Do you have a sore throat and hoarse voice? You might be suffering from laryngitis, a condition that occurs when the vocal cords or voice box become inflamed. Laryngitis is most often caused by overusing your voice but it can also be caused by viral infections. Most cases aren’t serious but persistent laryngitis may signal a more serious underlying problem. This is why it’s important to know what it is, why it occurs, and what you can do about it.
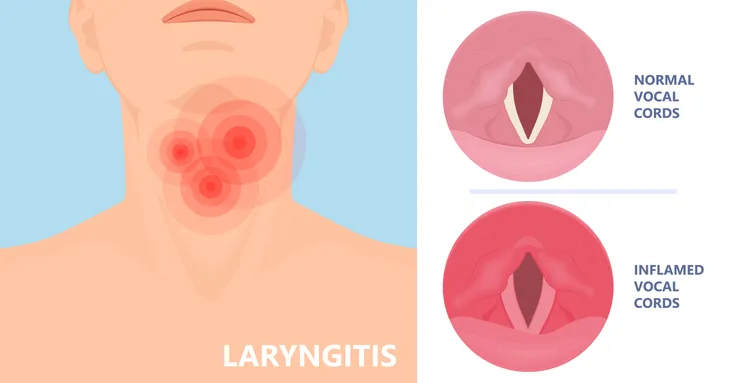
What Is Laryngitis?
Your vocal cords consist of two bands of smooth muscle tissue located in the larynx, also known as the voice box. Normally, they open and close, allowing air to pass through the cords from your lungs to produce the sound of your voice. But when you have laryngitis, the vocal cords are inflamed, which changes the way the air moves through your throat.
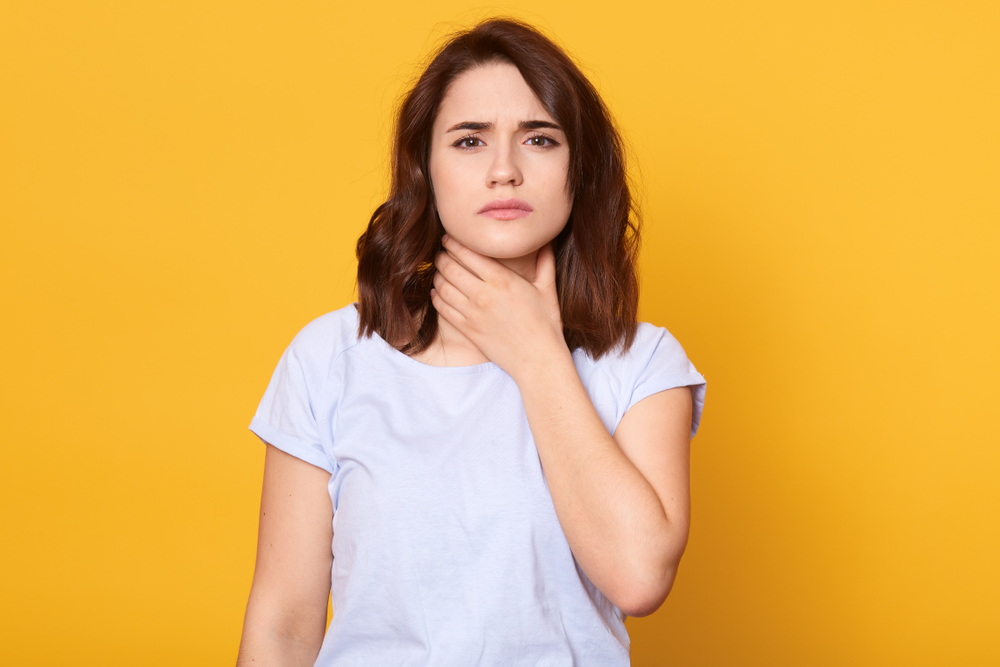
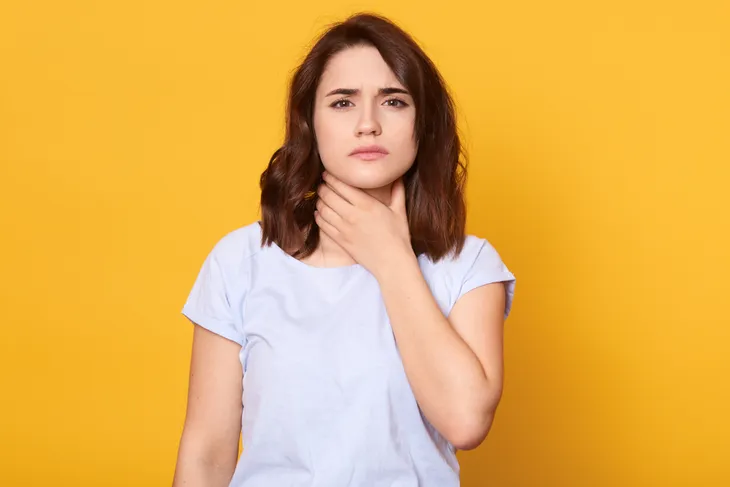
When this occurs, the change in airflow distorts the sound of your voice, which is why individuals with laryngitis typically have a hoarse and quiet voice.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Laryngitis
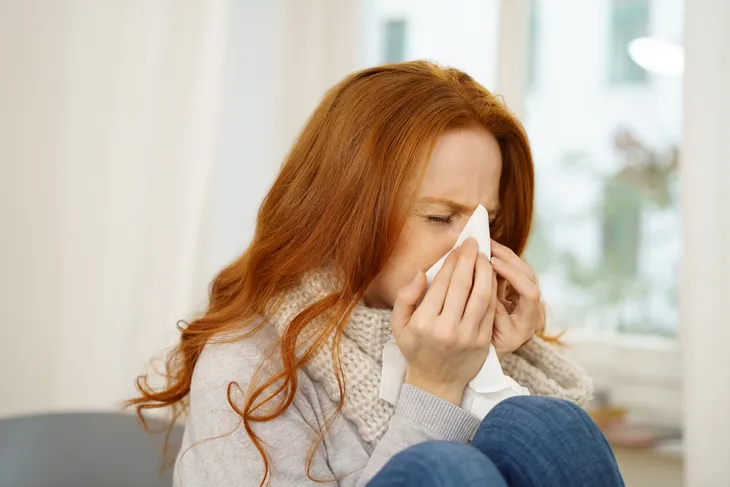
Telltale signs of laryngitis include a hoarse or weakened voice. Sufferers also typically experience a dry throat, tickling or irritation in the throat, and a dry cough. It’s also common to lose your voice completely.
Laryngitis symptoms typically begin suddenly and then become more severe over the next several days. However, if the symptoms last longer than 3-weeks, then your condition is considered chronic and this usually means there may be a more serious underlying cause.
