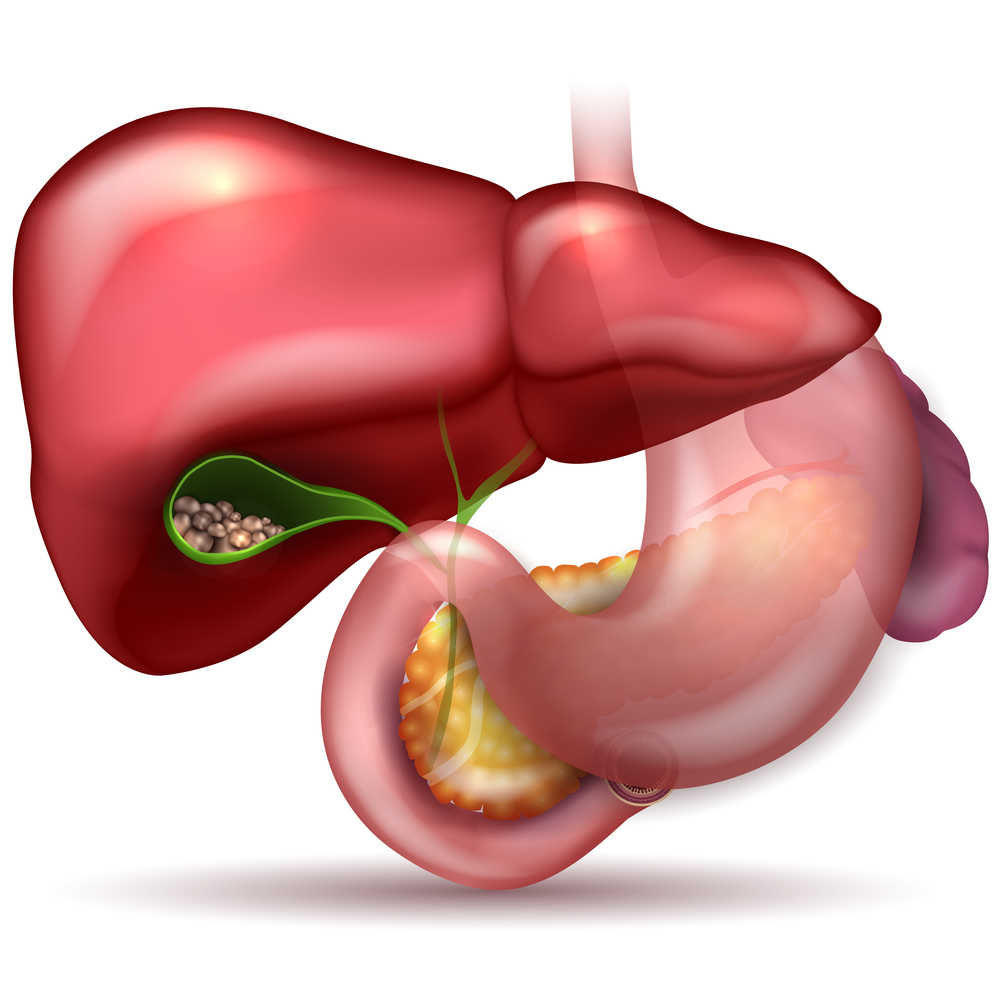
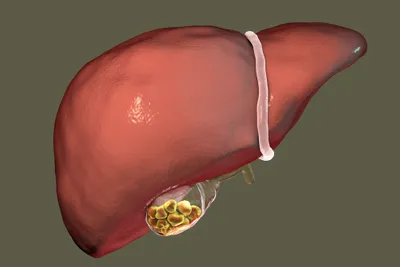
Gallstones are literally small stones that take shape in the gallbladder. Typically made of cholesterol, they can be completely harmless if they remain small and stay out of important passageways leading in and out of the gallbladder. However, should they become wedged in a duct of the gallbladder, they have the potential to cause serious discomfort and pain.
Additionally, if left untreated a problematic gallstone can lead to inflammation, jaundice and fever. The issue could leave a patient writhing in pain for hours at a time and could necessitate the complete removal of the gallbladder from the abdomen. So, what are the causes of gallstones and what are the chances that you may have to face this kind of condition in the future?
1. Excessive cholesterol
Gallstones, in many cases, are made up of cholesterol. They form in the gallbladder when the bile in our bodies contains so much cholesterol that the chemicals contained in our bile, and excreted by the liver, cannot effectively dissolve it. In the end, when our livers deliver more cholesterol than our bile can handle, the result is often gallstones.
