- As of October 17, 2022, over-the-counter hearing aids are available for purchase in the U.S.
- You can purchase these devices without a prescription, hearing exam, or even a visit to the doctor.
- They are only available for people over the age of 18 with mild to moderate hearing loss, which some doctors estimate will benefit 90-percent of the hearing loss population.
- Prices will likely range anywhere from $200 to as high as $3000.
The struggle of hearing impairment is not only frustrating, it can be very isolating. According to the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communications Disorders (NIH), 16-percent, or 1 in 8 Americans over the age of 12 and 25-percent of people aged 65 to 74 with hearing loss, use a hearing aid .
This is why a ruling by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for hearing aids to be sold over-the-counter without a prescription is being deemed a game changer for the millions of Americans with hearing loss. Before rushing out to purchase a set of over-the-counter hearing aids, take some time to learn about these need-to-know facts…
What are Over-The-Counter Hearing Aids?
Over-the-counter (OTC) hearing aids is a new category of hearing aids that consumers can now purchase without visiting a healthcare professional, explains the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIH). They are meant for adults (people over the age of 18) with mild to moderate hearing loss. You cannot purchase them for children or adults with severe hearing loss or significant difficulty hearing, notes the source.
Similar to prescription hearing aids, OTC hearing aids “make sounds louder so that some adults with difficulty hearing are better able to listen, communicate, and participating fully in daily activities,” writes NIH. They will be regulated by the FDA which has issued regulations that manufacturers of OTC hearing aids need to follow. These regulations ensure OTC devices are safe and effective with set standards for packaging so buyers can better understand the product they are purchasing, explains NIH.
These are an alternative to prescription hearing aids which are only available from hearing health professionals. They will fit a person for their hearing aid, adjust the device based on personal needs, and provide other related services. When someone purchases a OTC hearing aid, they must do these things themselves.
Why Do Hearing Aids Matter?
For people who suffering from hearing loss or hearing impairment it’s more than just a frustration. It impacts all aspects of their life on an everyday basis. They are essential for our physical and mental health. CNN refers to one study which found that people with hearing loss who don’t have hearing aids are more likely to have poor overall health and less likely to leave their home or exercise.
Other studies have found links between hearing loss and general frailty, as well as an increased risk of falls, which according to the World Health Association are the second leading cause of unintentional fatalities worldwide. There are even more additional studies which show a link between hearing loss and poor mental health, in addition to psychosocial health. Not surprisingly, CNN further suggests that hearing loss can lead to depression, loneliness, and isolation. In some cases, even dementia.
Who are OTC Hearing Aids For?
As we previously mentioned, OTC hearing aids are for people with mild to moderate hearing impairment. Unsure what this means? The nonprofit Hearing Loss Association of America (HLAA) provides a checklist of what constitutes mild to moderate:
- Trouble understanding conversations in groups, with background noise, or when the person talking isn’t visible
- Trouble hearing on the phone
- You need to turn up the volume of the television, or radio loud enough for others to complain
- Your friends or family complain they often have to repeat themselves
You cannot purchase OTC hearing aids for children or people with severe hearing impairment. Some ear problems require medical treatment. If you’re unsure, consult a doctor.
When and Where Can I Buy Them?
Starting on October 17, 2022 consumers can purchase hearing aids OTC at retail pharmacies and chain stores all across America. It’s important to note, the availability will vary as some retailers are able to move faster than others.
The Washington Post notes that some retailers might start by selling products online before they hit the shelves in the coming days or weeks. Retail chains we already know will be selling them are Best Buy, Walmart, and Walgreens. Best Buy made an announcement that they plan to open hearing centers in over 300 retail stores this month. Their staff will be trained to help customers choose a device from nine OTC brands ranging in price from $200 to $3000.
OTC vs. Prescription Hearing Aids
OTC hearing aids are a great option for people with mild to moderating hearing impairment, but prescription hearing aids are still the only option for people with severe hearing loss or those under the age of 18. This is because they require a much more customized approach. There will be a difference between those available OTC and what’s available by prescription.
“We do anticipate for there to be some differences in the devices because it would not be cost-effective for manufacturers to sell their high-level technology at these prices,” explains Dr. Lindsay Creed of the American Speech Hearing Association to CNN. “So they’re probably going to be comparable to entry-level hearing aids in the prescription market.”
For example, CNN explains that OTC devices might not have the same maximum volume as a prescription model or degree of customization and personalization. OTC devices will likely be softer in volume and have pre-established output levels by the FDA. “Because of how the FDA came out with very well thought-out regulations, they are really the range where it benefits…90-plus percent of people out there with hearing loss,” says Dr. Frank Lin, director of the Cochlear Center for Hearing and Public Health at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health to CNN.
People with severe hearing loss should go see an audiologist as they require a more customizable prescription option.
No Prescription or Exam Necessary
People with mild to moderate hearing impairment can go into a store and purchase a set of hearing aids without a prescription or even an exam. You can still opt to go see a doctor first which does have its advantages, notes NPR, but it’s not a requirement.
HLAA executive director Barbara Kelley told NPR, “when someone finds out they have hearing loss, they often wait five to seven years before they get a hearing aid.” Without this red tape, more people will undoubtedly be purchasing them which is a good thing.
Major Savings
Not only is it more convenient to not have to go see a doctor before getting a prescription for a hearing aid, but it can save thousands of dollars. According to NPR, in the past the cost of the device itself was a fraction of what people would spent.
The rest of the cost paid for doctor’s appointments, medical services, and Medicare and health insurance (which often doesn’t cover the cost of hearing aids). The source notes that the White House estimates people will save as much as $3,000 by purchasing OTC devices.