Other Accompanying Symptoms
Medical News Today points out that laryngitis is often related to other illnesses, such as a cold or flu, throat infection, or tonsillitis. As such, you may experience other symptoms too. They may include:
- Runny nose
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Pain while swallowing
- Swelling in the glands.
The good news is that your symptoms will typically resolve without treatment after a week. However, if any symptoms persist or become worse, be sure to see your doctor right away. There may be an underlying cause worth investigating.
What You Need to Know About Laryngitis in Children
Anyone can get laryngitis including children and, in some cases, it can be more serious in children too. WebMD says you should watch for serious symptoms such as a fever of 100-degrees Fahrenheit in children under 3-months old or a fever of 102-degrees Fahrenheit in children older than 3-months.
You should also watch for difficulty swallowing or breathing, as well as if their voice makes a high-pitched sound when inhaling. If your child displays any of these symptoms contact your doctor right away.
The source also notes, “In kids, it may lead to croup, a narrowing of the airways, or epiglottitis, an inflammation of the flap at the top of the larynx.” This can be life-threatening, so you must seek emergency treatment if your child has laryngitis and starts gasping or if they’re having difficulty breathing.
What Causes Acute Laryngitis?
Laryngitis can be acute or it can be chronic. Acute means it’s temporary and usually only lasts about a week. The common cause of acute laryngitis is overuse of the vocal cords from talking, yelling, or singing.
