- Your chance of developing hemorrhoids increases as you get older, as most people affected are over the age of 50.
- Most cases of hemorrhoids are mild, but it’s important to treat them before they contribute to more serious medical conditions.
- Changes to your diet and exercise routine can reduce your risk of hemorrhoids, including drinking more water and consuming more fiber.
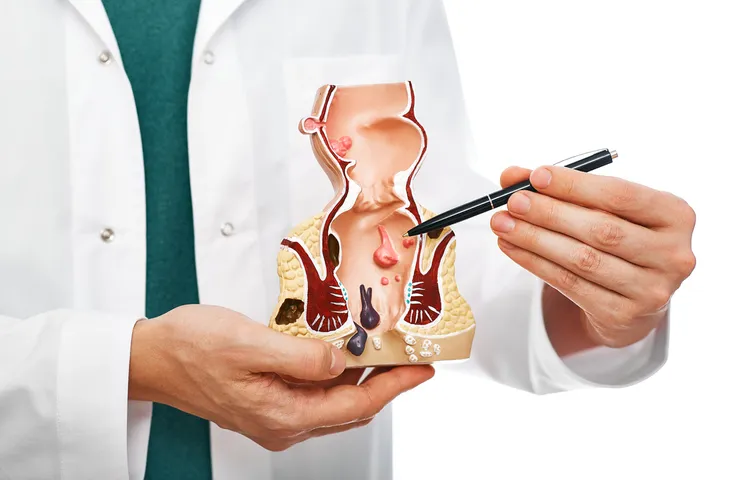
Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, are swollen veins in the rectum or in the skin around the anus, which may bleed or cause irritation. And they’re actually much more common than you might think.
As a person gets older, they’re at greater risk for developing hemorrhoids. Making improvements to both lifestyle and diet now can help. This guide reviews the common causes and symptoms of hemorrhoids, how they’re diagnosed and treatment options.
Causes of Hemorrhoids
Around one in two or half of all adults will experience hemorrhoids at some point in their lives. These swollen veins in the anus or rectum occur most often in people over the age of 50.
When left untreated, they can contribute to other medical conditions, including infection of the sores they cause, anemia due to blood loss, and blood clots. Fortunately, understanding the most common causes of hemorrhoids and taking action can help prevent them.
Chronic Gastrointestinal Distress
Chronic constipation or diarrhea elevates a person’s chance of developing hemorrhoids. This is due to the strain these conditions place on the veins in the rectum and anus.
Constipation may also cause someone to strain more during bowel movements, which contributes to the degradation of the veins. Sitting on the toilet for long periods of time can exacerbate this, increasing the risk of hemorrhoids even further. If you have any type of gastrointestinal disease, it’s a good idea to get screened for hemorrhoids regularly.
Sedentary Lifestyles
Sitting for extended periods can place added stress on the veins in your rectum and anus. Desk jobs that require a person to sit for most of the day and other sedentary lifestyles can increase your risk of developing hemorrhoids.
Finding ways to get up and move around throughout the day can alleviate some of the risks. This may include regular exercise, stretching, working at a standing desk, and taking breaks from sitting for long periods of time.
Obesity
Obesity is a contributing factor to a lot of medical conditions, including hemorrhoids. According to the Obesity Action Coalition, being overweight greatly increases the chance of developing hemorrhoids due to poor dietary choices, insufficient fiber intake, and a sedentary lifestyle.
Taking steps to lose weight can reduce a person’s risk by addressing some of these underlying causes of hemorrhoids. If you’re struggling with your weight, it’s important to speak with your doctor about any symptoms you experience to reduce complications.
Physical Exertion
While physical activity can be one of the ways to prevent hemorrhoids, it can also be a contributing factor if not done with proper form. Overexertion of certain muscles may cause veins to swell or rupture, which can result in irritating or painful hemorrhoids.
Furthermore, it’s also important that you don’t try to force a bowel movement when dealing with constipation, as this specific type of overexertion is a common cause of anal fissures and hemorrhoids.
Age
Around half of all adults will experience hemorrhoids at some point in their lives, though most cases are in patients older than 50.
Age is a factor in the development of other medical conditions as well, so it’s important to schedule diagnostic procedures each year to make sure you’re in good health. As an example, men over the age of 40 should undergo an annual colonoscopy to screen for polyps, hemorrhoids, and cancer.
Genetic Factors
Sometimes family history can have an impact on a person’s risk for hemorrhoids. If your parents or grandparents had hemorrhoids, you’re at a greater risk of developing them as well.
