Anyone who has dealt with or is currently dealing with a hernia understands the discomfort it can bring. The key symptoms of a hernia include a visible lump, an upset stomach, muscle weakness, vomiting, heartburn, fever, and pain. If you’re experiencing a hernia you must deal with it quickly. It may not be life-threatening right away, but it won’t go away on its own.
In this article, we dive deeper to find out what exactly causes a hernia and the factors that can put you at a greater risk for developing one. We’ll also look into treatment options and steps you can take to help prevent them from happening. Here’s everything you should know about a hernia.
What Is a Hernia?
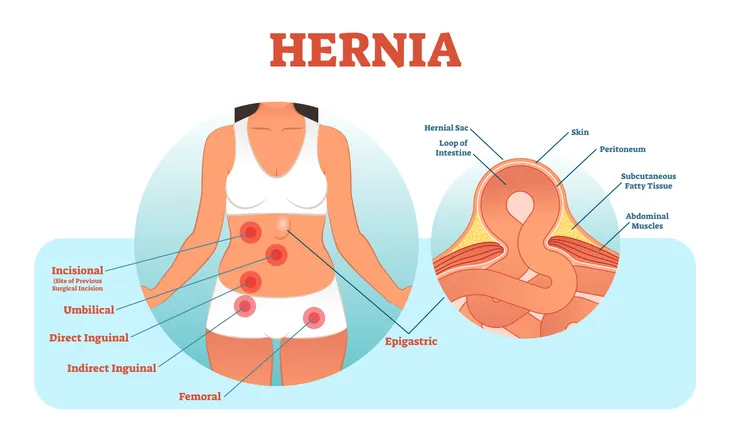
Dealing with a hernia is never an enjoyable experience and it can occur in any part of the body. Some of the more common areas include the upper abdomen (hiatal hernia), inner groin (inguinal hernia), outer groin (femoral hernia), close to the navel (umbilical hernia), or near the area of a recent surgical scar (incisional hernia).
But what is a hernia exactly? In short, a hernia presents as a lump, which occurs when the muscle wall becomes weak, letting fatty tissue squeeze through. In many cases, an internal organ, typically the bladder or bowel will push through the surrounding muscle. This can cause mild to extremely painful symptoms.
Hernia Causes
A hernia is typically caused by muscle weakness and strain. Some hernias can develop quickly while others can develop over a period of time. So the question is, what causes muscle weakness and strain in the first place?
Some common causes that can lead to a hernia, include aging, chronic coughing, pregnancy, constipation, and fluid in the abdomen. Other causes include being overweight, strenuous activity, such as lifting heavy weights, and damage from an injury or surgery.
Risks Factors
In addition to its common causes, certain factors may put you at greater risk for developing a hernia. This includes having a family history of hernias, your age, being pregnant, and being overweight.
Furthermore, chronic coughing and chronic constipation can also put you at greater risk for developing a hernia. Finally, smoking, cystic fibrosis, or being born with low birth weight or prematurely can also increase your risk.
Can a Hernia Go Away on Its Own?
A common question many people ask is can a hernia go away on its own? The answer is, no. The only effective treatment for a hernia is surgery.
That said, if you have a small hernia and don’t have any symptoms, your doctor may not recommend surgery. Instead, you and your doctor will need to monitor the hernia and be on the lookout for signs of enlargement as well as developing symptoms.
Surgery for a Hernia
Hernias typically grow larger over time. This happens when the muscle wall becomes weaker and more tissue bulges through. As the hernia grows larger you may develop more symptoms. As a result, it may begin to cause mild to severe pain. If this happens, your doctor may decide surgery is the best course of action for you.
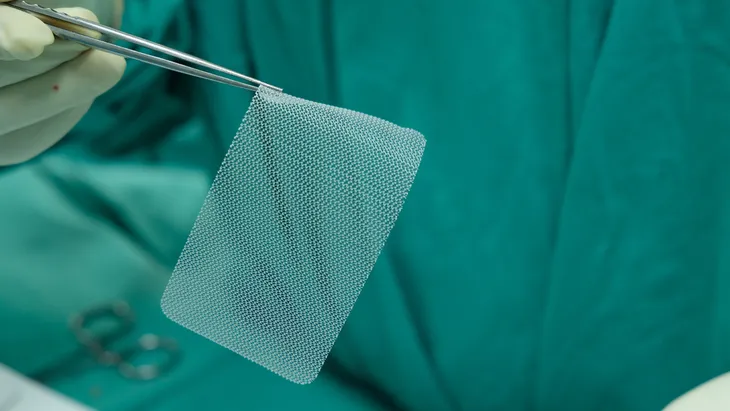
To repair the hernia, the surgeon may sew the hole closed. This is typically done by patching the area with surgical mesh. Before surgery, your doctor will be able to thoroughly walk you through the procedure to explain what to expect.
The Two Types of Surgery for a Hernia
There are two types of surgery for a hernia, laparoscopic or open. Laparoscopic surgery is often preferred because it’s less damaging and uses a small camera and surgical equipment to repair the hernia.
Unfortunately, not all patients are suitable for this type of surgery. If this is the case, your doctor will be able to determine the most suitable form of surgery for your situation.
