- The cause of muscle cramps is often unknown, but they can sometimes occur due to an underlying medical condition or circumstance.
- A few ways to prevent muscle cramps are to exercise regularly, stay hydrated, and avoid caffeine, among others.
- It’s best to contact a doctor if your muscle cramps are severe or frequent enough to interfere with your quality of life or ability to sleep.
Muscle cramps, which are often referred to as “charley horses,” are something that most everyone has experienced at one time or another. They most commonly occur in the calf or foot when the muscles involuntarily contract, becoming hard and painful.
In most cases, the cause of a muscle cramp is unknown; these are referred to as idiopathic leg cramps. Sometimes, however, muscle cramps occur due to an underlying medical condition or circumstance. Follow along as we outline 10 possible causes of muscle cramps, as well as ways to relieve and prevent them and when to contact a doctor.
Inadequate Blood Supply
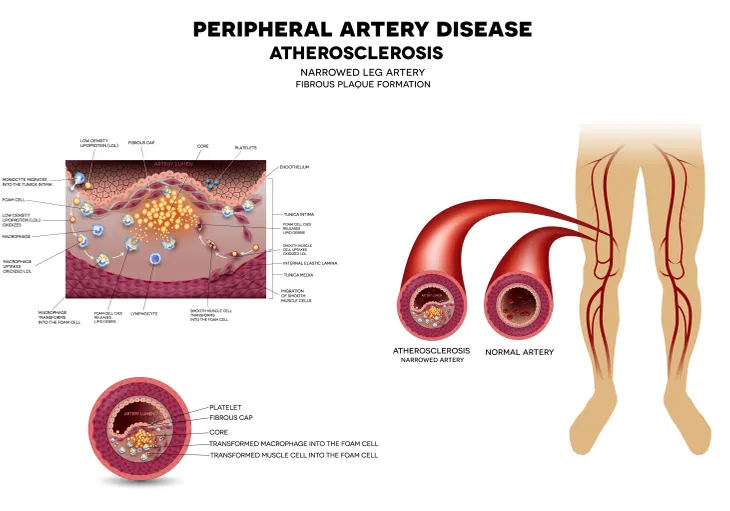
With a condition known as peripheral arterial disease (also commonly referred to as arteriosclerosis of the extremities), the arteries become narrow or, in some cases, blocked.
The American Heart Association tells us that constriction causes poor blood flow to the legs and feet, leading to the most common symptom of peripheral artery disease, painful muscle cramps. The Mayo Clinic says these cramps most commonly occur while exercising, and will typically go away soon after you stop.
Nerve Compression
When the nerves in the spine become compressed, as is the case with a condition called lumbar stenosis, painful cramps in the legs can occur. The Mayo Clinic suggests “walking in a slightly flexed position — such as you would use when pushing a shopping cart ahead of you — may improve or delay the onset of your symptoms.”
Healthline adds that peripheral neuropathy—a disorder that occurs when the nerves in your peripheral nervous system “malfunction because they’re damaged or destroyed”—may also cause muscle cramps. This is especially likely to occur if it is the motor nerves that have been affected, and may also result in muscle weakness and twitching.
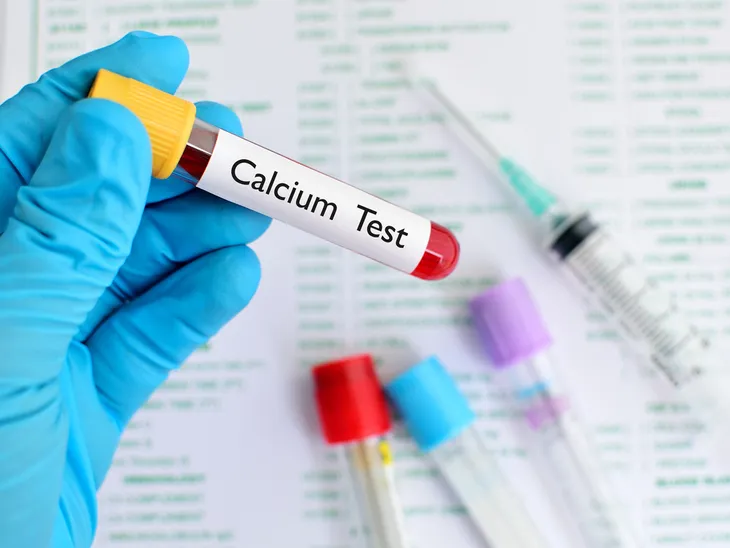
Mineral Depletion
Having too little calcium, potassium, or magnesium in the blood can also lead to muscle cramps. Low levels of these minerals “directly increase the excitability of both the nerve endings and the muscles they stimulate,” says MedicineNet.com.
The source adds that cramps can occur “in any circumstance that decreases the availability of calcium or magnesium in body fluids,” such as hyperventilation, excessive vomiting, or inadequate intake from one’s diet.
Dehydration
While engaging in physical exercise, the body can lose a lot of fluids through perspiration. If you’re not drinking enough water to compensate for this fluid loss, it can lead to dehydration, and dehydration can cause muscle cramps.