The development of cholesterol-based gallstones may not present serious health problems until one of these gallstones becomes lodged in a particularly sensitive area, such as the duct leading into the gallbladder. To limit the chances of this happening, and of gallstones forming in the first place, it’s wise to limit the amount of cholesterol in your diet.
2. Excessive bilirubin
Gallstones can form when the liver excretes too much cholesterol for your bile to break down in an effective manner. But cholesterol isn’t the only problem: issues can also arise when your bile contains too much bilirubin, a chemical the body creates when it starts the process of breaking down red blood cells.
So, why would your body create an excessive amount of bilirubin? Often, it’s because there’s a problem with your liver, such as cirrhosis — meaning excessive alcohol consumption could eventually result in gallstones. However, excessive bilirubin can also result from biliary tract infections and blood disorders.
3. Gallbladder structural problems
Not all gallbladder problems, such as the production of gallstones, can be linked to dietary issues like excessive consumption of alcohol or cholesterol. If there are problems with how the gallbladder functions — and specifically, how it empties — then the result can be the production of gallstones.
The problem is that, should the gallbladder fail to empty in a normal way, the bile in and around it can become highly concentrated. In the end, this can contribute to the formation of gallstones, including those large enough to cause blockages in the entryway to the gallbladder. Of course, this can lead to pain, fever, jaundice and other serious health conditions.
4. Genetics
If members of your family have experienced problems with their gallbladder and gallstones, then there’s a good chance you’ll face these issues at some point in your life.
To tackle this issue before it becomes a serious health problem for you, be sure to carefully monitor your diet and have regular conversations with your family doctor about the possibility of gallstones emerging. A healthy, low-fat diet and limited consumption of alcohol is a good way to limit the chances of gallbladder problems developing.
5. Sex and age factors
Many health conditions target specific demographic groups more than others — for example, older adults are more likely to suffer from Alzheimer’s Disease. It’s certainly not fair, nor is there always an easy explanation for why it occurs.
When it comes to gallstones, the group most likely to experience the problem are overweight or obese women who have had children and are currently taking the birth control pill. The chances of having gallstones develop further increases with age, particularly after one reaches age 40. Although all adults should be aware of their risk of developing gallstones, women with these characteristics are most threatened.
6. Obesity
Obesity and being overweight can come with an abundance of health concerns and risks and developing gallstones is one of them. People who are overweight and obese will generally have higher cholesterol. As we know, excessive cholesterol is a cause for gallstones, so if you have high cholesterol there’s a greater risk of developing this condition.
That being said, if you were to lose some excess weight and lower your cholesterol, your risk of developing gallstones would be decreased in theory if you do not possess any other gallstone related risk factors.
7. Rapid Weight Loss
Sometimes when we set out to fix our health, the drastic change might cause some unfavourable side effects or results. For example, losing a lot of weight is generally a positive result for people who are overweight and need to make a healthy change to avoid serious conditions such as heart disease. However, losing weight quickly could potentially cause gallstones.
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease explains that, when the body is breaking down fat after fasting and rapid weight loss, the liver will then excrete more cholesterol into bile. Losing excessive amounts of weight quickly can prevent the gallbladder from emptying properly which will result could produce gallstones.
8. Diet
As noted above, the NIDDK notes that in contrast, high calorie diets that consist of refined carbohydrates with low fiber content might be a cause of gallstones. The source explains that, these types of grains have the bran removed. The bran and germ contain an abundance of nutrients and fiber.
Fiber is important in preventing gallstones, which is why eating a well balanced diet is important. You can find fiber in an abundance of foods, such as whole grains, fruits and vegetables.
9. Pregnancy
Pregnancy is known to bring on a lot of changes to the female body and it is not uncommon for conditions to occur only during pregnancy. Medicinenet.com suggests that the reason being is that pregnancy hormones cause the release of more bile which consists of more cholesterol. If the gallbladder does not contract normally, gallstones will form.
It is important to note that gallstones during pregnancy should be monitored with caution. The Merck Manual notes that if the gallbladder is blocked by a gallstone or causes an infection, surgery might be necessary but is still safe for the fetus.
10. Related conditions
There are a number of health conditions that can increase one’s risk of developing gallbladder problems, including gallstones. First and foremost, any health problem that directly impacts the flow of bile in and out of the gallbladder can result in frequent issues with gallstones. These health problems can include cirrhosis of the liver (or liver scarring), primary sclerosing cholangitis, or obstetric cholestasis.
Additionally, people who have Crohn’s disease or irritable bowel syndrome (otherwise known as IBS) are more likely to struggle with gallstones at some point in their lives. And, because gallstones are often made up of cholesterol, people with poor diets and serious weight management issues are more likely to experience gallstones.