Are you on top of your blood sugar? If you don’t suffer from diabetes, you might not think about your blood sugar very often. However, if you aren’t knowledgeable about maintaining a healthy blood sugar level, you could find yourself dealing with hypoglycemia (and you might not even realize it). You should search online to learn about the causes and symptoms of hypoglycemia.
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, occurs when your body’s blood sugar level drops below 70-mg per deciliter. If left untreated, a severe case of hypoglycemia can be life-threatening. In order to get proper treatment, you need to know the facts about hypoglycemia. You should search online to discover how low blood sugar is treated.
Healthy blood sugar levels are important because your blood sugar, or glucose, is the body’s number one energy source. If your levels drop too low, your body can’t function – and hypoglycemia takes hold. While this commonly occurs in individuals with diabetes, it can happen to anyone. Hypoglycemia can be caused by a number of health changes or habits, and it can have serious consequences.
What Causes Hypoglycemia?
Hypoglycemia has different causes, particularly if you’re living with diabetes.
If you are diabetic, low blood sugar can happen when the body overproduces the hormone that regulates glucose in the blood after you eat. This is called reactive hypoglycemia.
If you aren’t diabetic, hypoglycemia can be caused by other health issues. It can happen due to the following:
- Drinking too much alcohol
- Taking certain medications, such as malaria medication, some antibiotics, and certain pneumonia medications
- Eating disorders, particularly anorexia
- Hepatitis
- Disorders of the adrenal or pituitary glands
- Kidney problems
- Pancreatic tumors
You can discuss your risk for developing hypoglycemia with your doctor. Certain health conditions may increase your odds of experiencing low blood sugar, and it’s a good idea to be aware of your risks.
Symptoms of Low Blood Sugar
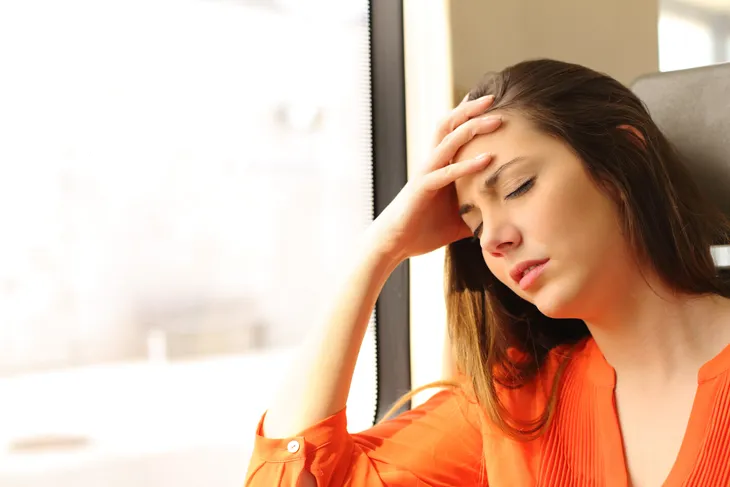
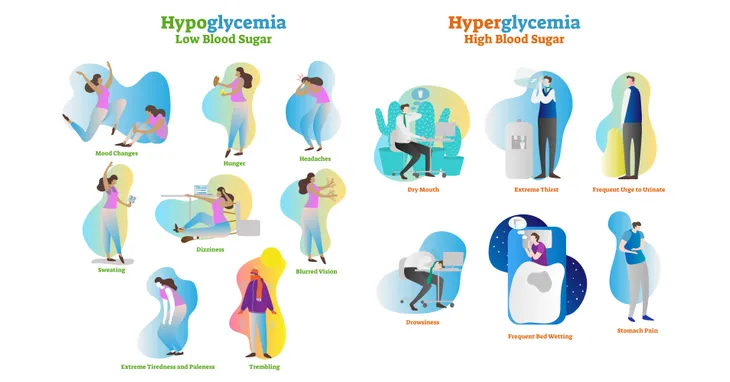
When hypoglycemia occurs, the signs and symptoms can be confusing. The effects of low blood sugar vary from person to person, and they typically aren’t seen or felt until your blood glucose level falls below 50-mg/dL, which is 20 points below the starting point of hypoglycemia.
So, when you start feeling symptoms, your body is already in the throes of the condition. You could experience any of the following effects as a result:
- Nervousness
- Sweating
- Intense hunger
- Feeling dizzy or lightheaded
- Trembling
- Weakness
- Palpitations
- Trouble speaking
- Paleness
- Difficulty concentrating
- Feeling irritable
- A change in behavior or personality
- Seizures
- Loss of consciousness
These symptoms are usually very recognizable when they happen. Typically, you’ll feel a sense of urgency to eat, which will resolve the symptoms. They’re essentially signals that your body needs more fuel in order to continue functioning.
Fuel Up!
Hypoglycemia symptoms are also a signal to you that you need more fuel before your brain becomes affected. If you cannot respond (or don’t respond) to these symptoms by eating, your blood glucose levels will continue to fall lower.
As a result, you’ll progress to a new level of hypoglycemia, and you’ll begin developing more serious symptoms or health changes. Once your brain is affected, you can fall into a coma or have a seizure.