This is quite a sensitive topic for most people, so it’s not uncommon for people to have no idea whether they have a family history of hemorrhoids. However, doctors usually consider other risk factors when advising patients on their risk, so not to worry if you’re not comfortable asking your grandparents or parents about their hemorrhoid history.
Common Symptoms of Hemorrhoids
Many cases of hemorrhoids aren’t painful, so people may be unaware they have them. When left untreated, however, hemorrhoids can increase the risk of developing other medical conditions, such as colorectal cancer.
If you’re nearing the age of 50, you should be scheduling regular screenings anyway, but there are other signs to look out for that might be indicative of hemorrhoids. Talk with your doctor if you’re experiencing any of the following.
Bleeding
Blood in the stool can be an indication of a wide range of medical conditions, so it’s important to identify the cause. The color of the blood can often reveal where it came from.
Many people discover they have hemorrhoids after bright red blood shows up on toilet paper after a bowel movement. While this isn’t a guarantee that you have hemorrhoids, it doesn’t hurt to chat with your doctor, especially if you’re also experiencing other symptoms.
Itchiness
Itchiness in or around the anus is a common symptom of hemorrhoids because the tissue surrounding the vein becomes irritated. Over-the-counter medications can be used to treat the itching, but if little to no improvement occurs after a week, medical attention is warranted.
That said, if you’re experiencing frequent and severe itching – even if you’re not sure of the cause – you should call your doctor to schedule an appointment. They’ll be able to diagnose the problem and provide an appropriate treatment plan.
Swelling
If you discover swelling near your anus or lumps near your rectum, you should seek medical treatment. You may also experience pain if your anus is swollen. The pain might also increase when sitting down.
Another indication of hemorrhoids is if the pain becomes more severe while in the bathroom or if it occurs when straining to pass a bowel movement.
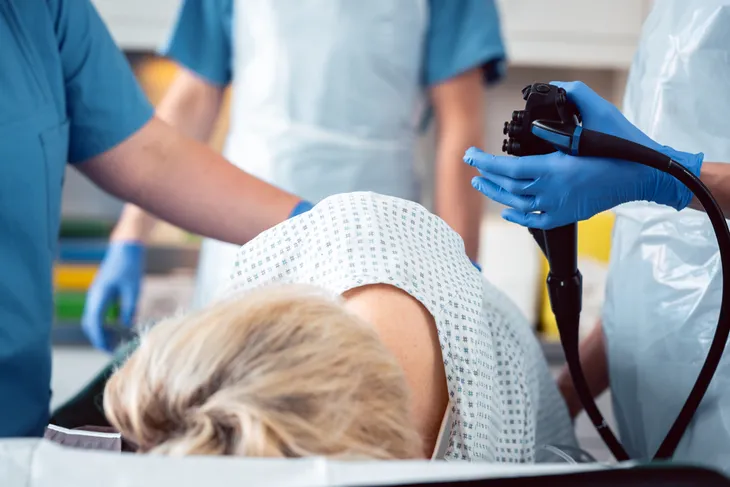
Diagnosis
Your doctor may be able to diagnose hemorrhoids through a physical examination. If that’s not sufficient, they may order additional tests, such as an anoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, or colonoscopy.
Each of these tests uses a small camera to identify hemorrhoids, polyps, and any other type of growth inside the colon. The doctor will then review the test results and discuss the best treatment options based on the type and severity of the hemorrhoids.
Treatment Options
A doctor may discuss lifestyle and dietary changes that can help while prescribing at-home remedies. Suppositories or creams are commonly used to address pain and itching. Extra attention to hygiene to alleviate any additional irritation is also generally recommended. Most people who have hemorrhoids are advised to add a fiber supplement to their diet and soak in a warm bath for about 15-minutes each day.
If these measures don’t resolve the issue, there are medical procedures that can help. Options include rubber band ligation, injection therapy, and sclerotherapy.
Ways to Prevent Hemorrhoids
There are steps you can take to prevent hemorrhoids if you know you’re at an elevated risk. These include drinking more water, adding more fiber to your diet, and exercising regularly. These lifestyle changes can soften your stool and reduce the chance of constipation, which is a significant factor for hemorrhoids.
Further, if you experience frequent constipation, speaking with your doctor about treatment options can reduce the risk of developing hemorrhoids.
 Shutterstock/NDAB Creativity
Shutterstock/NDAB Creativity