Jaundice is a condition that affects 60-percent of all infants born in the U.S. but it can happen to anyone of all ages. This is why it’s important to know what it is and what you can do about it.
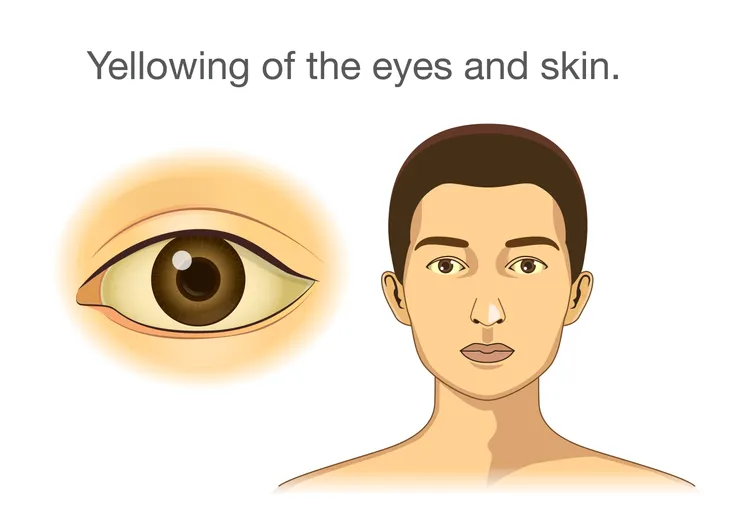
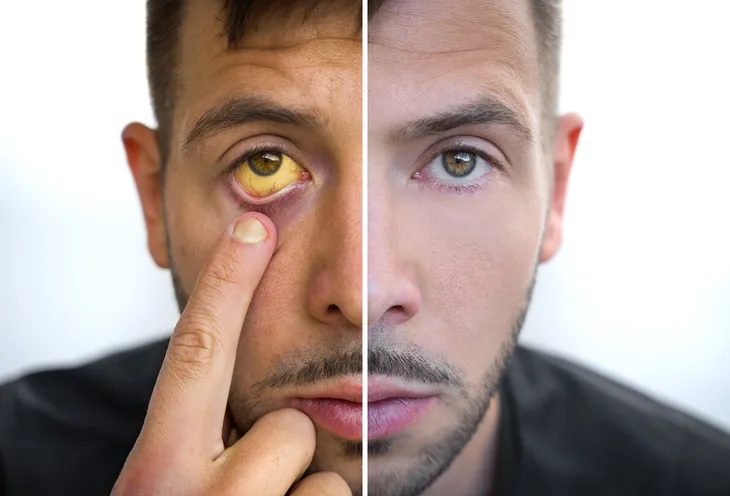
It’s a disease that turns your skin and whites of the eyes yellow due to high bilirubin levels. And bilirubin is a waste product found in the blood. When an individual has jaundice, it typically occurs due to an underlying condition. So, in an effort to better understand it and the risks associated with the disease let’s take a look at everything you need to know about jaundice.
Types of Jaundice
Before we dive into the symptoms, causes, and treatment, we must first establish that there are three main types of jaundice: hepatocellular, hemolytic, and obstructive. Hepatocellular jaundice is caused by liver disease or liver injury.
Hemolytic jaundice develops as a result of hemolysis. In other words, it’s an “accelerated breakdown of red blood cells, leading to an increase in production of bilirubin,” says Medical News Today. The last type is obstructive jaundice. This occurs due to an obstruction in the bile duct, which then prevents bilirubin from exiting the liver.
Common Symptoms of Jaundice
The most common sign of jaundice is yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes. These symptoms typically begin at the head and then spread down the body.
Other common symptoms of jaundice include pale stools, dark urine, and itchiness. If you notice any of these symptoms contact your doctor right away.
You can also have low bilirubin levels which have their own set of accompanying symptoms. Some key indicators of low bilirubin levels include fatigue and abdominal pain. An individual may also experience vomiting, fever, and weight loss.
Complications
Some of the symptoms associated with jaundice can lead to serious complications. For example, the skin can become so itchy that the individual scratches their skin raw.
Other complications include insomnia and in severe cases suicidal thoughts. It’s important to point out that the complications occur due to the underlying problem that is causing jaundice.
Jaundice in Newborns
Jaundice can be frightening especially for first-time parents. It turns out jaundice is a lot more common than you might think, affecting about 60-percent of newborn infants. Medical News Today says that number jumps to 80-percent for premature babies born before 37-weeks of pregnancy.
Signs of jaundice typically appear within 72-hours of birth. The good news is, the symptoms will typically resolve without treatment within 2-weeks. That said, it’s still important to follow the guidance of your doctor.
