While people certainly share characteristics and even some personality traits, we each have our own unique personality. Our personality is shaped by not only our genetic makeup but also life experiences. Our thoughts and even personalities will change throughout life as we get older and gain new perspectives, but this change is often very gradual.
Fluctuations in a person’s mood each day is normal, but drastic changes in personality could be a sign of a medical or mental condition. These changes can be portrayed in different ways, but usually consist of any behavior that is inconsistent with how a person would typically react under those same circumstances, says Healthline. Here’s a list of 14 health conditions that can affect a person’s personality…
Depression
Depression is a mental health condition that does more than just cause a person to feel sad. It affects every aspect of a person’s life. Not only their mood, but also their perspective on the world and life in general, their memory, and how they make decisions. This is particularly true for major depressive disorder, also known as clinical depression, says Buoy Health.
It causes a person to feel hopeless, and may even result in them struggling to get through minuscule daily tasks like getting out of bed and showering. Unfortunately, it’s also not that uncommon. The American Psychiatric Association states that one in six people will get depression at some point in their lives. “The condition may be caused by abnormal levels of brain chemicals, hormonal imbalances, stress, and chronic medical conditions like heart disease,” writes Buoy Health.
According to WebMD, it can sometimes affect men and women differently. Women feel worthless, sad, and guilty, while men feel tired, irritated, and angry.
Dementia
Dementia, including Alzheimer’s, is a health condition that affects a person’s brain. It targets their thinking and decision-making capabilities, as well as their judgment. People with Alzheimer’s disease often become very confused, which WebMD explains can change how they act. In the early stages of this disease, people will usually be anxious or easily annoyed.
As it progresses the effects become more serious, warns the source. These effects are often seen in personality changes. “A sweet, thoughtful person might become bossy and demanding. Or someone who used to worry a lot or get stressed easily might be easygoing and content,” writes WebMD.
Dementia with Lewy bodies is the second most common type of dementia. It occurs when clumps of unusual proteins (Lewy bodies) form in areas of the brain that control memory, movement, and thinking. “People who have it tend to become more passive, showing little emotion and losing interest in hobbies and other activities,” says WebMD.
Bipolar Disorder
Another mental health disorder that can drastically change a person’s personality is bipolar disorder. This condition is characterized by episodes of mania (or hypomania) followed by depression, explains Buoy Health. The frequency and intensity of these episodes vary from person to person, so not everyone experiences this condition the same.
It can cause people to sleep more, engage in risky behavior (i.e. gambling, drinking too much, and overspending), have racing thoughts, feel invincible or grandiose, as well as hyperverbality. Thankfully, bipolar disorder is treatable, but they must seek outside help. It often leads to relationship problems, difficulty holding a job, and financial trouble, warns Buoy Health.
Parkinson’s Disease
When we think of Parkinson’s disease, we often think of shaky or trembling hands, but it’s so much more than that. This neurological disorder can affect how a person walks, talks, sleeps, and even thinks. While the trademark symptoms pertain to motor problems, such as tremors and shakiness, it can also lead to “Parkinson’s personality,” says Healthline. This is a result of changes in the brain.
People with advanced Parkinson’s disease may become apathetic, pessimistic, or inattentive. Healthline warns they might even develop Parkinson’s disease dementia. “Even in the earlier stages of the disease, people may become more depressed, obsessive, or stubborn,” writes the source.
Brain Tumor
The brain is an extremely complex organ. To this day, researchers and experts alike still don’t fully understand the human brain. What we do know is that certain parts of the brain are responsible for our personality and behavior. Therefore, a brain tumor in the frontal lobe, temporal lobe, or parts of the cerebrum can result in personality changes, explains Healthline.
People who were usually very agreeable might become irritable and an active person may become passive, says the source. Mood swings are also a possibility. Healthline provides the example of quickly becoming angry after being happy.
Traumatic Brain Injury or Post-Concussion Syndrome
Similar to a brain tumor, any injury to the brain, such as a traumatic brain injury (TBI) or concussion can result in personality changes. This is particularly true if the injury affects the frontal lobe of the brain (located underneath the forehead), says Healthline. This area is referred to as the “control panel” because it’s responsible for speech, emotional expression, and cognitive skills.
Concussions are the result of any impact on the head and can sometimes linger in the form of post-concussion syndrome. According to Healthline, the symptoms of this are dizziness, headaches, and in some cases, personality changes. “An injury to the brain may affect how you understand and express emotions. It could also result in a personality change due to your emotional reaction to the changes in your life brought about by the brain injury,” writes the source.
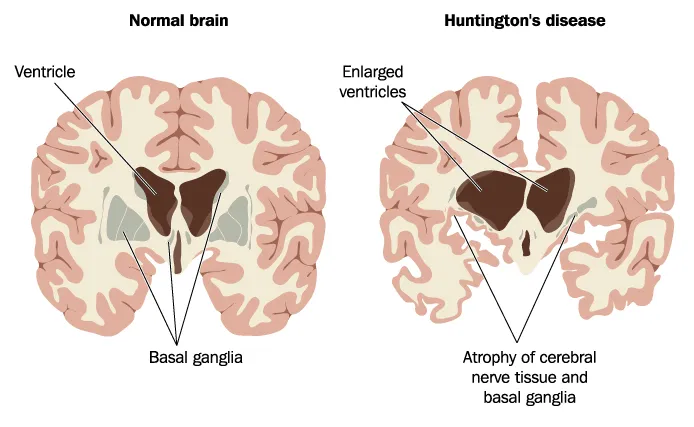
Huntington’s Disease
Huntington’s disease is a rare, inherited disease that causes progressive degeneration of nerve cells in the brain, explains the Mayo Clinic. Not surprisingly, this has a major impact on a person’s overall functioning. It impacts their movement, and cognitive function, and can even lead to psychiatric disorders, adds the source.
