High cholesterol (clinically known as hyperlipidemia) is a common problem for people in the U.S. It’s estimated that around 93 million adults aged 20 and older have cholesterol levels higher than those recommended by the medical establishment, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). High cholesterol can put you at risk of developing serious complications such as coronary heart disease, heart attack, and stroke.
Since the symptoms of high cholesterol are not usually obvious, it’s important to understand what cholesterol actually is and the common risk factors involved. Here is what you should know…
What Is High Cholesterol?
The first step to achieving healthy cholesterol levels is to understand what they even mean. According to Healthline, cholesterol is a fatty substance produced by your liver. It’s essential for producing cell membranes, vitamin D, and certain hormones.
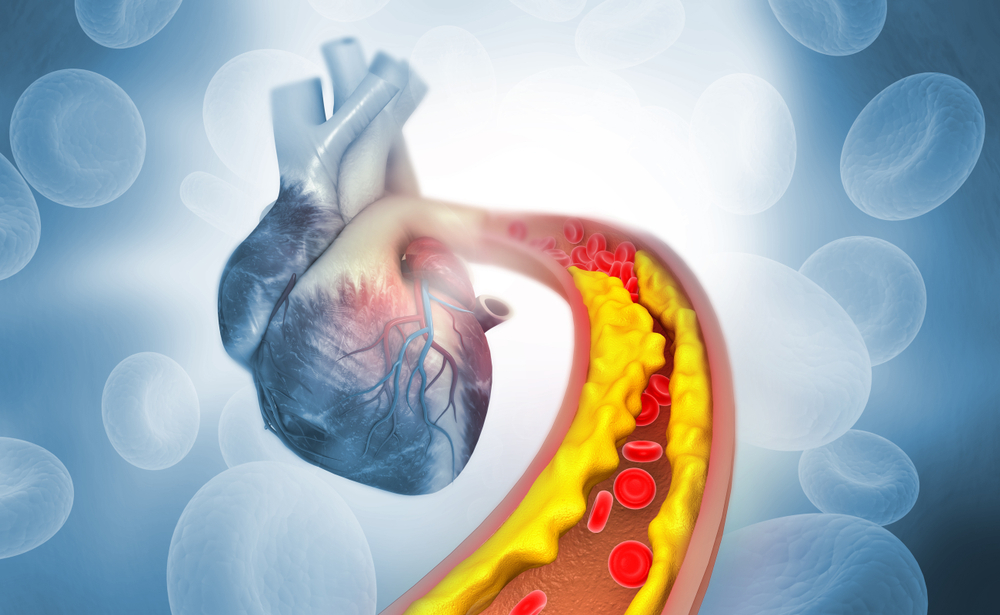
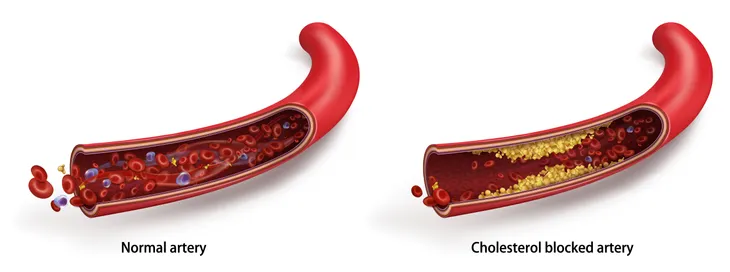
The problem is that cholesterol does not dissolve in water, so it needs to be transported through the bloodstream. Lipoproteins help make this happen. When you have high cholesterol, fatty deposits build up in your blood vessels (a condition referred to clinically as atherosclerosis). This makes it difficult for blood to flow through your heart, brain, and other important arteries.
High Cholesterol Red Flags
There are usually no symptoms that indicate you have high cholesterol. You can’t just feel whether your cholesterol is high or not. Rather, Verywell Health says any symptoms you might experience are related to the consequences of the disease rather than the disease itself.
If you are experiencing health problems due to high cholesterol, here are some of the red flags to look out for:
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Fatigue
- Difficulty breathing
- Headaches
- Visual problems
- Irregular heartbeat
- Chest pain
- A dermatologic condition called xanthomas (only in severe cases)
Diagnosing High Cholesterol
So, if there aren’t any symptoms that directly relate to high cholesterol, how do you know whether you have it or not? Simply, you will have to go through a blood test called a lipid profile (which is usually obtained while you are fasting). WebMD says different results help doctors interpret your cholesterol health.
Earlier we talked about how lipoproteins help dissolve cholesterol in order to transport it throughout the body in the bloodstream. A lipid profile test measures different forms of lipoprotein, each with its own purpose in maintaining healthy cholesterol. A lipid profile includes:
- Total cholesterol
- Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol
- High-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol
- Triglycerides
The Risks of High LDL Cholesterol Levels
The CDC says LDL cholesterol, also known as “bad” cholesterol, makes up most of the body’s cholesterol. High LDL levels put you at higher risk of heart disease and stroke because it can build up on the walls of your blood vessels, blocking proper blood flow throughout your organs. The desirable LDL cholesterol level is less than 100-milligrams/deciliter (mg/dL).
HDL Cholesterol
HDL cholesterol is also known as “good” cholesterol. This lipoprotein absorbs cholesterol and carries it back to the liver, where it is then flushed from the body. You want a higher level of HDL to lower your risk for heart disease and stroke. Ideally, the HDL levels should be ≥ 60-mg/dL in men and ≥ 50-mg/dL in women. Levels ≥ 60 mg/dL are most desirable (although rarely achieved), as this can greatly reduce your risk of cardiovascular disease.
Triglycerides and Total Cholesterol
The CDC says triglycerides are a type of fat in your blood that your body uses for energy. If you have high levels of triglycerides along with unhealthy LDL and HDL cholesterol levels, your risk of heart attack and stroke increases. Normal levels of triglycerides in adults are < 50 mg/dL.
Your total cholesterol is simply the total amount of cholesterol in your blood based on your HDL, LDL, and triglycerides results. The ideal total cholesterol level in adults is ≤ 150 mg/dL.
Risk Factors
It’s recommended that healthy adults over the age of 20 get their cholesterol levels checked at least once every 5-years. The Mayo Clinic says you might have to get your levels checked more often if you fall under one of the risk factors for high cholesterol.
Some factors that increase your risk of high cholesterol are:
- Consuming diets high in cholesterol, saturated fat, and trans fat
- Having a body mass index (BMI) of ≥ 30-kg/m2
- Lack of exercise
- Smoking cigarettes
- Age
- Diabetes
Preventing High Cholesterol
Whether you’re trying to lower your cholesterol or maintain healthy cholesterol levels, you can do so by living a healthy lifestyle. Making positive choices related to your diet and overall lifestyle can lower your risk of complications that comes from having high cholesterol.
Here are some simple ways to reduce your risk of high cholesterol:
- Prioritize fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your meals
- Eat a low-salt diet
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Quit smoking
- Drink alcohol in moderation (no more than 2 drinks/day for men and no more than 1 drink/day for women)
- Aim for 30 minutes of daily physical activity
- Manage stress levels