Most often, it’s athletes that are considered most prone to concussions, a brain injury that is either caused when the head suffers a severe blow or when the body is shaken and the brain is jostled as a result. The truth is, we are all at risk for concussions whether we play sports regularly or not. Concussions are also a common injury in car accidents, falls, fights, or passing out and hitting the head.
In rare cases, concussions can cause brain injury, particularly with repeated instances. Here are the 20 most common symptoms of a concussion…
1. Headaches
Due to the fact that the majority of concussions are caused by a direct blow to the head, a severe headache can occur which is comparable to a nasty migraine headache that comes in ebbs and flows with sensitivity to light and sound.
2. Decreased Cognitive Function
This might be difficulty concentrating or suffering from loss of memory. A concussion may also cause slow or encumbered decision making, a total lack of focus, or the inability to recall normal routine.
3. Lack of Coordination
Concussions can cause immediate dizziness, vertigo, and difficulty staying balanced and coordinated, culminating in the individual having trouble standing up and walking in a straight line.
4. Pupil Dilation
Following serious head trauma, it is common for the pupils—either one pupil on the side of the head affected or both pupils—to appear dilated or unusually large in size.
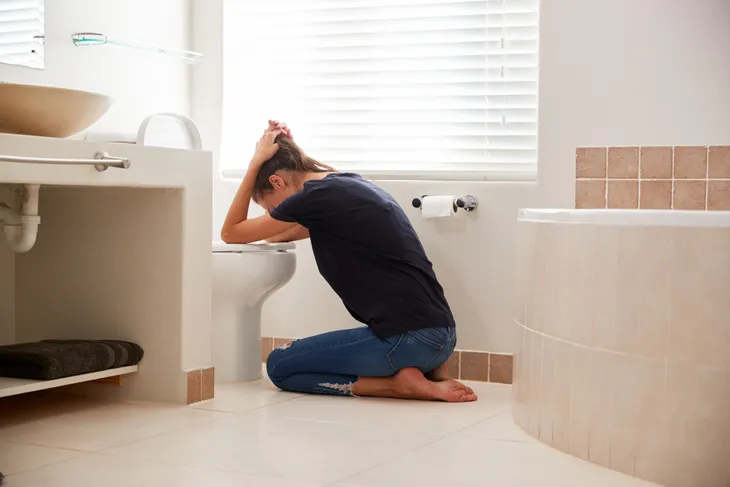
5. Nausea
Nausea, and in more severe concussion cases, repeated vomiting may occur due to head trauma, headache, and compromised balance and vision.
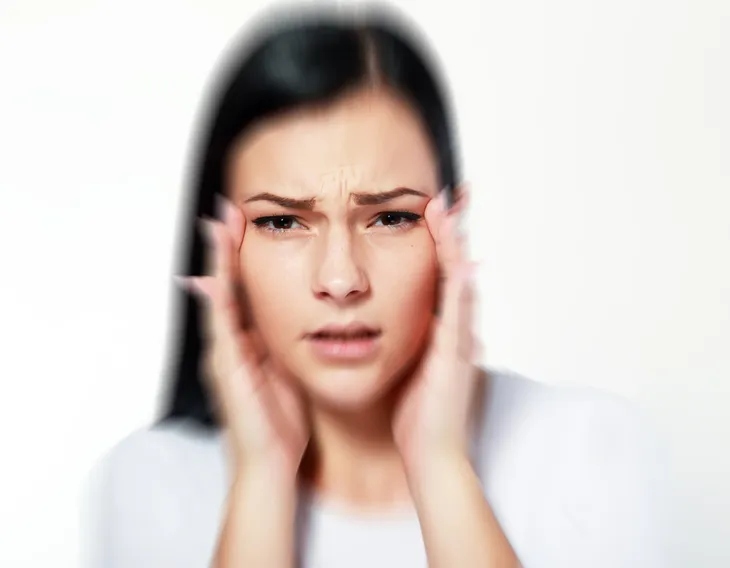
6. Blurred Vision
Blurry vision may occur and signal a concussion when you ask the individual to tell you how many fingers they are holding up post-injury. Concussion victims also often complain of light sensitivity following an injury.
