Although we may feel uncomfortable talking about gastrointestinal problems, they’re incredibly common and affect most everyone at some point or another in their life. In fact, in the United States alone, digestive diseases presently affect an estimated 60- to 70-million people.
But because of the sometimes embarrassing symptoms associated with digestive diseases and disorders, people avoid seeking treatment. While some of these conditions are simply minor annoyances that can be easily remedied, others have the potential to cause serious, potentially life-threatening damage if left untreated. Read on to learn more about the 12 most common digestive diseases and disorders (including symptoms and treatments of each)…
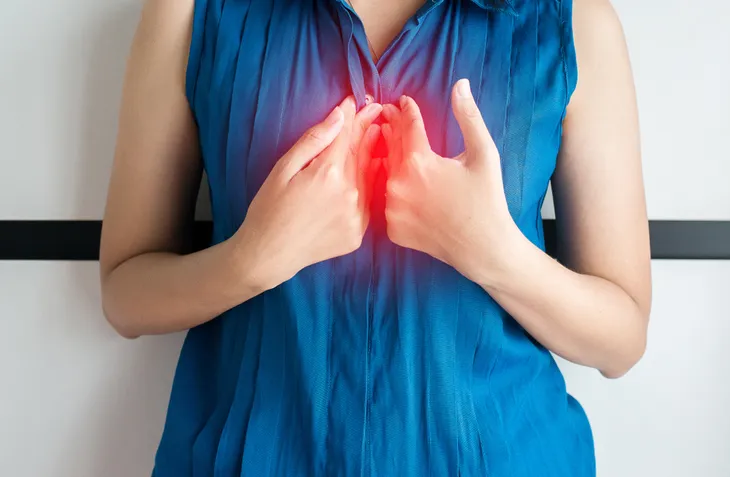
1. GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), or acid reflux for short, is a condition that affects approximately 20-percent of Americans. It occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter becomes weak or relaxes when it shouldn’t, which allows the stomach acid to flow back up into the esophagus.
This commonly triggers heartburn—a burning sensation in the chest that is often accompanied by a sour taste in the mouth. Other symptoms of GERD include wheezing, sore throat, chronic cough, and difficulty swallowing. Depending on the severity of the condition, treatment may include lifestyle changes, medication, and possibly surgery.
2. Gallstones
The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ that is attached to your intestine. It stores bile, a fluid that is used to aid in digestion. Sometimes, however, this bile can form into hard deposits known as gallstones, typically as a result of there being “too much cholesterol or waste in your bile, or if your gallbladder doesn’t empty properly,” says Everyday Health.
Gallstones are incredibly common, affecting around 20-million Americans. While, for many, gallstones don’t cause any symptoms, they can lead to symptoms such as pain, nausea, fever, and infection in about 25-percent of cases. As a result, these individuals need treatment, which often involves surgery to remove the gallbladder.
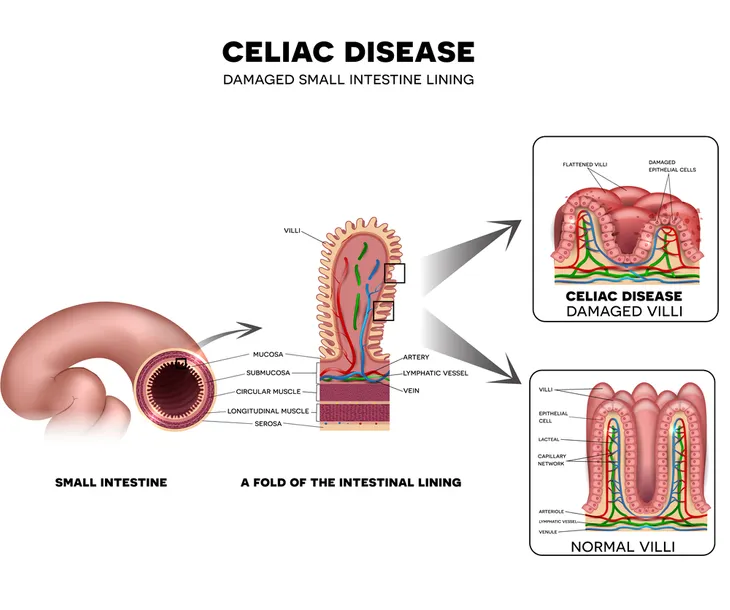
3. Celiac Disease
Celiac disease is a condition where individuals have an immune reaction to consuming gluten, a protein that is found in wheat, rye, and barley. Although celiac disease is quite rare, affecting less than 1-percent of Americans, HealthGrades.com says that gluten sensitivity is more common—affecting about 5-percent of Americans.