Medical News Today adds that “if conditions are warm and the athlete has sweated profusely and lost a lot of sodium (salt), the risk of developing a muscle cramp is greater.” Remember, exercise isn’t the only way to become dehydrated. An illness that leads to vomiting or diarrhea can quickly cause dehydration and lead to muscle cramps.
Certain Medications
Taking certain medications can also increase a person’s likelihood of having muscle cramps. According to WebMD, these medications can include antipsychotics, birth control pills, diuretics, statins, and steroids.
Diuretics, for instance, can cause cramps by “depleting body fluid and sodium,” says MedicineNet.com. The source adds that they also cause the loss of potassium, calcium and magnesium, which, as mentioned earlier, can lead to muscle cramps.
 Shutterstock/Rido
Shutterstock/RidoStrain or Injury
Among the most common causes of muscle cramps is strain. “If a muscle is placed under severe stress or used for a long time,” Medical News Today says, “a leg cramp may occur during the exertion or afterwards.” These types of cramps are more likely to occur in athletes or those who play a lot of sports.
Muscle cramps may also occur to protect an area of the body that has been injured, such as a broken bone, as the cramp “tends to minimize movement and stabilize the area of injury,” says MedicineNet.com.
Aging
As we age, it’s common for our muscles to cramp more often. MayoClinic explains that older people lose muscle mass over time, which can put strain on the muscles. This can cause the remaining muscle to get overstressed more easily which can lead to cramps.
It’s normal to notice an increase in muscle cramps as we age. If the spasm disrupts your daily activity, try to apply a hot or cold compress to the muscles to ease the pain of muscle cramps.
Hypothyroidism
In some cases, a medical condition can cause muscle cramps. Having a thyroid gland that is less active than normal may be a cause of muscle cramps. VeryWellHealth explains that muscle cramps, weakness and aches are common in those with hypothyroidism or low thyroid gland function.
This feeling is typically experienced in the muscles of the thighs or shoulders. Be sure to stretch frequently if you struggle with hypothyroidism to avoid your muscles from cramping.
 Shutterstock/Burdun Iliya
Shutterstock/Burdun IliyaTight Muscles
If you tend to have tight muscles, this may be causing your muscle cramps. Cleveland Clinic explains that inactivity and not stretching enough can cause the muscles to contract and cramp up involuntarily.
If you have tight muscles and are struggling with muscle cramps, try to add more stretching into your daily routine. Be sure to stretch before and after you plan to exercise for an extended period of time. If you tend to have muscle cramps when you sleep, you could do this stretching routine before bedtime as a preventative measure.
 Shutterstock/Maridav
Shutterstock/MaridavHow to Relieve Muscle Cramps
There are two main steps you can take to relieve muscle cramps when they occur. First, you could try to apply heat or ice to the muscle until the pain subsides. This can be done by placing a warm towel or heating pad on the tight muscle or by taking a warm bath. Alternatively, you could try holding a covered ice pack to the cramped muscle to relieve pain.
Another tip is to gently massage the muscle with your hands or a foam roller until the cramping stops. Also, if you do feel a cramp coming on, be sure to stop the activity causing the cramp before it worsens.
 Shutterstock/Sergey Mironov
Shutterstock/Sergey MironovHow To Prevent Muscle Cramps
As with all medical conditions, the best means of treatment is prevention. In terms of preventative measures when it comes to muscle cramps, it’s recommended to avoid caffeine as this may trigger cramps and cause dehydration.
It’s also crucial to drink plenty of water throughout the day and before or during exercise. Another tip is to incorporate a stretching routine into your daily life and be sure to stretch your muscles both before and after exercise.
 Shutterstock/Leszek Glasner
Shutterstock/Leszek GlasnerWhen to Contact a Doctor
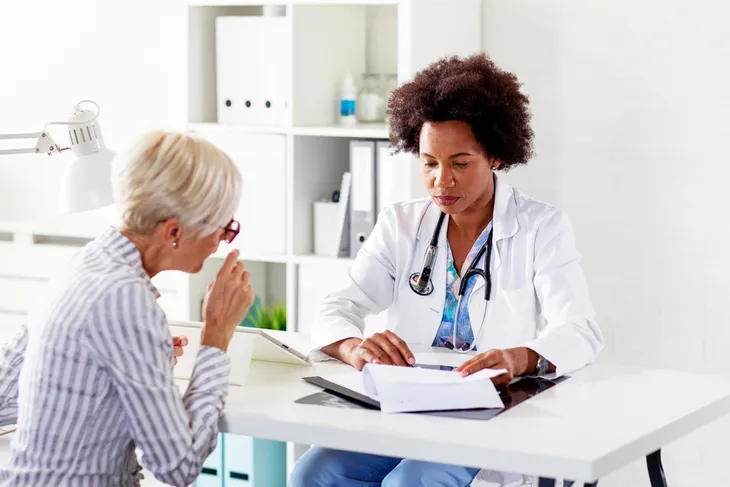
Muscle cramps typically aren’t a reason to be alarmed, but there may be circumstances where it’s best to contact a doctor. The Cleveland Clinic explains that if your muscle cramps are severe or frequent enough to interfere with your quality of life or sleep quality, it may be time to contact a doctor.
A few other signifiers that it might be time to contact a doctor is if the cramps last longer than 10-minutes or if the cramps don’t improve with exercise, massage, or increased hydration.