Treating Hypoglycemia
Diet
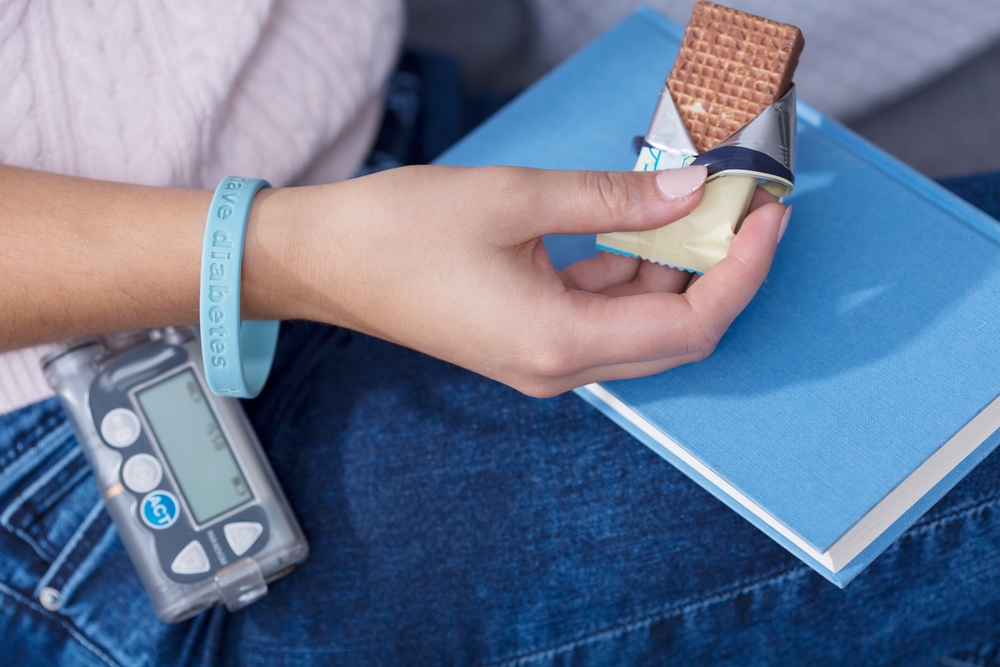
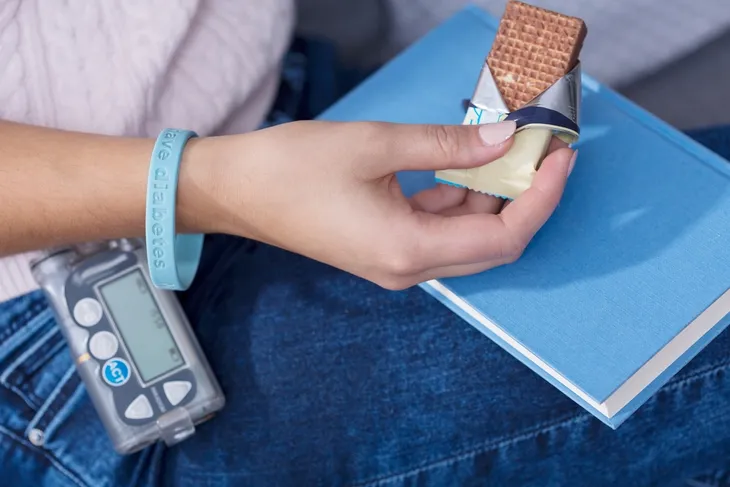
There’s good news for anyone who develops hypoglycemia: this condition can be treated, and it can typically be treated very easily. It can actually be solved if you have a snack.
When you begin experiencing the symptoms of hypoglycemia, you need to act and eat. The best choice is to eat something that’s made with carbohydrates. It’s especially important to choose a high carbohydrate food if you’re diabetic. Diabetics should aim for foods with 15-grams of carbohydrates or more.
You can grab a granola bar, fresh or dried fruit, pretzels, or even a cookie when your blood sugar is low. As a glass of fruit juice can also be a good choice.
Glucose Tablets
If your blood sugar is too low and you need to get it back on track quickly, you can also take glucose tablets. Glucose tablets will rapidly raise your blood sugar, and you don’t need a prescription for them. Like any food you might eat when your blood sugar is low, it’s a good idea to take glucose tablets with 15-grams of carbohydrates or more.
It’s a good idea to try eating something before you take a glucose tablet. You can have a snack, wait 15-minutes, and see if you’re still experiencing hypoglycemia. If so, then a glucose tablet can help.
How to Manage Hypoglycemia
You can work to combat hypoglycemia by following a balanced diet. Eating slow-release carbohydrates can help you sustain blood sugar levels, and eating small meals (instead of large meals) can help you prevent significant spikes and drops. You should try to eat every 3-hours, and make sure you’re eating protein, healthy fats, and fiber. You should avoid sugary foods, as they can cause crashes and spikes in blood sugar.
You should also speak with your doctor if hypoglycemia is becoming a concern. Often, the best treatment plan is to deal with any underlying causes of low blood sugar. If you can treat a larger health issue that’s causing hypoglycemia, you can avoid its symptoms and dangerous effects altogether.