Rheumatoid arthritis is a long-term autoimmune disease that can occur at any age. It causes inflammation in the joints and tissues of the body. It is unknown what causes the disease, but women gets it at a higher rate than men, and it is most common in middle aged individuals.
The symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis can be debilitating. They include stiffness, pain, and deformity. Thankfully there is a multitude of treatment options available. They are classified into four categories: medication, surgery, lifestyle, and therapy. Here are 19 of the most common and most effective treatments for rheumatoid arthritis. Talk to your doctor before starting a new treatment plan.
19. NSAID’s
NSAID’s are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. NSAID’s are used in the treatment of Rheumatoid arthritis strictly to reduce pain and inflammation. They will not slow down the progression of the disease, but merely aid in helping patients to cope with the pain and swelling.
18. Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are generally used for short-term flare-ups in those with Rheumatoid arthritis. They can reduce pain and inflammation, with the added benefit of slowing down joint damage. These drugs are known for rapid pain relief and are often prescribed when NSAID’s aren’t effectively helping the patient.
17. DMARD’s
This classification of drug is usually the first that rheumatoid arthritis suffers take. They are called “disease modifying antirheumatic drugs”. Most of these drugs were developed to treat other illnesses, like cancer. Used in a much lower amount, these are some of the most effective rheumatoid arthritis drugs available.
16. Biologics
Biologics are one of the newest treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis sufferers. They are used when other medication fails. These drugs were engineered from human gene proteins. They inhibit the immune response to inflammation. Biologics are typically given by injection or through IV.
15. COX-2 Inhibitors
COX-2 inhibitors are also known as cyclooxygenase. They are a NSAID that stops the body from inflammation and swelling. COX-2 inhibitors are different from NSAID’s because they don’t block COX-1, which is an enzyme that creates chemical messengers,, prostaglandins, in the body. They protect the lining of the stomach. COX-2 inhibitors protect from some of the side effects of NSAIDs, including ulcers.
14. Immunosuppressants
Suppressing the immune system of patient’s with rheumatoid arthritis is useful because it helps reduce the damage to good tissue in the body. There are a few different types of immunosuppressants that are typically prescribed. Patients need to be careful because with the use of immunosuppressants comes increased risk for infection.
13. Occupational Therapy
Occupational Therapy can be an effective treatment for rheumatoid arthritis patients because it can assist them with planning alternative ways to carrying out daily tasks which they might find painful or challenging for their bodies. For instance, an Occupational Therapist could recommend a tool for helping a patient put on his or her socks.
12. Surgery
If other avenues for treatment options have been exhausted, then a doctor may recommend surgery for rheumatoid arthritis patients. Surgery can repair damaged joints, correct deformities, or reduce pain. It can allow patients to achieve a higher quality of life. The surgery could range in complexity from tendon repair to Arthroplasty, which is a total replacement of the joint.
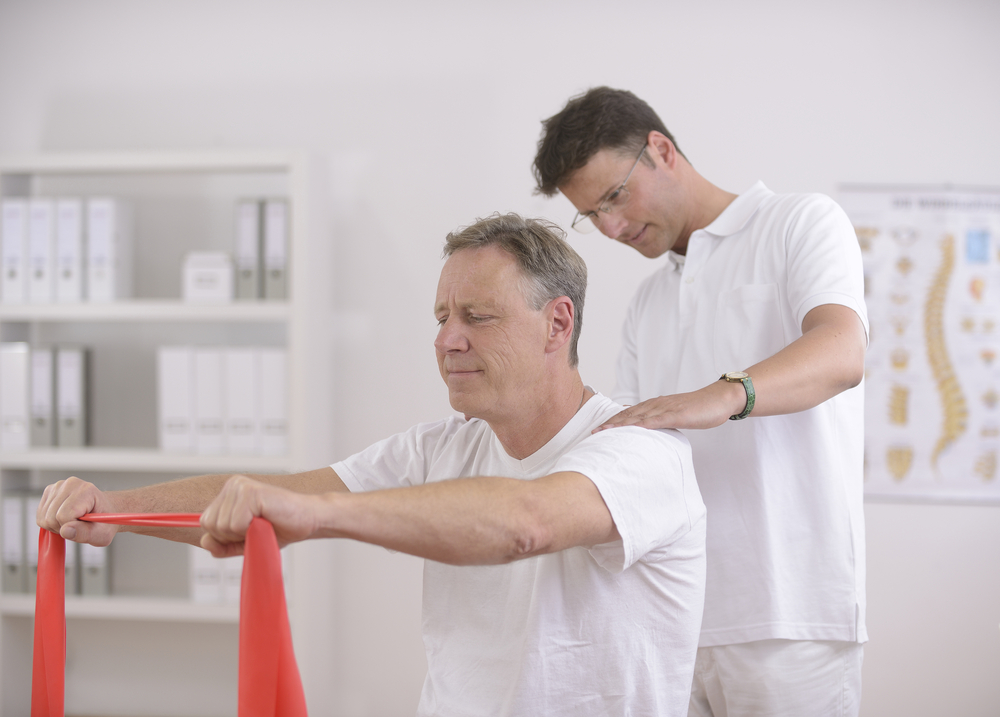
11. Exercise
When flare-ups are not experienced by the patient, exercise has proven very useful for those with rheumatoid arthritis. Muscles around the joints can become weak, and exercise can assist in strengthening them. Some exercises such as swimming may prove to be easier on the body. Check out these exercises to help manage rheumatoid arthritis!