It can also be caused by an infection, including viral infections and bacterial infections. Healthline says it can also be caused by drinking too much alcohol.
What Causes Chronic Laryngitis?
Chronic laryngitis means it’s longer-lasting, typically 2-weeks or more. The symptoms are also usually more severe than acute laryngitis.
Common causes of chronic laryngitis include overusing your vocal cords and frequent exposure to harmful chemicals or allergens. Acid reflux, frequent sinus infections, and smoking or being exposed to second-hand smoke can also be culprits of chronic laryngitis.
Healthline says, “Cancer, paralysis of the vocal cords, or changes in vocal cord shape as you age can also cause persistent hoarseness and sore throats.”
Risk Factors
While anyone can get laryngitis, certain factors can increase your risk of getting it. For starters, the Mayo Clinic says having a respiratory infection (such as a cold or bronchitis) can increase your risk.
Overusing your voice regularly, such as talking a lot or too loudly, as well as singing or shouting, can also increase your risk of laryngitis. Finally, the source also notes exposure to irritating substances, such as stomach acid, cigarette smoke, excessive alcohol intake, or chemicals in the workplace, are also risk factors.
Can There Be Complications?
Laryngitis isn’t usually serious; however, in rare cases, the inflammation may cause respiratory distress. If this occurs, it requires immediate medical attention.
Healthline says, “A bacterial infection causing epiglottitis can also spread beyond the epiglottis and larynx to other areas in your respiratory tract and into your bloodstream,” which can be serious. Finally, another potential complication is an underlying condition such as vocal cord paralysis or throat cancer. These conditions can be serious if left untreated.
 Ahmet Misirligul / Shutterstock
Ahmet Misirligul / ShutterstockWhen to See a Doctor
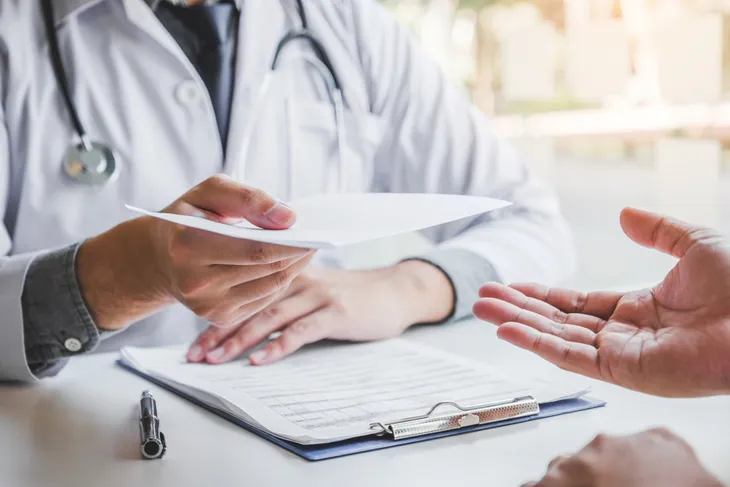
If you’re showing signs of laryngitis, talk to your doctor. Since laryngitis can be caused by more serious underlying conditions, it’s always important to rule them out.
Some signs of a more serious underlying issue include trouble swallowing or coughing up blood. If you have a fever that doesn’t go away with treatment or extreme pain in your throat, this could also indicate a more serious issue.
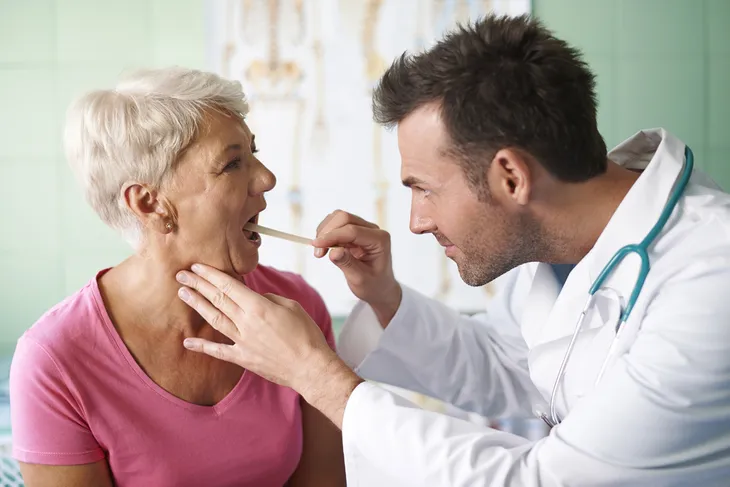
How Is Laryngitis Diagnosed?
