The liver is the largest glandular organ in your body. It has a critical job of filtering blood and keeping our body free of toxins and harmful substances. Cancer can start in the liver when cells in the body begin to grow out of control. It’s estimated that about 34-000 people will be diagnosed with liver cancer annually in the United States.
If liver cancer is detected early, the 5-year survival rate is about 33-percent. But, if liver cancer spreads to surrounding organs, tissue, or lymph nodes the survival rate drops to 11-percent. This is why early detection is so important! The good news is there are several treatments available that can help improve your quality of life. Here are the signs, symptoms, and treatment options for liver cancer.
What is Liver Cancer
If cancer starts in the liver, it’s considered primary liver cancer. That said, most diagnoses are secondary or metastatic liver cancer, which means the cancer started elsewhere in the body then spread to the liver.
The liver is made up of different types of cells, and because of this, different types of tumors can form. WebMD explains, “Some of these are benign (noncancerous), and some are cancerous and can spread to other parts of the body (metastasize).” Since the tumors have different causes, each tumor will be treated differently.
Causes of Liver Cancer
When liver cells develop changes in their DNA, also known as mutations, liver cancer forms. A cell’s DNA is in charge of instructing every chemical process in your body. When mutations happen, it can cause changes in these instructions.
One of the outcomes of cell mutation is they can begin to grow out of control and result in a tumor. It is sometimes clear what causes liver cancer, such as chronic hepatitis infections. That said, it can also happen to people who show no underlying diseases. In these cases, it’s not clear what is causing the cancer.
Risk Factors
While it’s unclear why some people get liver cancer, there are a few factors that may increase your risk of developing it. For starters, excessive alcohol consumption, such as two or more alcoholic beverages a day for many years can put you at a greater risk.
If you’ve had a chronic hepatitis B or hepatitis C infection, you can also be at risk for developing liver cancer. Diabetes and obesity can also increase your risk, as well as your age, as liver cancer is more common in people over 50.
Signs and Symptoms of Liver Cancer
Early prevention is so important, and one of the best ways to detect it early is to know the warning signs. Some common symptoms of liver cancer include abdominal pain, tenderness, and discomfort. You may also experience jaundice, which presents as yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes.
Furthermore, other common symptoms include white, chalky stools, nausea, vomiting, weakness, fatigue, unexplained weight loss, and loss of appetite. You may also experience bruising and/or easy bleeding. You should be on the lookout for these warning signs and speak to your doctor immediately if you are concerned, as it could be a sign of liver cancer.
Diagnosing Liver Cancer
If you suspect you might have liver cancer make sure you speak with your doctor right away. Diagnosing liver cancer can be done through a few different tests and procedures. First, your doctor may perform a liver function test that determines the health of your liver. This is done by measuring levels of proteins, bilirubin, and liver enzymes in your blood.
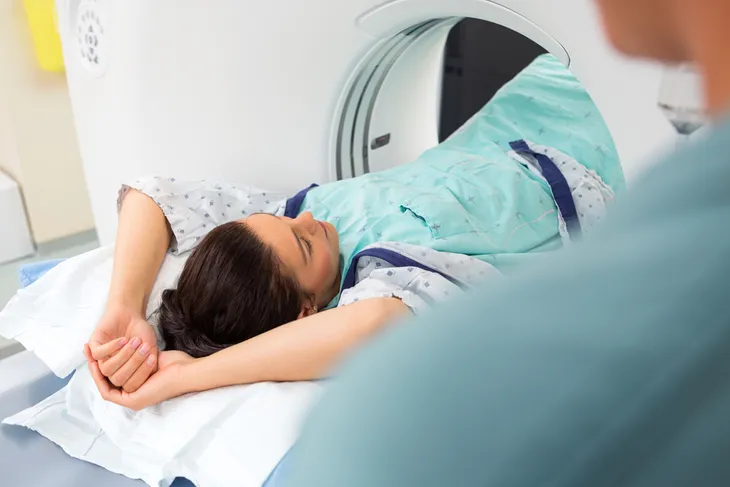
Next, another test is an abdominal CT or MRI scan. This will produce detailed images of your liver, as well as other organs, located in the abdomen. Your doctor will be able to see if a tumor is developing, and if so, he/she will be able to assess its size and whether or not it has spread to other organs.