10. Diet
Diet is an important part of living a healthy and balance life. It is particularly important for those with rheumatoid arthritis to eat a balance diet. A diet that is rich in Omega-3 fatty acids or fish oils may be recommended by doctors.
9. Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy may be a great way for rheumatoid arthritis sufferers to regain range of motion with their bodies. It is a good way to stretch and work joints and muscles in a safe and supervised setting. Physiotherapists can recommend exercises that are safe for patients to try on their own as well.
8. Hot/Cold Bathing
Hot/Cold bathing or compresses that are hot and cold are sometimes recommended for patients with rheumatoid arthritis. This can help to ease joint pain, and may provide relief between drug doses, or other treatment options. It is best to follow your doctor’s advice on whether or not hot/cold bathing may be appropriate for you.
7. Acupuncture
Acupuncture is employed to stimulate the major meridians in the human body, which can help relieve pain caused by rheumatoid arthritis. This type of treatments releases endorphins which work to decrease the pain that the patient is feeling. This type of treatment is usually part of a regiment and not a sole treatment for rheumatoid arthritis.
6. Chiropractic Treatments
Chiropractic treatments focus on your nervous system, along with muscles and joints. This treatment help ease joint stiffness, which is common with rheumatoid arthritis. When you visit a chiropractor they will perform an assessment which will determine your treatment. Your plan could include mobility training, support exercises, and heat application.
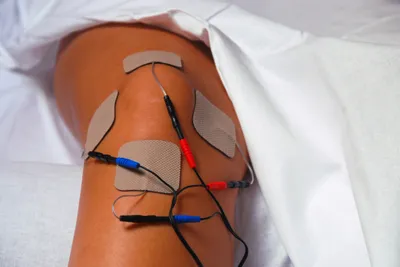
5. Electrotherapy
Electrotherapy is used to stimulate muscles or a nerve by using electrical impulses. There are a number of ways that electrotherapy is delivered to patients including electrical nerve stimulation, lontophoresis, and interferential current. Electrical nerve stimulation is the most common treatment form and is used to treat musculoskeletal pain, peripheral nerve injuries and regional pain.
4. Hydrotherapy
Hydrotherapy is conducted by having the patient submerged in water to exercise or soak for a period of time. This type of treatment is well suited to combat joint pain and stiffness. Hydrotherapy works to reduce the swelling around joints, which can significantly reduce pain. This treatment is often performed with warm water or jets.
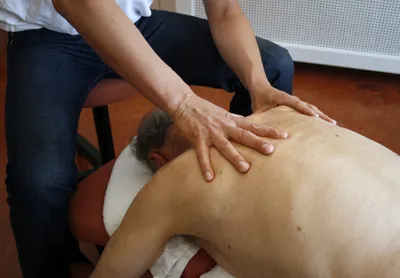
3. Massage
Taking part in frequent massage of the joints and muscles can significantly reduce the pain levels of individuals with arthritis. Taking advantage of this simplistic process regularly has been show to offer improvements in stiffness, range of motion, strength, pain reduction, and overall function.
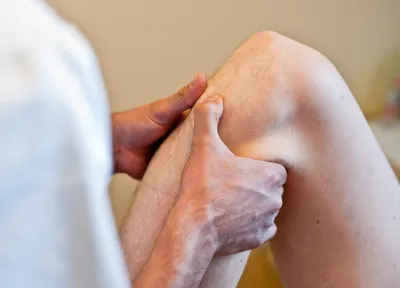
2. Osteopathy
Osteopathy is a combination of manual techniques that are performed on your joints, muscles, and ligaments. This treatment helps to reduce swelling, pain levels, and improve motion. There are a number of different techniques involved including stretching, mobility training, and traction procedures. This techniques can be performed in warm salt water to ease tension.
1. Supplements
There are a number of extracts and supplements that can help treat rheumatoid arthritis. Some of the most commonly taken supplements for arthritis include omega-3 fatty acids and borage plant extract. The omega-3 fatty acids, when taken in large quantities can reduce swelling of the joints. The oil from the borage plant works in a similar fashion to typical NSAID’s.