To diagnose laryngitis, your doctor will start by reviewing your symptoms. Then, they’ll look at your vocal cords using a special mirror. In some cases, your doctor may perform laryngoscopy. During this procedure, your doctor will stick a thin, flexible tube that has a microscopic camera on it into your mouth or nose. This allows them to get a better view.
During the exam, your doctor will be looking for signs of irritation, swelling, and lesions on the voice box. They’ll also look for signs of swelling on the vocal cords, which can indicate overuse. If your doctor sees a suspicious mass, they may recommend a biopsy (which removes a small piece of tissue) to rule out throat cancer.
Treatment: At-Home Remedies
In many cases, you can recover from laryngitis at home without any formal treatment. Doctors often recommend resting your voice to help ease the symptoms. Medical News Today points out that even though whispering seems like a better alternative, it actually requires the vocal cords to be tightly stretched and ultimately will hinder your recovery.
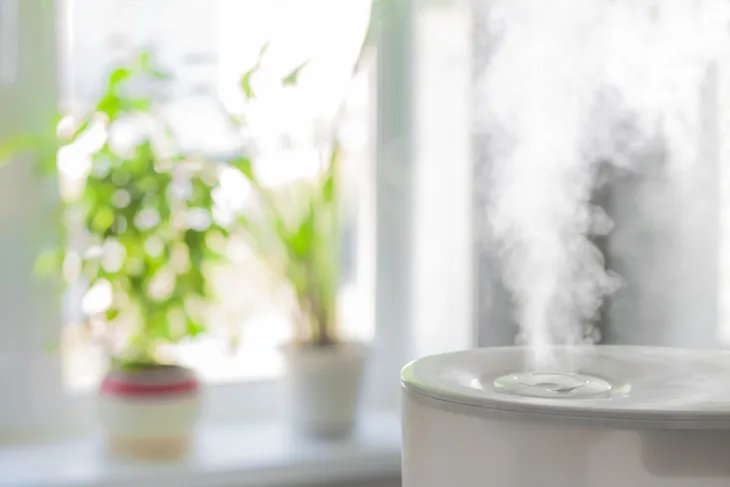
Other home remedies you can try include drinking lots of fluids, avoiding inhaling irritants, taking an over-the-counter pain reliever, and avoiding decongestants because they can dry out the throat. The source also recommends breathing moist air. If you don’t have a humidifier yet, you might want to invest in one now.
Other Treatments for Laryngitis
In some cases, at-home treatments aren’t enough, especially if you have bacterial laryngitis. Keep in mind bacterial laryngitis is rarer but it can be treated with antibiotics.
Your doctor may need to prescribe corticosteroids, which are medicines used to help reduce inflammation and swelling. If you have chronic laryngitis, your doctor will want to find out if there is an underlying cause, and if there is, you’ll need to treat that issue.
Finally, WebMD points out that voice therapy is another treatment option. In speech therapy, a speech-language therapist will teach you how to care for your voice and how to avoid habits that cause strain.
Prevention Tips
While you can’t always prevent laryngitis, there are things you can do to help keep your voice box and vocal cords healthy. For starters, be sure to avoid the irritants we mentioned earlier, such as cigarette smoke and toxic chemicals, as well as reducing your alcohol intake and foods that cause heartburn.
To prevent catching a cold or another respiratory illness, be sure to wash your hands regularly, practice good hygiene, and stay away from individuals who are sick. Finally, Healthline notes you should also try to avoid clearing your throat, as this can cause inflammation and irritation of the vocal cords.