The thought of having parasites squirming around your innards is enough to make most of us squirm as well, but it’s unfortunately more common than you might think and may be the underlying cause of some health issues.
These parasites can cause stomach upset, itchiness, diarrhea, fatigue, dizziness, and a host (no pun intended) of other problems. Let’s have a look at seven parasites that regularly make a home in humans (make sure you’re not reading this while enjoying a meal)…
1. Hookworm
This not-so-friendly little guy is a type of roundworm, and is transported into the human body from sources like contaminated water, or even fruits and vegetables, according to NewScientist.com. The hookworm’s larvae develop in the intestines, from which they attach to and drink blood from.
Because these worms are essentially draining blood from you, they can cause a condition in some patients called anchylostomiasis, a form of anemia, adds the source. Other related symptoms include abdominal pain and weakness, it notes.
2. Flatworm Blood Fluke
This is probably not something you want to hear coming out of your doctor’s mouth, as it sounds quite terrifying. The blood fluke is a member of the fluke parasite family (there’s also the intestinal fluke, liver fluke and lung fluke) and none of them will lead to pleasant sensations once they’re inside you.
These parasites can suck the nutrients from your food, and can be contracted from uncooked fish, meat, vegetables, and fruits that have been exposed to “fluke-infested water.” The blood fluke in particular causes a blood infection that can lead to a fever and spread to other organs and glands in your body since it has the perfect vehicle, notes Wellness24.org.
3. Scabies
This is actually an infestation of the human itch mite (known scientifically as Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). At least this one doesn’t live in your guts, but it can cause a lot of problems just below the surface of the skin. “The microscopic scabies mite burrows into the upper layer of the skin where it lives and lays its eggs,” explains the source.
This leads to “intense itching” and a “pimple-like” skin rash at the site of the infestation, it adds. Scabies is usually passed by direct and prolonged skin-to-skin contact with another human host, and affects people of all races and social classes, it explains.
4. Tapeworms
This may be the reigning king of the human parasite world, as you will probably hear this one first when people are talking parasites (hopefully not at the family dinner table). MedicalNewsToday.com says tapeworms get their name because they look like a tape measure, and can measure up to… wait for it… 50-feet.
Tapeworm eggs can be ingested accidentally through infected meat and fish, and the dwarf tapeworm variety can be passed from human contact, adds the source. You may even contract a dwarf tapeworm egg from an insect that has eaten the excrement of an infected rat or mouse, but that’s more common in places with poor hygiene, it adds. Tapeworms cause all the usual symptoms from tummy pain to weakness, but can also lead to more serious effects such as weight loss, dizziness and even convulsions, explains the source.
5. Pinworms
These are “an extremely common infection” that causes itching and irritation around the anus, according to Healthline.com. These “tiny, narrow” worms are actually the most common worm infection in the U.S., adds the source.
The infections are highly contagious, and you can easily ingest one of the microscopic eggs from an object after an infected host has touched it, explains the source. Pinworm infections commonly affect children aged 5 to 10-years, although there’s medication available and long-term health effects are rare, it adds.
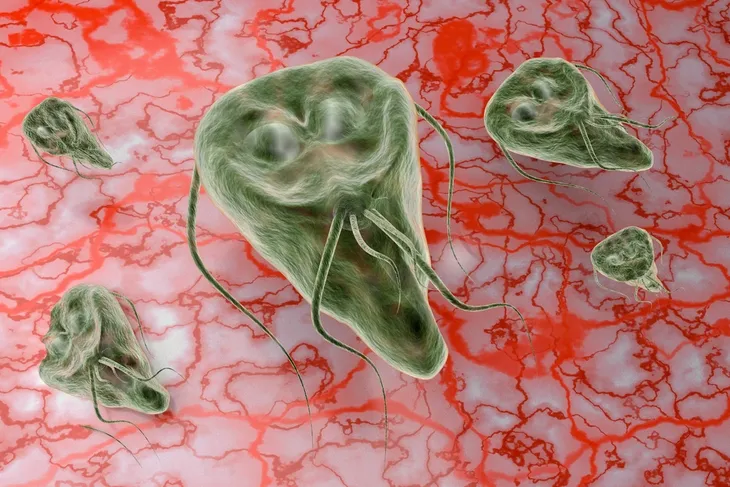
6. Giardia
Livestrong.com says these are single-celled parasites that live in the human intestines (but can also take up residence in your pet or your livestock). They are also the 2nd-most common parasite in the U.S., adds the source.
After contracting the parasite from infected water, food or surfaces, you’ll experience symptoms including diarrhea, flatulence (passing gas), “greasy bowel movements,” cramps and stomach upset, it explains.
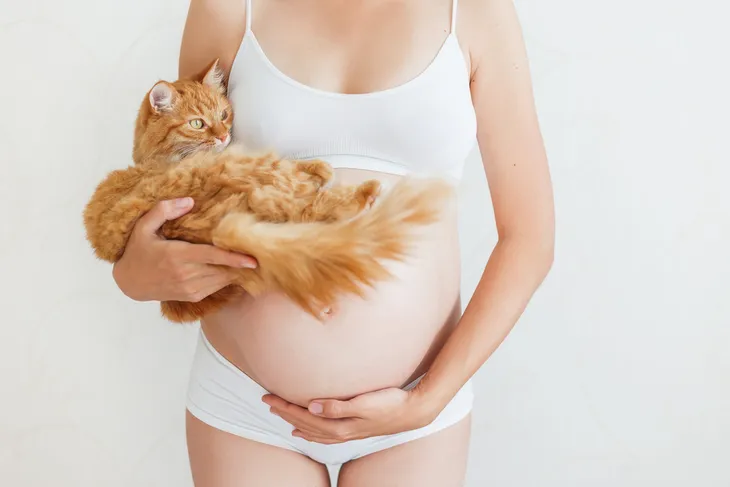
7. Toxoplasmosis
The CDC says this parasitic infection is “considered to be a leading cause of death attributed to foodborne illness in the United States.” However, while more than 30-million people in the U.S. carry this parasite at any given time, only a small percentage of patients have actual symptoms because immune systems generally keep them at bay, it explains.
The biggest risk associated with this parasite is pregnant women, as toxoplasma infections during pregnancy “can have severe consequences,” according to the CDC. The parasite can be found in cat feces, which is why pregnant women are generally advised to stay away from litter boxes. While this parasite is common, it’s on the CDC’s “Neglected Parasitic Infections” list for public health action.