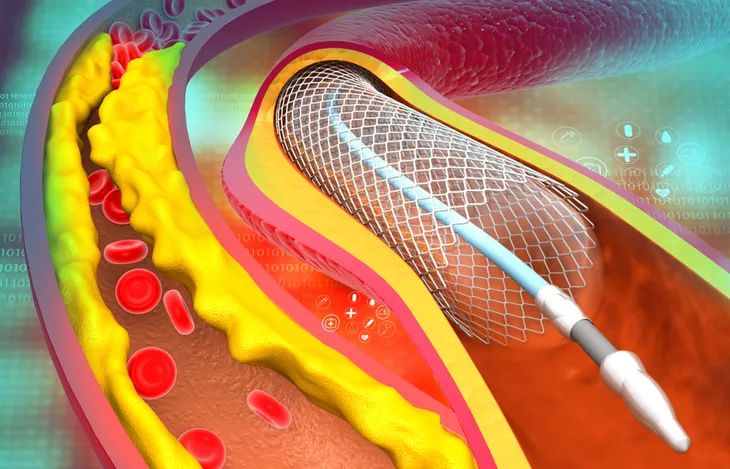
Four main coronary arteries sit directly on top of the heart muscle. They have a very important job of supplying your heart with oxygen-rich blood. But when you have coronary artery disease, that blood flow is impaired.
Coronary artery disease is a condition that can lead to life-threatening consequences which is why it’s important to learn everything there is to know about it and how you can prevent it from happening. So let’s take a look at what coronary artery disease is, the common signs to look for, what causes it, and how you can treat it and prevent it from happening. Let’s dive in!
What Is Coronary Artery Disease?
Coronary artery disease, also known as coronary heart disease or ischemic heart disease, is the most common form of heart disease. It is serious and can be life-threatening. In fact, it caused 360,900 casualties in 2019 alone, reports the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
The source also notes roughly 18.2 million American adults (age 20 and over) have CAD. So, what is it exactly? Coronary artery disease impairs blood flow in the arteries that supply blood to the heart due to plaque buildup.
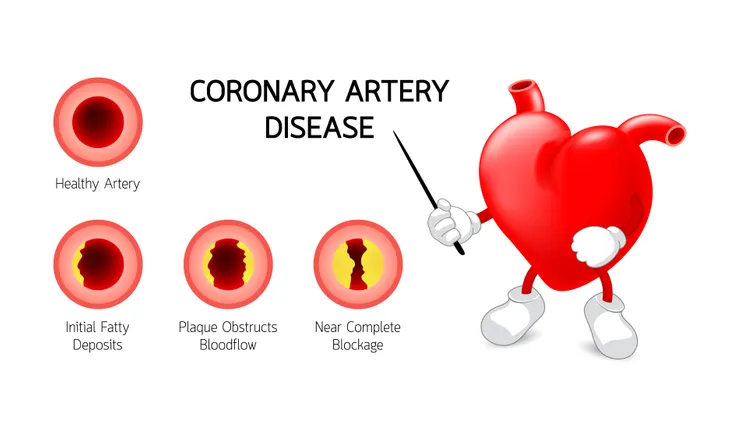
Common Signs and Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease
If your heart isn’t getting enough blood, it can lead to a variety of symptoms. The most common symptom of coronary artery disease is chest discomfort, also known as angina. The discomfort can be felt differently from person to person but most individuals describe it as chest pain, a tightness, a heaviness, a squeezing feeling, or a burning sensation.
Chest discomfort can often be mistaken for heartburn so be on the lookout for the other symptoms of coronary artery disease. They are a pain in the arms or shoulders, shortness of breath, dizziness, and sweating.
Are These Symptoms Serious?
Yes, symptoms of coronary artery disease are serious and should not be ignored. When your blood flow is restricted even further you begin to experience more symptoms. If blood flow is completely (or almost completely) blocked, your heart muscle will begin to stop which is known as a heart attack.
These symptoms are very serious. If you notice any signs of coronary artery disease contact your doctor right away. If you develop any symptoms of a heart attack dial 911 to get immediate medical attention.
Symptoms Unique to Women
Women can experience the same symptoms we just mentioned, however, there are a few symptoms unique to women that are worth mentioning. For starters, women are more likely to also experience nausea and vomiting, as well as back pain, and jaw pain. Shortness of breath without chest pain is also common.
In general, men have a higher risk of developing heart disease than women. That said, once a woman is postmenopausal and age 70, they then have the same risk as men, says Healthline.
When to See a Doctor
As mentioned, since symptoms of coronary artery disease are serious, it’s important that you see a doctor right away. If your symptoms are severe or last longer than 5-minutes it could be a sign of a heart attack that warrants immediate medical attention.
Although rare, if a blood clot in a coronary artery breaks loose, it can move to your brain and cause a stroke, says Cleveland Clinic. Signs of a stroke include arm weakness (or numbness), slurred speech or difficulty speaking, and drooping on one side of your face. If you develop any of these signs, dial 911 right away. “Every minute you spend without treatment increases your risk of long-term damage,” says the source.
