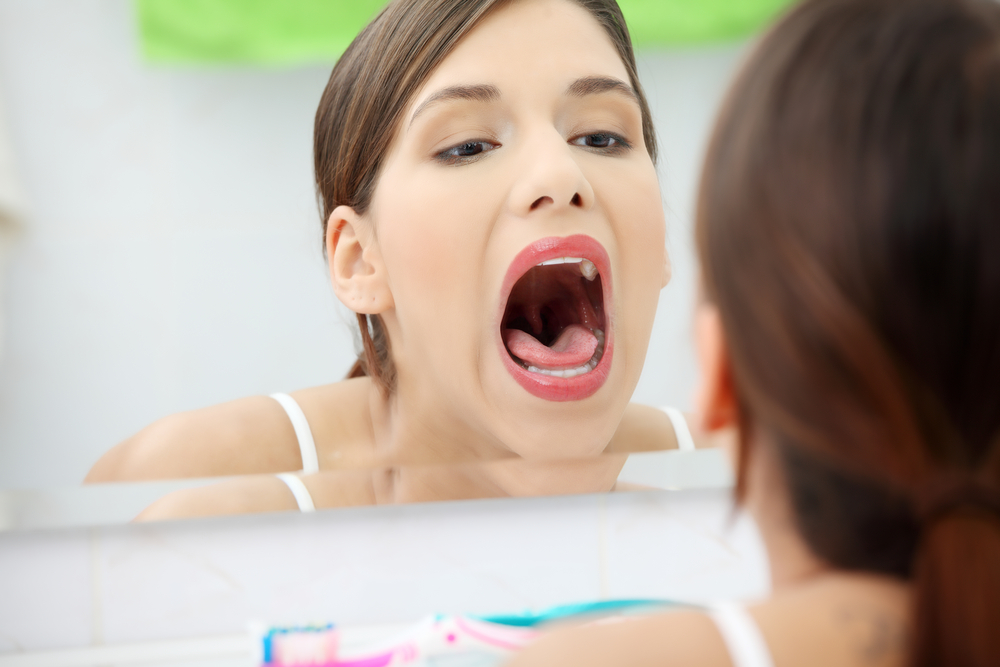
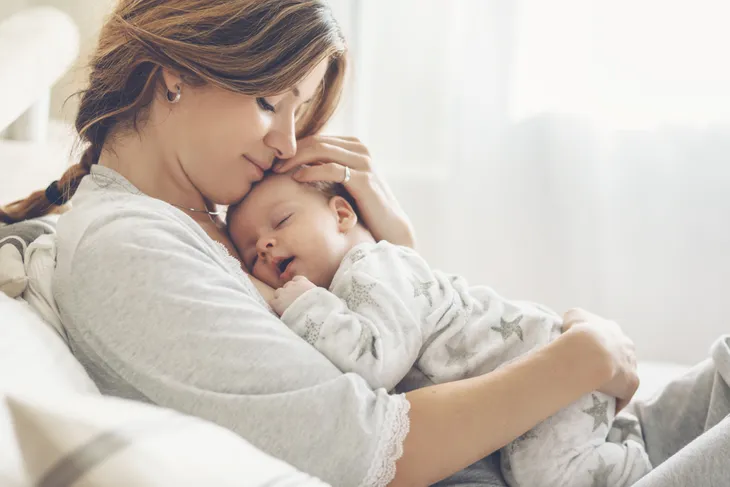
Do you have an unusual white rash inside your mouth? You might have a condition known as oral thrush. This unsightly (and sometimes painful) condition happens when a yeast infection develops inside your mouth.
The good news is oral thrush is usually mild and doesn’t typically lead to life-threatening complications. But there’s a lot more to know about it and what you can do if you get it. Here’s everything you should know about oral thrush, including the common symptoms, causes, complications, and treatment options.
What Is Oral Thrush
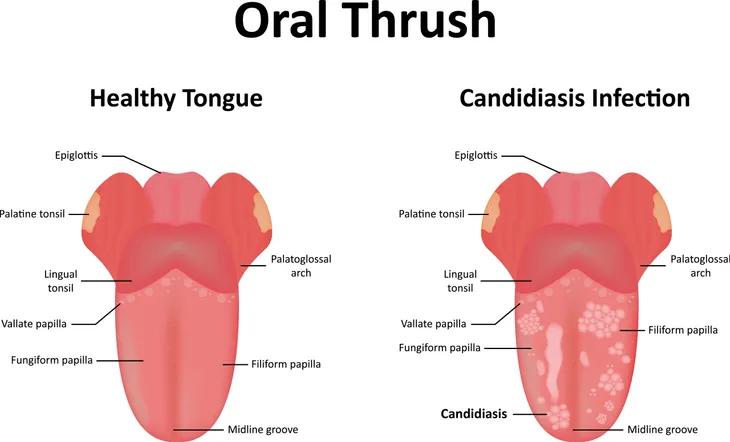
Oral thrush, also medically known as oral candidiasis, occurs when the fungus Candida albicans accumulates inside your mouth. Mayo Clinic points out, “Candida is a normal organism in your mouth, but sometimes it can overgrow and cause symptoms.”
Oral thrush can affect anyone, however, it’s more likely to develop in infants and older adults. This is because they have reduced immunity. The good news is, oral thrush is usually mild and rarely leads to serious problems.
Common Symptoms of Oral Thrush
You may not notice any symptoms in the early stages of oral thrush, but as the infection progresses you may begin to develop one or a few symptoms.
Some common symptoms of oral thrush include white or yellow bumps inside your mouth (inner cheeks, tongue, gums, tonsils, or lips), soreness or a burning sensation in your mouth, and a cotton-like sensation in your mouth. You may also have difficulty swallowing, a bad taste in your mouth, a loss of taste, and you may develop dry, crack skin in the corners of your mouth.