Even though people are born with this health condition, it doesn’t usually show up until a person is in their 30s or 40s. People with Huntington’s will notice a change in their mood and behavior. “You might have a hard time thinking clearly, or get angry to the point of hitting walls, or ignore basic things like brushing your teeth,” says WebMD. Oftentimes, these people aren’t even aware of these changes.
Stroke
A stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures or oxygen to the brain is interrupted. Since it involves the brain, personality changes can occur. Healthline points out that some stroke survivors will experience apathy and not care about anything.
Or, if the stroke happened in the right hemisphere of the brain, they might have difficulty with one side of their body or objects (i.e. ignore one side of the body or food on one side of the plate). A right hemisphere or frontal lobe stroke can also induce impulsive behavior. “This may include being unable to think ahead or understand the consequences of their actions,” writes the source.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
When we think of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) we often think of perfectionists. People who need everything to be neat and tidy all the time, or are exceptionally organized. While those traits might not be shared among the majority, it doesn’t make someone OCD. This condition is much more about anxiety and having thoughts or urges that cannot be controlled.
A common example is someone who obsessively washes their hands, over and over again. It can also present in ways that might be more subtle to others, such as continuously doubting yourself or taking a long time to finish a task. Sometimes the condition worsens if someone shares criticism because it can feed into that anxiety, says WebMD.
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a disabling disease that impacts the central nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord. When a person has MS, their immune system attacks the protective sheath (myelin) that covers nerve fibers which results in communication problems between the brain and the rest of the body, explains the Mayo Clinic.
This results in a wide range of problems, from bladder issues to not being able to walk, notes WebMD. “In some cases, it can lead to a feeling of euphoria, where your happiness is beyond normal and out of touch with reality. It can also bring on laughing or crying that seems out of control or not in line with how you really feel,” writes the source.
Thyroid Disease
Thyroid disease is a general term used to describe a medical condition that impacts the thyroid, mainly its ability to produce the right amount of hormones. Located in the front of the neck, the thyroid gland is responsible for releasing and controlling thyroid hormones that control metabolism, explains the Cleveland Clinic. These hormones tell the body how fast or slow to work, so when it’s not working properly, it can impact the entire body.
Symptoms include everything from weight loss/gain to forgetfulness, fatigue, vision problems, and even cause anxiety, irritability, and nervousness. WebMD points out that people with thyroid issues may showcase intense mood swings and if their thyroid isn’t making enough hormones, their personality might seem flat. They might be forgetful or have a hard time thinking things through. If it goes untreated, WebMD warns it can have long-lasting effects on the brain.
Menopause
Menopause can wreak havoc with hot flashes and weight gain. According to Healthline, it can also cause some personality changes. These changes are the result of hormonal changes. “The decreased production of estrogen during menopause reduces the level of serotonin produced in your brain,” writes the source. “Serotonins are chemicals that help regulate your moods.”
What many menopausal women will feel is anger, sadness, anxiety, and even panic. It can cause mood swings and make them more irritable. Healthline warns that these symptoms typically continue for 4 years after a woman’s last period.
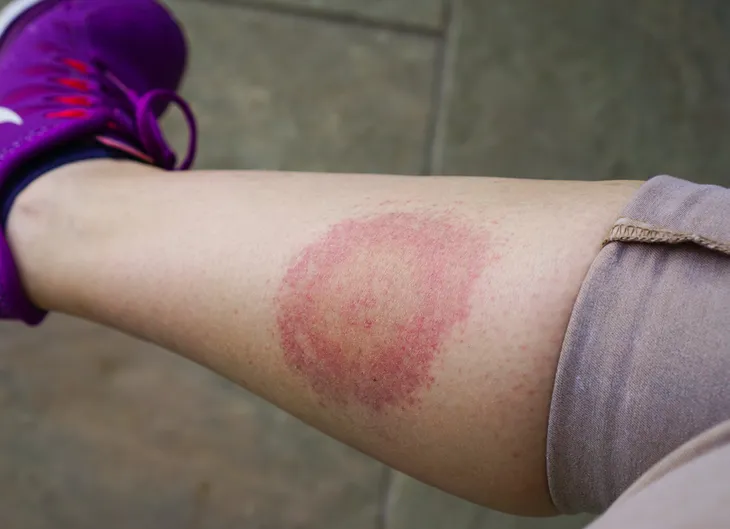
Lyme Disease
Lyme disease can be tricky to diagnose because people react to it differently and the symptoms can vary greatly, particularly in severity. This condition is an infectious disease that results when a human is bitten by an infected black-legged or deer tick, says Healthline. For an infection to occur, the tick has to be present on the skin for 36 to 48-hours. These bites go undetected, so most people with have no memory of the bite.
People with Lyme disease can experience both physical (i.e. rash) and psychological symptoms, such as mood swings. A study conducted in 2012 found that nearly a quarter (21-percent) of people in the early stages of Lyme disease felt irritable. Another 10-percent of people in the study reported feeling anxious.
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a very serious mental illness that affects how people interpret reality. According to the Mayo Clinic, it can cause hallucinations, delusions, and distorted thinking and behavior. Not surprisingly, this all impacts their ability to function on a daily basis and can even be disabling.
Obviously, due to the nature of this condition, it can have a major impact on personality and behavior. At first, these changes might just pertain to their social life. They might not be as social as normal, but as the condition progresses the changes become more severe. WebMD explains that they might have difficulty keeping their thoughts on track and find it hard to talk to people. “You may act in ways that are way out of character, hard to predict, and out of control,” adds the source.