Causes of Jaundice in Newborns
So we know that jaundice is a common health issue for newborns but what causes it to occur in the first place? Medical News Today notes the red blood cells in the body of an infant are frequently broken down and replaced causing the production of increased bilirubin.
Furthermore, an infant’s liver is less developed. This means their liver is less effective at filtering bilirubin from their body.
Treatment for Newborns
As mentioned earlier, mild cases typically resolve on their own without treatment. However, if the levels are extremely high, it’s vital for the infant to receive treatment.
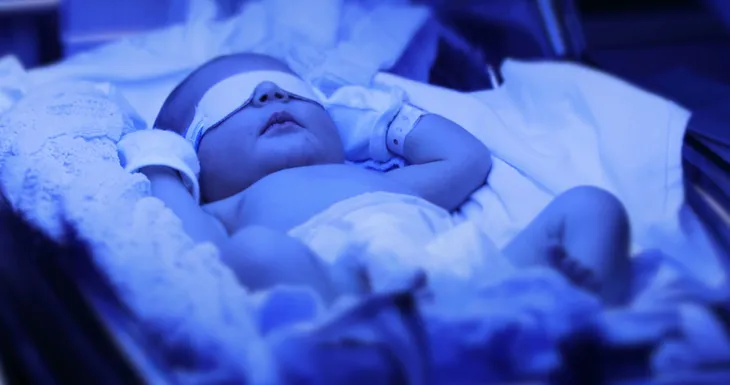
A common treatment option for newborns is phototherapy which requires a special type of light for a process called photo-oxidation. This process adds oxygen to the bilirubin to help it dissolve easily in water. Another treatment option is a blood transfusion.
Leaving high levels untreated can result in serious consequences as it can lead to kernicterus, a rare type of permanent brain damage.
Jaundice in Adults
Although jaundice is rarer in adults (especially compared to newborns), it can still occur and for many reasons. Some common causes of jaundice in adults include hepatitis, alcohol-related liver disease, or pancreatic cancer.
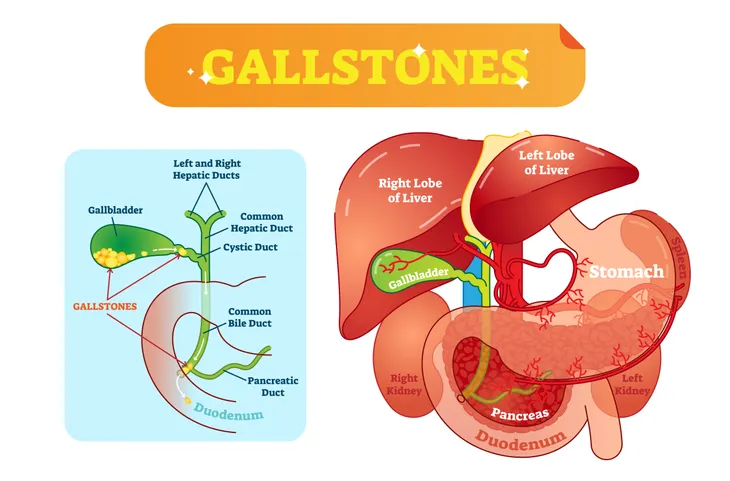
In some cases, bile ducts (which are thin tubes that carry bile from the liver/gallbladder to the small intestine) can get blocked from gallstones, rare liver disease, or cancer which can also lead to jaundice. Let’s take a closer look at the causes of jaundice next.
Causes
Cleveland Clinic says, “jaundice can be caused by a problem in any of the three phases in bilirubin production.” If jaundice occurs before the production of bilirubin, you may have unconjugated jaundice. The increased levels of bilirubin can be caused by the reabsorption of a large hematoma or hemolytic anemias.
If jaundice occurs during the production of bilirubin the root cause may be viruses such as Hepatitis A, chronic Hepatitis B or C, or Epstein-Barr virus. It can also be caused by alcohol, autoimmune disorders, medication, or a rare genetic metabolic defect.
Finally, if jaundice occurs during the last phase after bilirubin is produced, then the cause may be obstruction of the bile ducts. Some things that cause this include gallstones, inflammation of the gallbladder, gallbladder cancer, or pancreatic tumor.
Risk Factors
Having certain conditions can increase your risk of developing jaundice. For starters, acute inflammation of the liver may hinder your liver’s ability to get rid of bilirubin causing it to build up. Further, inflammation of the bile duct can also prevent the removal of bilirubin and lead to jaundice.
Other conditions that can increase your risk include Gilbert’s syndrome, hemolytic anemia, and cholestasis. Essentially, any condition that either causes too much bilirubin production or a condition that impairs the liver from getting rid of it may lead to jaundice.
