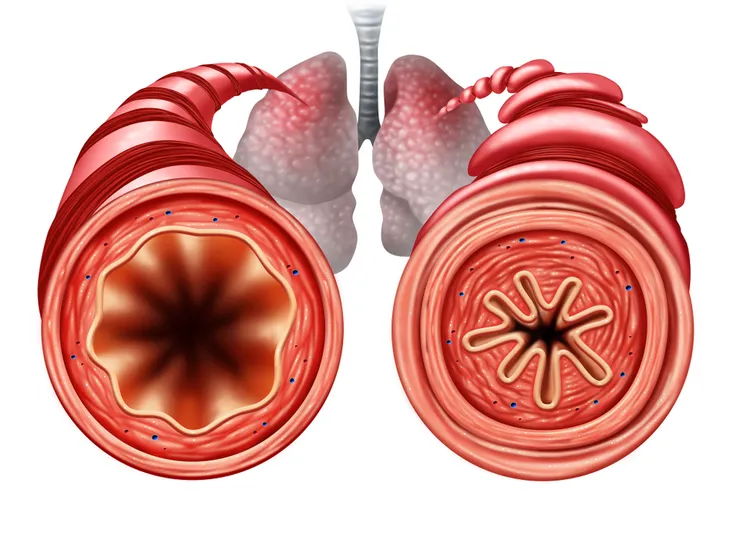
Chest pain, wheezing, and breathlessness are the all too common symptoms asthma sufferers experience. Asthma is a chronic lung disease that causes inflammation in the lungs which can make an individual sensitive to triggers like mold, dust, pet dander, and more.
Approximately 25 million Americans have asthma and unfortunately, it cannot be cured. The good news is that asthma can be managed to the point where your symptoms become minor. All the more reason to get informed. If you or a loved one is suffering from asthma, here’s what you need to know including the common symptoms, causes, and treatment options available. We’ll also find out if asthma is preventable. Let’s dive in!
What Is Asthma?
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) explains that asthma is a disease that affects your lungs. Asthma causes the lining of your airways to swell and the muscles to tighten, making it difficult for air to pass through.
Asthma sufferers often have difficulty breathing. Engaging in physical activities is also often a challenge (or in some cases, impossible!). The CDC also notes that 1 in 12 children have asthma, making it one of the most common long-term diseases in children. That said, adults can have asthma too.
Types of Asthma
Asthma is categorized into different types depending on the cause and the severity of your symptoms. The Cleveland Clinic says the following types of asthma are:
- Intermittent which is a type of asthma that comes and goes.
- Persistent is a type of asthma that presents symptoms most of the time. Your symptoms can be mild, moderate, or severe.
- Allergic is a type of asthma that is caused by allergies.
- Non-allergic is a type of asthma that is caused by other factors such as illness, stress, or weather.
 novak.elcic / Shutterstock
novak.elcic / ShutterstockOther Types
Asthma can also be categorized into a few other types. For example, asthma can be adult-onset, which means it develops after the age of 18. In contrast, it can also be defined as pediatric which means asthma develops in childhood, typically before the age of 5. The Cleveland Clinic also mentions children may outgrow asthma.
There are also a few other types of asthma including:
- Occupational asthma, which means it develops in individuals who work with irritating substances.
- Exercise-induced asthma is triggered by exercise.
- Asthma-COPD overlap syndrome (ACOS) is a type of asthma that develops when you have both asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Common Symptoms of Asthma
A telltale sign of asthma is wheezing, a high-pitched whistling sound that occurs while breathing. While wheezing is the most common symptom, you may experience others too.
For starters, asthma sufferers may experience coughing attacks, especially during exercise, at night, or when laughing. Shortness of breath or a tightness in the chest is also a sign of asthma. As is, fatigue, frequent infections, and difficulty sleeping, says Healthline. The source also notes that the symptoms you experience can vary depending on which type of asthma you have.
What Is an Asthma Attack?
When you breathe, the muscles around your airways are relaxed, allowing air to move easily (and quietly). However, when your airways are swollen and inflamed, an asthma attack (also called asthma exacerbation) can occur, explains the Mayo Clinic. An asthma attack can also cause your body to create more mucus which can clog the airways even further, making it even more difficult for air to pass through freely.