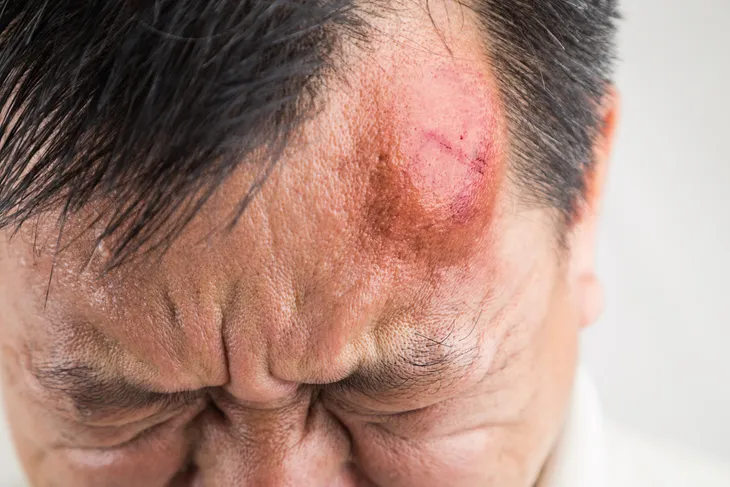
7. Bruising
If you can see the area where the head suffered impact, you may notice a large, swollen bump or even bruising where the trauma took place.
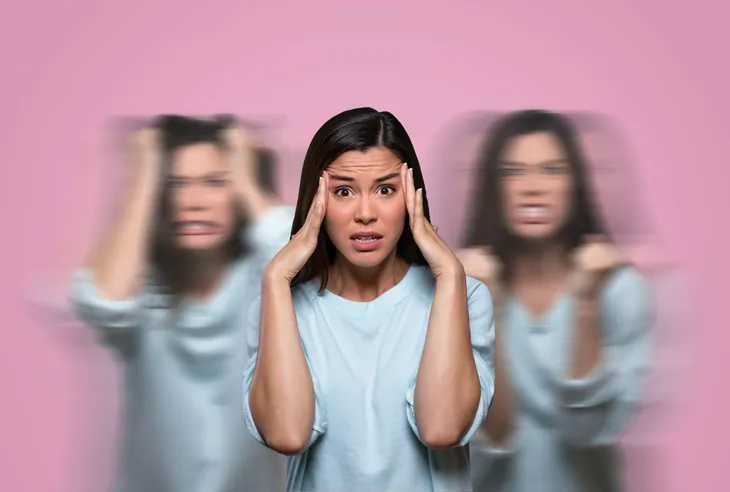
8. Emotional Outbursts
It’s common for concussion victims to suffer from emotional highs and lows following head trauma. For instance, they may suffer extreme mood swings, get easily irritated and upset, suffer from depression, or seem exceedingly anxious and agitated.
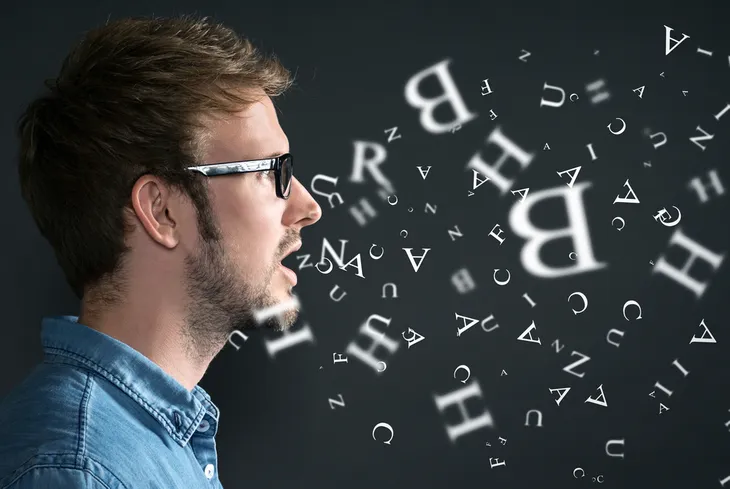
9. Slurred Speech
Because a concussion sends the brain into a spinning motion, normal speech patterns often sound slurred, incomprehensible, or the victim will have difficulty speaking.
10. Disrupted Sleep Patterns
One of 2 extremes can occur with concussion victims—either they will sleep more than usual or suffer from lack of sleep and have trouble getting adequate rest—following their head trauma.
