia. Or rather, what caused you to be among the 30,000 adults and 2,000 kids who are diagnosed with this common cancer of the blood cells, annually in the U.S.?
Although the exact cause of leukemia hasn’t been pinpointed, medical researchers have pinpointed a list of nine specific risk factors that increase the risk for developing leukemia during a lifetime…
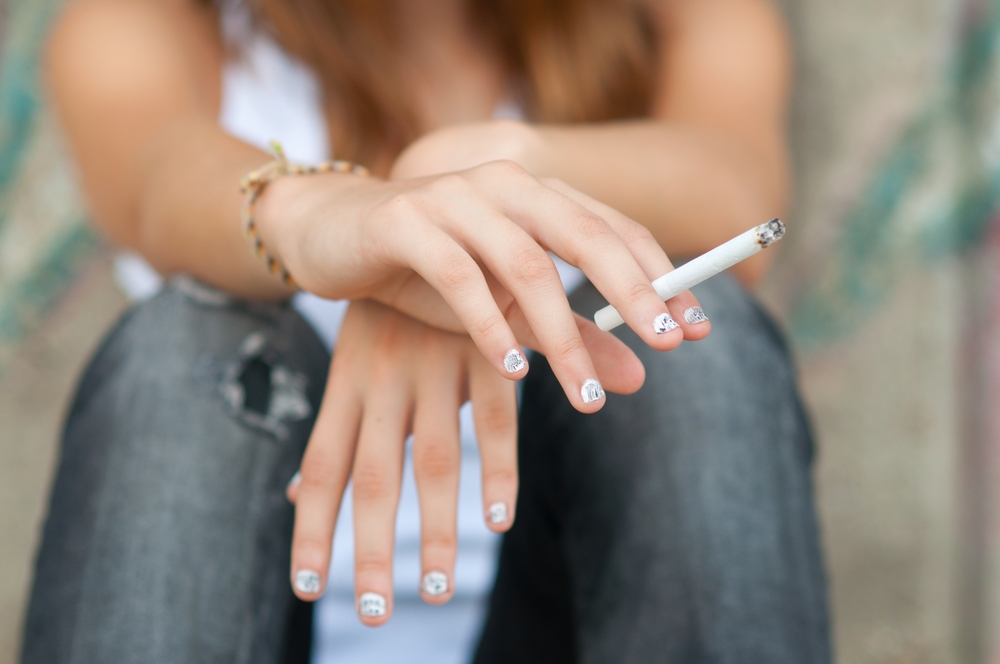
1. Smoking
Even though smoking doesn’t outright cause leukemia, a cigarette-sucking habit is clearly linked to increasing the propensity of acute myeloid leukemia. In fact, studies show that smoking increases your chances of developing leukemia by 30-percent, which amounts to approximately 3,600 new diagnoses each year in the U.S.
2. X-rays & CT Scans
Even though your yearly dental x-ray isn’t enough to cause leukemia due to the low levels of radiation, researchers suspect that numerous x-rays and CT scans throughout childhood may raise the risk of developing leukemia later in life.
3. Radiation Exposure
Akin to the radiation we’re exposed to via x-rays and CT scans, we can also be exposed to low levels of radiation through our smart phones, glow-in-the-dark watch faces, and through our use of microwave ovens. Even though moderate usage is perfectly safe, over-use can put us at risk for developing 3 types of leukemia—acute myeloid, chronic myeloid, and acute lymphocytic leukemia.
4. Radiation Therapy
A third way that radiation can increase your risk of leukemia is if you undergo extensive radiation therapy, which is often used to treat other types of cancers and medical conditions—such as cancerous and benign prostate, breast, or skin tumors.
5. Benzene Exposure
Benzene is a substance that is commonly used in workplaces within the chemical industry as well as in gasoline. Studies link extensive benzene exposure to acute myeloid leukemia as well as acute lymphocytic leukemia.
6. Atomic Bomb Explosions
Although this hasn’t been a concern in North America, exposure to the particles released after an atomic bomb leukemia risk, especially children.
7. Inherited Diseases & Conditions
Medical experts point to those with certain types of inherited diseases and medical conditions—such as myelodysplastic syndrome (a blood disorder), Human T-cell leukemia virus type I (or HTLV-I infection), and Downs Syndrome—and link them to a higher risk of developing certain types of leukemia.
8. Chemotherapy
Sadly, patients undergoing chemotherapy, a popular cancer-fighting drug therapy that employs the use of alkylating agents or topoisomerase inhibitors, raise their risk of certain types of emergent acute leukemia following their treatments.
9. Heredity
In rare cases, family history has been shown to play a role in leukemia development. For instance, in the case of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, if your father, mother, brother, sister has leukemia, you can also develop the disease.