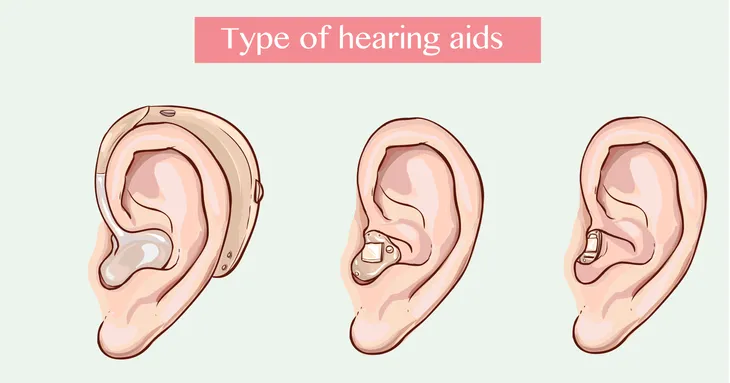
Types of Hearing Aids and Fit
There is more to consider than just going to the retail store and picking up the most affordable option. According to the FDA, the following are the four different types of hearing aids to consider:
- “Behind-The-Ear” (BTE) aids: a small plastic case sits behind the ear which is connected to an earmold by a piece of clear tubing. Great for children, they are easy to clean, handle, and relatively sturdy.
- “Mini” (BTE) or “On-The-Ear” aids: A newer, smaller behind the ear product with a nearly invisible tube connecting the aid to the ear canal (open fit or traditional earmold). Better comfort, less feedback, and cosmetically more preferable.
- “In-The-Ear” (ITE) aids: All parts are in a shell that fills the outer part of the ear. Easier to handle than smaller aids.
- “In-The-Canal” (ITC) aids and “Completely-In-The-Canal” (CIC) aids: The smallest version, they are in a tiny case that fits partly or completely in the ear canal. Offer cosmetic and some listening advantages.
Elizabeth Convery, a former National Acoustic Laboratories researcher who studied self-fitting hearing aids tells the Washington Post that fitting a hearing aid can be tricky. In general, it should never fall out when bending over to pick something up. If it does, it’s not fitted properly.
How Long Does it Take to Adjust to a Hearing Aid?
People aren’t able to just pop a hearing aid in and then suddenly be able to hear as good as new again, notes Kelley when talking to the Washington Post. There is an adjustment period because hearing involves both the ears and the brain. Our brain needs time to relearn how to process sound.
This is especially true for people who have gone untreated for a long time, warns Hill. While it might be a frustrating experience at first, the source notes that it should never be uncomfortable or painful. To speed the process up, wear the hearing aid often, even when alone. Start with 6-hours a day, easing into a variety of different settings, says the Washington Post.
What Features to Look For
The connivence of being able to purchase hearing aids OTC comes at the cost of consumers having to do their own research. To help, the Washington Post has put together some important features to look for:
- Return Policy: according to FDA regulations, return policies should be on the outside of the box. This is important because it can take several weeks to adjust to a hearing aid, warns HLAA.
- Customization: We come in all shapes and sizes so adjustable wires, tubes, and tips are necessary to better fit a person’s ear.
- Tip Options: The “tip” goes inside the ear. Open dome creates a more natural sound, whereas a closed dome boosts sound. Your need depends on hearing loss.
- Ear Wax Filters: Prevents earwax buildup and helps the device last longer.
- Custom Volume Adjustment: Look for devices that self-adjust the volume at different frequencies.
- Directional Microphone: Automatically detect noisy environments and adjust the direction of the microphone. The accuracy of this feature varies between manufacturers.
- Background Noise Filter: A filter to dampen the background noise in noisy environments, such as restaurant, parties, etc.
- Bluetooth Connectivity: Hearing aids that connect to a smartphone can help with activities, such as speaking on the phone, listening to music, and streaming movies.
- Warranty: Most prescription hearing aids have a min. warranty of one year, and some up to three, says Heidi Hill, an audiologist with the Hearing Health Clinic in Minnesota to the source.
The association also urges people to consider whether the device requires a smartphone, has long-lasting batteries, or if they are rechargeable.
Get a Hearing Test First
The main benefit of OTC hearing aids is that a person can just go to the store and purchase one without any outside input or assistance. However, it’s strongly suggested that people go get a hearing test prior to visiting a store or making any purchases. Not only will this help determine a person’s sensitivity to sound, it can also let someone know if their condition is simply from earwax buildup.
“It would be helpful to know exactly what your hearing levels are, because the research really suggests that individuals aren’t great at accurately determining their hearing loss levels,” says Dr. Creed when talking to CNN. Dr. Lin adds that knowing your hearing number is just as important as any other piece of health data.
There are many different options available to go get a hearing-test, many of which are inexpensive. You can go to any hearing center in stores like Costco or Sam’s Club or even do an audiologist-recommended online test. Retail stores selling OTC hearing aids like Best Buy will offer online hearing screenings, notes the source.
How Much Should I Expect to Pay?
You are certainly going to pay less as experts estimate the price of hearing devices will go down, however high quality products will still be expensive. Some retailers have already announced their pricing and they range from $199 to upwards of $3,000, says the Washington Post.
According to Reuters, Walgreens said it would sell Lexie Lumen hearing aids for adults in stores across America for $799. Walmart also told Reuters their products would start at $200.
If someone is considering a OTC hearing aid over $1,000, the Washington Post suggests doing a comparison with prescription hearing aids. You might find a better product with the added benefit of a custom fit from an audiologist.