11. Amnesia
As mentioned earlier, a concussion may cause memory loss or, more specifically, amnesia. There are two different types of amnesia, either of which can occur as a result of a concussion.
The first type is retrograde amnesia, where people forget things in the past, oftentimes including the moments surrounding the brain injury. In some cases these memories may come back to them over time, but it’s also possible that they may never remember them. And the second type of amnesia is called anterograde, where a person is unable to form new memories after the concussion occurs.
12. Ringing in the Ears
In addition to experiencing sensitivity to sound, people who have had a concussion may also suffer from tinnitus, which Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre defines as “a ringing, buzzing or hissing noise in your ears.”
The source says that tinnitus may occur “due to damage to the inner ear or to the hearing nerves and the part of the brain that controls hearing.” While some may be plagued by tinnitus all the time, others may only experience it intermittently. Tinnitus is an especially common symptom soon after a concussion occurs and, generally speaking, tends to improve over time.
13. Fatigue
Fatigue is considered among the most common symptoms of a concussion. This tends to present itself as extreme tiredness or lack of energy. In comparison to fatigue experienced by the average person after a long day, however, HeadInjurySymptoms.org says, “The sort of fatigue people get after a mild head injury can come on after less activity than normal and can seem more severe and longer lasting.”
Unfortunately, the usual remedy of rest is often ineffective for treating fatigue caused by a concussion. In fact, the source says it can “make you feel worse,” causing a loss of physical fitness in addition to other issues such as “joint stiffness, back pain, loss of confidence, and social isolation.”
14. Loss of Smell and Taste
Another commonly reported symptom of a concussion is loss of smell. Changes to or loss of taste can also occur, often because of a loss of smell. Because both of these senses are large contributors to appetite, individuals who suffer a loss of smell or taste may also find that their appetite is reduced or they lose interest in food altogether.
Unfortunately, there is no treatment or cure for a lost sense of smell or taste, and “Typically, if a person doesn’t regain his ability to smell six months after the injury, the loss will likely be permanent,” says BrainLine.org.
15. Memory Loss
There are two ways memory loss can occur with a concussion — loss of memory surrounding the event itself, or recurring memory loss after the injury. Even mild concussions can lead to a foggy memory. It may be harder to memorize small details like a grocery list or calendar events, meaning you may be more reliant on writing things down.
16. Post-Concussion Syndrome
In some cases, patients won’t recover in the average two week to one month timeline. They may have lasting symptoms that occur longer than one or two months. This is known as post-concussion syndrome.
This complication has people experiencing concussion-like symptoms either at rest, or in response to too much physical or cognitive activity. This can be disruptive in everyday life and lead people to restructure their routines in order to make life more comfortable.
17. Symptoms in Babies and Toddlers
It’s important for parents to notice concussion symptoms in babies, especially since they may not be able to properly vocalize what they’re feeling. They may cry when you move their head, be irritable, or a noticeable change in their sleeping habits. Babies may also vomit or have a visible bump or bruise on the head.
These symptoms also apply to toddlers. Additional signs of concussion for this age group may be behavioural changes or loss of interest in doing their favorite activities.
18. Symptoms in Children
The symptoms in children are pretty much the same as they are for adults. But since kids may not always be vocal about their symptoms, it’s important to observe their behavior .Kids may look like they are daydreaming or have sudden changes in mood. The head trauma may also cause sensitivity to light and noise.
19. Other Symptoms
There are a variety of other symptoms related to concussions. These include feeling confused, dazed, or like you are in a fog. Or, when asked a question, people who have had a concussion may be delayed in their response, have trouble recalling the right words, or use language incorrectly.
It’s important to remember, however, that while many of the symptoms listed in this article may occur immediately after the concussion has happened, it’s also possible that they may take time to develop—sometimes just a few hours, but in other cases months. Should you experience any symptoms, at any time after the injury, be sure to notify your doctor as soon as possible.
20. When to See a Doctor
If you experience a head injury, it’s important to get it checked out within one to two days. If you or a child are experiencing symptoms, then see a doctor right away. This includes repeated vomiting or nausea, loss of consciousness, a worsening headache, slurred speech, and more. Getting an official diagnosis will ensure there is nothing other than a concussion you need to recover from.