Complications
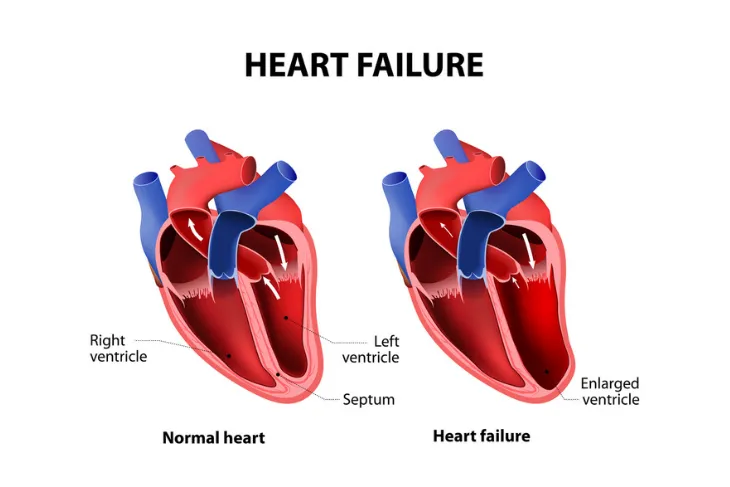
Coronary artery disease can lead to a variety of serious complications with the two most serious being heart attack and heart failure. The Mayo Clinic explains, “if cholesterol plaque ruptures and a blood clot forms, complete blockage of your heart artery may trigger a heart attack.” Further, if reduced blood flow causes the heart to be chronically deprived of oxygen and nutrients, or if the heart is damaged from a heart attack, your heart may become too weak, causing heart failure.
Other complications of coronary artery disease are chest pain (angina) which also causes shortness of breath and can be particularly noticeable during physical activity. CAD can also cause abnormal heart rhythm, known as arrhythmia. If there is damage to the heart tissue or if there isn’t enough blood supply to the heart, the heart’s electrical impulses can be affected, resulting in abnormal heart rhythms.
Causes of Coronary Artery Disease
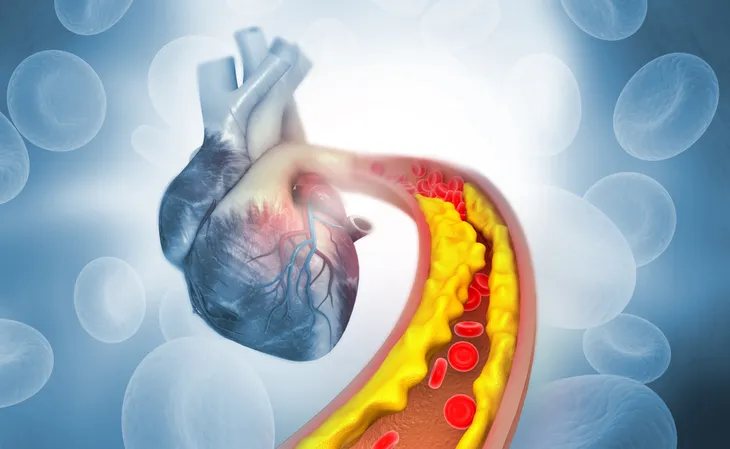
The CDC says coronary artery disease is caused by “plaque buildup in the walls of the arteries that supply blood to the heart (called coronary arteries) and other parts of the body.”
The plaque consists of deposits of cholesterol as well as other substances. Over time, the plaque causes the arteries to narrow which can decrease blood flow, or completely block it. This is called atherosclerosis.
Risk Factors
Certain factors can increase your risk of developing coronary artery disease. While some are completely out of your control such as age, some factors are within your control. For example, having high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels can increase your risk. Tobacco smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, an unhealthy diet, and a sedentary lifestyle can also increase your risk for CAD.
Healthline also says the risk increases as you grow older. Men have a greater risk for the disease starting at age 45 while women develop a greater risk starting at age 55. Finally, CAD can also be genetic, meaning you have an increased risk of developing it if you have a family history of the disease.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing coronary artery disease starts with a visit to your doctor. They will review your medical history, symptoms, and start with a physical examination.
Along with this, there are a variety of medical tests they may use to help diagnose CAD. Some of these include an echocardiogram, electrocardiogram, a heart computed tomography (CT) scan, cardiac catheterization, and a stress test. Let’s look into what these entail next.
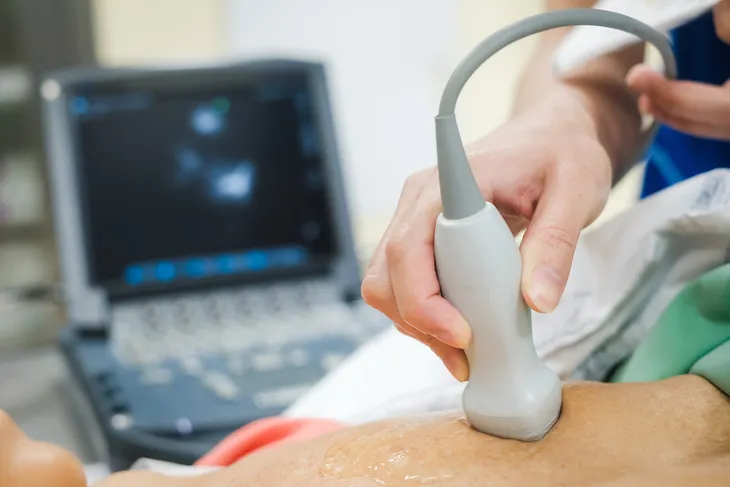
Echocardiogram and Electrocardiogram
An echocardiogram is an imaging test that uses ultrasound waves to generate a photo of your heart. This can help your doctor see how your heart is functioning.