Treatment Options
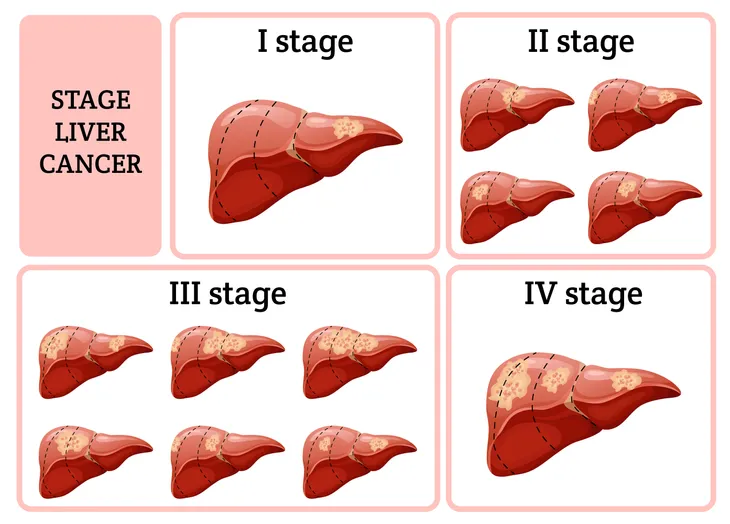
If your doctor does diagnose liver cancer, he/she will then determine the stage of cancer. The staging tests will determine the location and size of your cancer and whether it has spread to other parts of the body.
Once this is determined, your doctor will explain your treatment options and prognosis. Let’s explore the treatment options for liver cancer next.
Surgery
Hepatectomy is a surgery that removes a portion of the liver. This surgery is reserved for people who are healthy, have a good functioning liver, and who only have a single tumor that has yet to grow into blood vessels. This a complex procedure because the surgeon will have to remove enough of the liver to ensure all cancer has been removed, but they also have to leave enough to ensure your liver still functions properly.
While surgery can be successful, there are some side effects you should be aware of. Some risks and side effects include infection, blood clots, pneumonia, bleeding problems, and the development of new cancer.
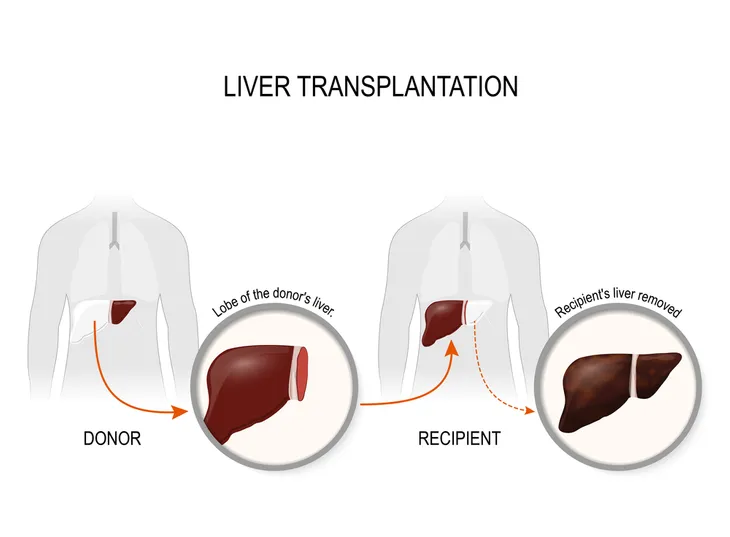
Liver Transplant
Instead of surgery to remove a part of your liver, your doctor may recommend that you undergo a liver transplant. This involves replacing your unhealthy liver with a healthy liver from a suitable donor.