Severe Symptoms of Oral Thrush
As mentioned earlier, oral thrush rarely causes serious problems, however, the infection may spread to other parts of the body in individuals with weakened immune systems which in turn can cause potentially serious complications.
Healthline says, “without proper treatment, the fungus that causes thrush may enter your bloodstream and spread to your heart, brain, eyes, or other body parts.” If this occurs, it’s called systemic candidiasis which can lead to a potentially life-threatening condition called septic shock.
Infants and Mothers
If your infant has oral thrush, not only will they develop white/yellow mouth lesions, they may also become fussy and irritable, and have trouble feeding. Breastfeeding mothers also need to be cautious because their babies can pass the infection to them. Even worse, the infection can continue to pass back and forth between mother and child.
Breastfeeding mothers should be on the lookout for symptoms like unusual pain during nursing or stabbing pains. If you suspect you or your child have oral thrush, book an appointment with your doctor.
What Causes Oral Thrush?
Small amounts of candida fungus can be found in many parts of your body including your skin, mouth, and digestive tract. WebMD says, “It’s supposed to be there, and it’s usually kept under control by the other bacteria in your body.” So what causes it to accumulate and grow out of control?
Certain factors can disturb the balance of your bacteria such as certain illnesses or medications (typically antibiotics or corticosteroids). When this happens, the fungus can grow out of control, causing oral thrush.
Risk Factors
Certain factors can increase your risk of getting oral thrush. For example, having a compromised immune system can cause the fungus to grow out of control. Certain medications like antibiotics may reduce your friendly microorganisms which can disrupt the balance and lead to oral thrush.
Furthermore, cancer treatments such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy can also damage healthy cells making you more susceptible to oral thrush. Finally, other conditions that weaken your immune system such as HIV, diabetes, and leukemia can also increase your risk.
When to See a Doctor
You should visit your doctor or dentist if you notice white/yellow lesions inside your (or your child’s) mouth. WebMD explains that oral thrush is not common in healthy older children, teenagers, or adults so if you do develop oral thrush, make sure you visit your doctor to find out if there’s an underlying condition.
You should also make sure to contact your doctor if you are immunocompromised and develop thrush. Getting the right treatment as soon as possible is vital if you want to prevent serious complications.
How Is Oral Thrush Diagnosed?
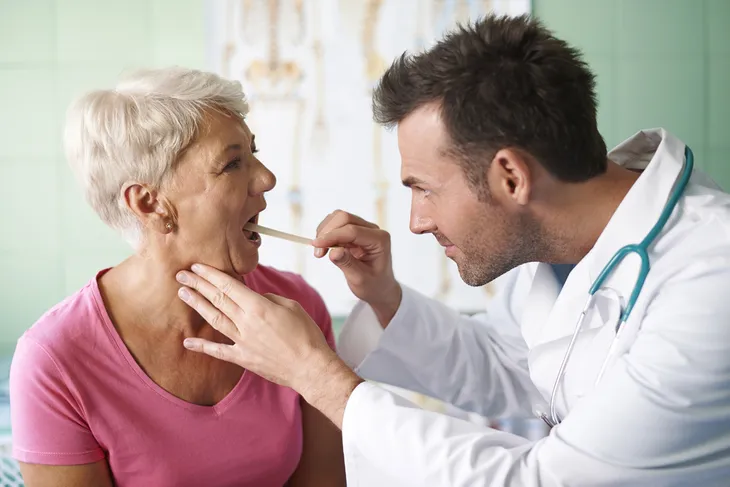
To diagnose oral thrush, your doctor or dentist will begin by examining the inside of your mouth. They may even take a sample of the spot and have it tested to be sure.
If the fungus has spread into your esophagus, you may require other tests. Some of these include endoscopy of your esophagus, stomach, and small intestine, an X-ray of your esophagus, or a throat culture which is a swab of the back of the throat.
Treatment
There are a variety of medications used to help treat oral thrush. Your doctor may prescribe one or more. Healthline lists the following medications as potential treatment options for oral thrush:
- fluconazole (Diflucan)
- amphotericin B (AmBisome, Fungizone)
- clotrimazole (Mycelec Troche)
- itraconazole (Sporanox)
- nystatin (Nystop, Nyata)
How Long Does It Take Oral Thrush to Clear Up?
The good news is, oral thrush doesn’t typically last for a long time. If you have a healthy immune system and with the right treatment, it should clear up within 2-weeks.
Keep in mind, in some cases, it can return. If you have recurring cases of oral thrush and there is no known cause, your doctor will evaluate you for underlying medical conditions. This will help them determine if another condition is contributing to thrush.
Home Remedies
In addition to the medication, there are several home remedies you can try to help ease the discomforts of oral thrush. For starters, a saltwater gargle (1/4-teaspoon of salt in 8-ounces of warm water) can be effective in easing your painful symptoms.
Other rinses may help too. You can try a mixture of water and baking soda, water and lemon juice, or water and apple cider vinegar. Finally, eating yogurt that contains beneficial bacteria or taking a probiotic supplement may help ease your symptoms too.
How to Prevent Oral Thrush
Your doctor may also recommend lifestyle changes to help treat oral thrush and prevent it from coming back. For starters, brush your teeth with a soft toothbrush to prevent scraping the bumps caused by thrush. Further, once your treatment is complete replace your toothbrush, and if you have dentures be sure to properly clean them.
They may also recommend changes to your diet and fitness regimen in order to support a healthy immune system. Finally, you should also practice good oral hygiene to help prevent oral thrush. This includes brushing your teeth twice a day, flossing daily, and visiting your dentist regularly.