In contrast, an electrocardiogram monitors electrical signals that travel through your heart. Electrodes which are small plastic patches are placed on your body in certain spots like the chest, arms, and legs. The electrodes are connected to an ECG machine which measures the electrical activity. But don’t worry this is a quick and painless procedure. The results of this test can help reveal whether or not you’ve had a heart attack.
Heart CT scan and Cardiac Catheterization
In some cases, a heart CT scan is necessary to diagnose coronary artery disease. Doctors use this imaging test to look for calcium deposits in your arteries.
Your doctor may also recommend a cardiac catheterization. During this procedure, a small thin, flexible tube (catheter) “is guided through a blood vessel to the heart,” says the Mayo Clinic. This test provides your doctor with detailed images to see if there are any calcium deposits in your arteries. It can also be used to “deliver treatments, or remove a piece of heart tissue for examination,” says the source.
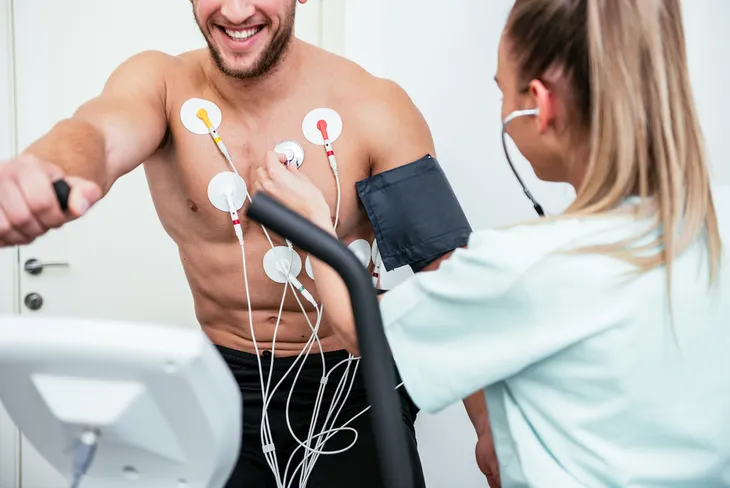
Stress Test
Sometimes your doctor might recommend a stress test. This shows how your heart is working during physical activity and during rest.
For the test, a technician will place electrodes (which are connected to a computer) on your chest, legs, and arms. You’ll also wear a cuff on your arm which measures your blood pressure during the test. Then you’ll be asked to exercise on a treadmill or stationary bike.
You’ll start slow and then gradually increase the speed until your heart has reached a target level. However, if you develop certain signs during the test you may be asked to stop. These include moderate to severe chest pain, severe shortness of breath, dizziness, fatigue, certain changes in our electrocardiogram, abnormal heart rhythm, or abnormally high (or low) blood pressure.
Coronary Artery Disease Treatment
Once you’ve been diagnosed with coronary artery disease your doctor will recommend a treatment plan. Keep in mind, treatment will vary depending on your current health condition as well as your risk factors. But it’s vital that you control or reduce your risk factors to help reduce your risk of a heart attack or stroke.
For starters, your doctor may prescribe medication to treat high blood pressure or high cholesterol. If you have diabetes, your doctor will prescribe medication to control your blood sugar. Finally, your doctor will likely also recommend a variety of lifestyle adjustments to help treat the disease.
More Treatment Options
In some cases, your doctor may recommend a procedure to restore blood flow to your heart. One procedure is balloon angioplasty which widens blocked arteries and typically involves the insertion of a stent to help keep the artery open.
Another potential procedure is coronary artery bypass graft surgery. This is used to help restore blood flow to the heart, however, it is an open chest surgery.
Finally, your doctor may recommend an enhanced external counterpulsation. This is done “to stimulate the formation of new small blood vessels to naturally bypass clogged arteries in a non-invasive procedure,” says Healthline.
How to Prevent Coronary Artery Disease
Lifestyle adjustments are essential for treating coronary artery disease but they are also important for preventing it. A healthy lifestyle isn’t only good for your overall health, but it can help keep your arteries clear of plaque. So what can you start doing to help prevent CAD?
If you’re not already physically active, it’s time to start. You can start with daily walks and work your way up to harder workouts. It’s also important to eat a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables and whole grains. The Mayo Clinic says to eat low-fat, and a low-salt diet as well. Managing your stress is also important.
All of these lifestyle changes will help you manage a healthy weight and help you control your blood pressure and cholesterol levels, all of which are important for preventing CAD. Finally, quitting smoking can also help prevent CAD in the future.