When to See a Doctor
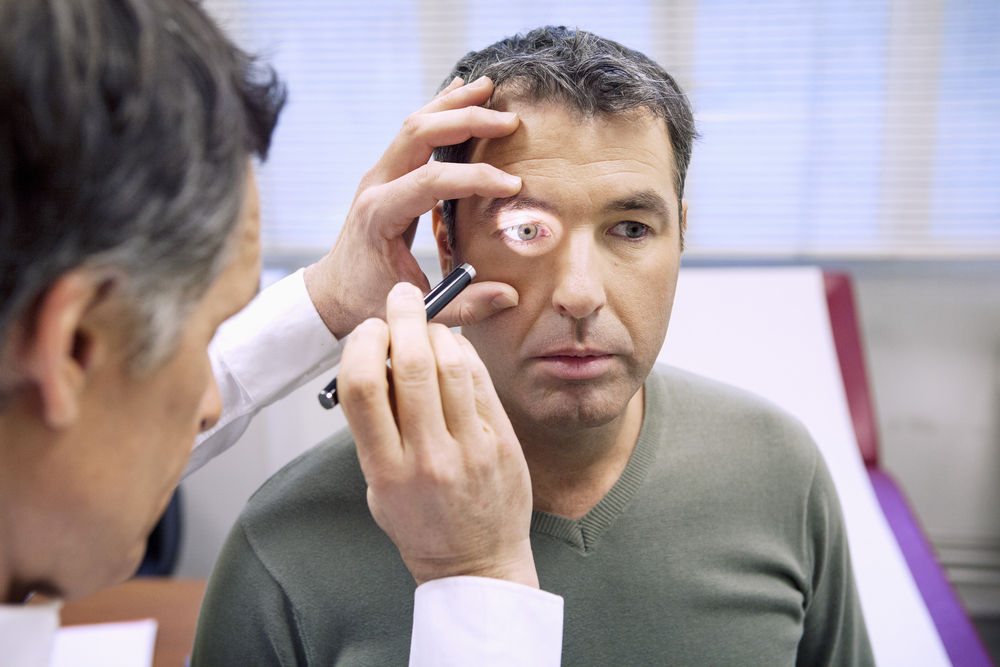
Now that we know the telltale signs of jaundice and who’s at risk, when should you see a doctor? If you ever develop any of the symptoms of jaundice you need to see the doctor right away. Jaundice could be a symptom of a liver, gallbladder, or blood problem which can be serious.
After a diagnosis (which we’ll get to next) your doctor will then be able to run a series of tests to determine what is causing jaundice. This information will help them develop the best treatment plan for you.
Diagnosis
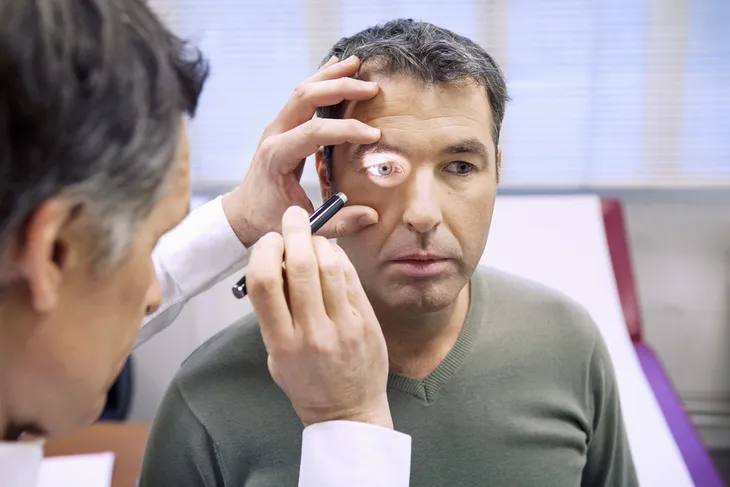
At your visit, your doctor will likely first perform a physical exam as well as consider your medical history. There are several tests that can confirm you have jaundice. First is a liver function test which looks to see if your liver is functioning properly.
If the root cause is still undetermined, your doctor may request blood tests to examine your bilirubin levels. These tests include bilirubin tests, full blood count or complete blood count, and Hepatitis A, B, and C tests.
Your doctor may also examine the structure of your liver through imaging tests or they may require a biopsy of the liver to check for inflammation, fatty liver, cirrhosis, or cancer.
Treatment Options
Jaundice itself isn’t directly treated but instead, your doctor will have to treat the underlying problem that is causing too much bilirubin in your blood. Some individuals can benefit from a few lifestyle adjustments such as diet and exercise, while others may require long-term treatment or surgery.
It’s vital that you see your doctor right away if you start showing signs of jaundice so that they can determine the root cause and begin treating the underlying problem.