Keep in mind, liver transplants are only reserved for patients whose cancer hasn’t spread to other organs. Once the transplant is complete, your doctor may provide medicine to help prevent rejection of the transplant.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is another form of treatment for liver cancer. It uses high-energy rays to get rid of cancer cells. The procedure is painless and the treatment only takes a few minutes, but the setup time may take longer. In many cases, radiation therapy will require small doses of radiation given five days a week for a few weeks.
Radiation therapy might be a good option if the liver cancer can’t be removed by surgery or isn’t responding to other treatments. It may also be a good option if your cancer has spread to other areas in your body or for those with a tumor that is blocking the portal vein.
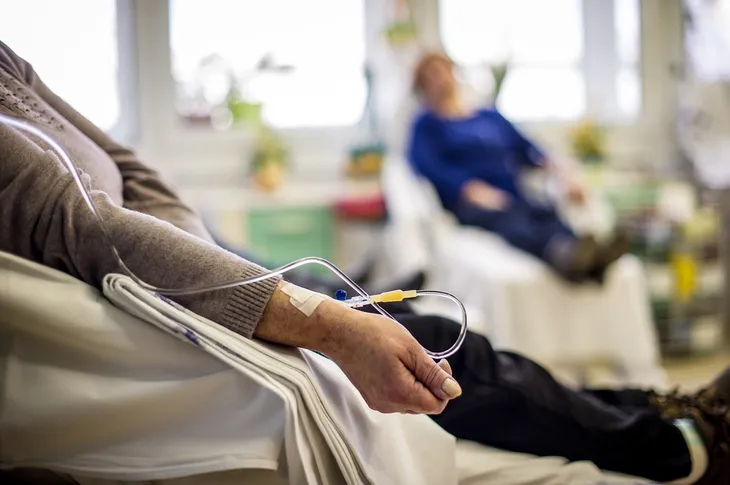
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy, also known as “chemo,” is a type of treatment that uses drugs to kill cancer cells. To receive this treatment, the drugs are injected intravenously.
Chemo may be recommended if your liver cancer can’t be treated with surgery or isn’t responding to other types of treatment. Sadly, most chemo drugs don’t have the best effect on liver cancer. However, the American Cancer Society explains, “Recent advances have shown that a combination of drugs may be more helpful than using just a single chemo drug.”
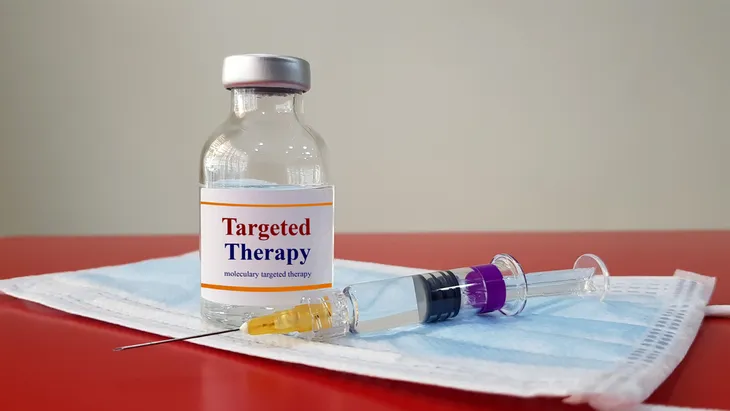
Targeted Drug Therapy
Targeted drug therapy uses medications that are designed to strike vulnerable cancer cells. This type of treatment will help shut off the blood supply to the tumor and decrease tumor growth.
A popular drug used to treat liver cancer is sorafenib (Nexavar). Keep in mind, targeted drug therapy can have many side effects so make sure you ask your doctor to find out what you should expect.
Immunotherapy
Another treatment option for liver cancer is immunotherapy. The American Cancer Society explains, “Immunotherapy is treatment that uses certain parts of a person’s immune system to fight diseases such as cancer.”
This treatment is often reserved for patients with advanced or metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma, which is the most common type of primary liver cancer. The treatment aims to shrink tumors and control the symptoms of liver cancer.