An asthma attack can bring on the frightening symptoms of wheezing, coughing, and difficulty breathing. “The key to stopping an asthma attack is recognizing and treating an asthma flare-up early,” explains the source. This is why it’s important to work closely with your doctor to determine the best treatment plan for you.
Symptoms of an Asthma Emergency
In some cases, an asthma attack can be a medical emergency. This is especially true if a rescue inhaler fails to improve your symptoms, or if you don’t have it on you. The Cleveland Clinic explains, “A rescue inhaler uses fast-acting medicines to open up your airways. It’s different than a maintenance inhaler, which you use every day.”
It’s vital that you seek emergency care if you are having severe difficulty breathing, gasping for air, coughing that won’t stop, severe wheezing, chest pain, or difficulty talking. You should also seek emergency help if you have pale or bluish fingernails or lips.
What Causes Asthma?
Unfortunately, “no single cause has been identified for asthma,” explains Healthline. However, researchers do believe asthma is caused by a variety of factors such as genetics. If you have a parent or sibling with asthma, you may have an increased risk of developing it too.
The Cleveland Clinic also notes having allergies or certain respiratory infections may make you more susceptible to developing asthma. Environmental factors such as exposure to allergens or toxins that can irritate the airways may also increase your risk of asthma.
Common Asthma Triggers
If you have asthma, it’s important that you identify your triggers and do your best to avoid them to help prevent an asthma attack. Certain factors may trigger asthma and cause your symptoms to worsen. It’s also important to point out that triggers can vary from person to person and some individuals may be more sensitive to some triggers than others.
The Cleveland Clinic says the most common triggers for asthma are allergens (such as mold and dust), environmental irritants, strong chemicals, smoke, pests, pets, and exercise. Certain health conditions (such as respiratory infections), intense emotions, extreme weather, and some medications may also trigger asthma.
How Is Asthma Diagnosed?
If you’re experiencing any of the symptoms of asthma and haven’t been diagnosed yet, talk to your doctor. To diagnose asthma, your doctor will start by reviewing your medical history and ask you about your symptoms. Provide them with as much information as possible.
The Cleveland Clinic says your doctor may also order spirometry, which is a test that “measures airflow through your lungs and is used to diagnose and monitor your progress with treatment.” Your doctor may also require a chest X-ray, blood test, or skin test to confirm a diagnosis, says the source.
Treating Asthma
Once you’ve been diagnosed with asthma, you’ll need to work closely with your doctor to determine the best treatment plan for you. Healthline says there are four main categories of treatment including quick-relief medications, long-control medications, a combination of quick relief and long-control medications, and biologics.
The type of treatment you need will depend on a few factors such as the type of asthma you have, your asthma triggers, as well as your age. The source also notes that identifying your triggers, monitoring your symptoms, and taking proper steps to avoid asthma attacks is also a vital part of treatment.
Once you’ve been diagnosed with asthma, you can expect to visit your doctor at least once a year, or more often if you still have symptoms after treatments, says the source.
Prevention
Unfortunately, there is no known way to prevent asthma from developing, says the Mayo Clinic. That said, you and your doctor can develop a treatment plan to help you manage your condition and prevent asthma attacks.
To prevent asthma attacks you may need to get an allergy shot, known as allergen immunotherapy, which helps your body become less sensitive to allergy triggers. Your doctor may also recommend that you reduce your exposure to allergens and products that cause breathing problems. Finally, your doctor may also prescribe medication that you take daily to help prevent asthma attacks.
Prevention: Lifestyle Adjustments
Certain lifestyle adjustments may also help reduce your risk of asthma attacks. Healthline says, asthma can be worse in individuals who are overweight or obese. So, losing weight or maintaining a healthy weight may help. Eating a healthy diet is also important for your overall health.
The source also notes that irritants like cigarette smoke can trigger asthma. If you smoke, it’s really time to quit! Furthermore, exercise can be a trigger, however, if you exercise regularly, you may be able to help reduce your breathing problems.
Finally, pay attention to your stress levels because stress can also be a trigger for asthma. It can also make it more difficult to stop an asthma attack. With this in mind, try to manage your stress every day. This can be done by journaling or practicing meditation, yoga, or breathing exercises.