Hernia Treatment
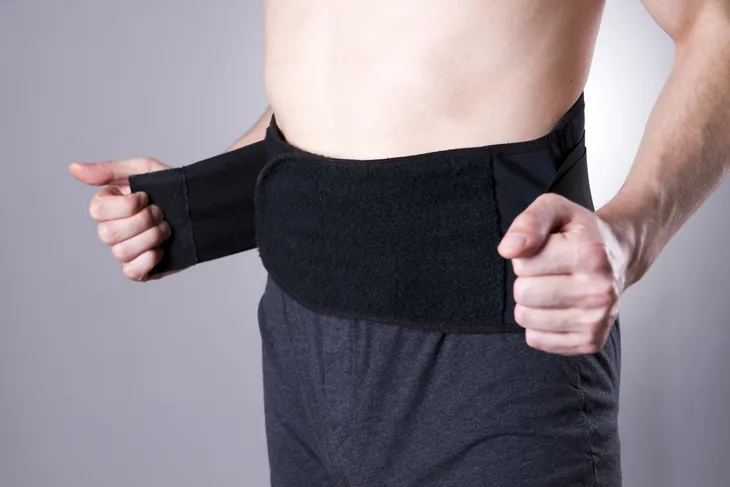
As we now know, a hernia cannot be treated without surgery. However, if your hernia has not caused complications and is small, your doctor will want to keep an eye on it. Wearing a truss may help in the meantime. This is a supportive undergarment that helps hold the hernia in place.
Keep in mind, only wear a truss if it’s recommended by your doctor and have them examine it to ensure it fits properly. An improper fitting truss can cause adverse effects.
Furthermore, if you have a hiatal hernia (this occurs in the upper abdomen when your stomach pokes through the hole in your diaphragm and invades your chest cavity), some over-the-counter (OTC) medications or prescription medication may help relieve the discomfort and improve your symptoms.
How To Relieve Hernia Pain
Even though home remedies can’t treat your hernia, there are some things you can try to help manage your symptoms. For starters, dietary changes may help relieve the pain of a hiatal hernia. Avoid large and heavy meals, and ensure you don’t lie down or bend over after eating.
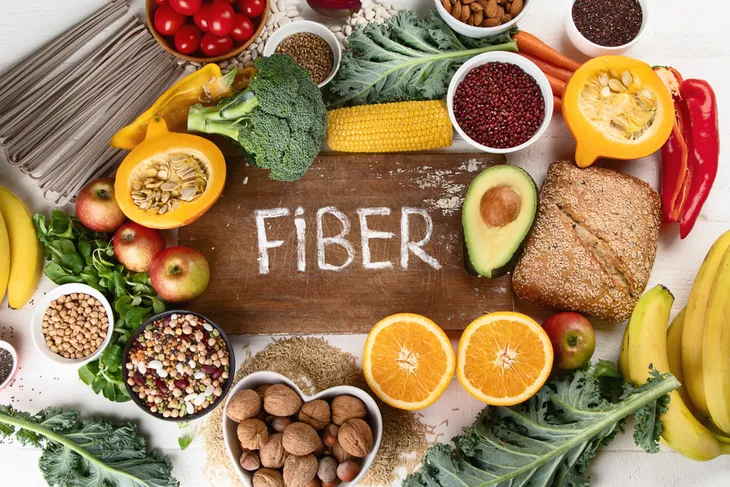
Furthermore, straining during bowel movements can irritate a hernia, so to prevent this you can increase your fiber intake. This will help relieve constipation and prevent straining. Some great examples of high-fiber foods include whole grains, leafy greens, other vegetables, and fruits.
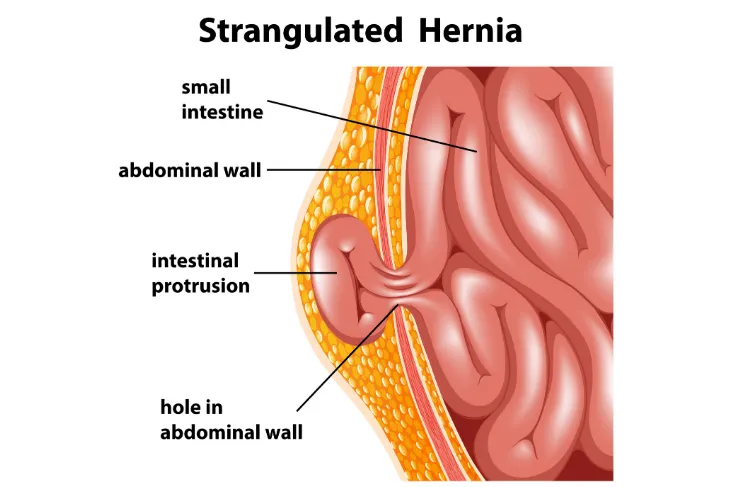
The Risks of Leaving a Hernia Untreated
Leaving a hernia untreated could lead to a more serious condition called strangulation. Healthline explains, “This occurs when a loop of intestine or a piece of fatty tissue is trapped inside the hernia and is cut off from its blood supply.” To prevent this, your doctor may recommend surgery.
When To See a Doctor
Hernias can cause complications. In some cases, they can even be life-threatening. If you experience symptoms such as fever, sudden pain, nausea, or vomiting make sure you seek emergency care.
An untreated hernia will not go away on its own and learning the signs of one will help ensure you get the help you need. Your doctor will be able to access the area, diagnose a hernia, and determine the best course of action.
Hernia Prevention Tips
Unfortunately, it is not always possible to prevent a hernia. Some existing conditions or surgeries cause hernias to occur no matter what you do. That said, there are some lifestyle changes you can make to help prevent them the best you can.
For starters, maintain a healthy body weight and if you smoke, quit. Next, try your best to not strain during a bowel movement. Ensure you’re consuming enough high-fiber foods to prevent constipation.
Finally, stay active by engaging in regular physical exercise and perform exercises that strengthen your core. Just be careful and don’t lift anything too heavy. Start with a lower weight and increase the weight as you build strength.