The symptoms of both are similar and include abdominal pain, diarrhea, and bloating. The distinguishing difference between them, however, is that celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder. So, when people with the condition consume gluten, it actually causes damage to the lining of the small intestine.
4. Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is part of a group of conditions that fall under the umbrella term “inflammatory bowel disease.” Everyday Health says that the disease “most commonly affects the terminal ileum, which connects the end of the small bowel and the beginning of the colon, but it can affect any part of the digestive tract.”
The Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation estimates that it affects as many as 780,000 Americans, causing symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, fever, and loss of appetite. Treatments are largely dependent on what symptoms a person experiences, but can include anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, and surgery to repair the damaged digestive tract.
5. Ulcerative Colitis
In addition to Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis is considered another primary type of inflammatory bowel disease. In fact, it is even more common than Crohn’s disease, with the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation estimating it affects as many as 907,000 people in the United States.
While the symptoms of ulcerative colitis—such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and weight loss—closely mirror those of Crohn’s disease, a major distinguishing difference is that ulcerative colitis only affects the large intestine (or the colon). Medications can help treat the condition, but in severe cases, surgery to remove the colon may be necessary.
6. Irritable Bowel Syndrome
According to the Cleveland Clinic, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is “a condition in which the colon muscle contracts more often than in people without IBS.” It may be triggered by diet, medications, or stress and can lead to symptoms such as gas, abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea.
It is estimated that IBS affects about 10- to 15-percent of adults worldwide, with women twice as likely to be affected than men. Treatment varies, but is primarily centered on removing trigger foods from the diet and minimizing or better managing stress. In some cases, medication may also be prescribed.
7. Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are swollen blood vessels at the end of the digestive tract, in the anal canal. They are oftentimes painful, itchy, and can cause blood in the stool. Typically, they occur due to constipation, chronic diarrhea, and pregnancy.
This makes hemorrhoids a common ailment among adults. In fact, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services indicates that they affect 75-percent of people over the age of 45. To help alleviate the discomfort they cause, try using hemorrhoid creams or suppositories. And to prevent them from occurring in future, be sure to eat plenty of fiber and drink lots of water.
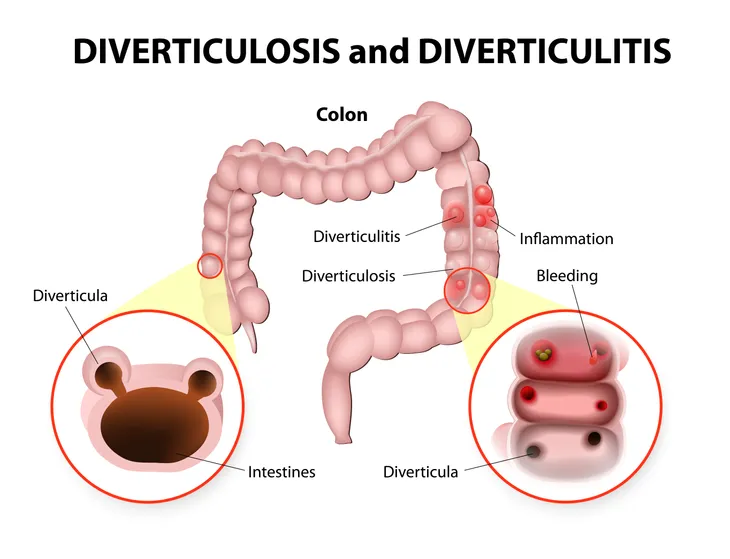
8. Diverticulitis
An estimated 50-percent of people between the ages of 60 and 80 have diverticular disease, a condition in which small pouches (diverticula) form where there are weak spots in the lining of the digestive system—most commonly in the colon (or large intestine).
Everyday Health indicates that when diverticula develop but there are no symptoms, it is referred to as diverticulosis. “But if the pouches become inflamed,” the source says, “it’s called diverticulitis.” With diverticulitis, people can experience symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, fever, diarrhea, or constipation. If the condition is mild in nature, it tends to be treated with antibiotics and a clear liquid diet. In severe cases, however, the source says, “You may need surgery to remove the diseased part of your colon.”
9. Anal Fissures
The Cleveland Clinic defines anal fissures as “splits or cracks in the lining of the anal opening.” They can be caused by straining and hard bowel movements (as with constipation), as well as passing loose, watery stool (as with diarrhea).
The symptoms of an anal fissure are similar to those of a hemorrhoid, including “intense burning pain, bleeding, or spasm after bowel movements.” When it comes to treatment, increased intake of dietary fiber is crucial, but medications, topical ointments, and sitz baths may also be beneficial.
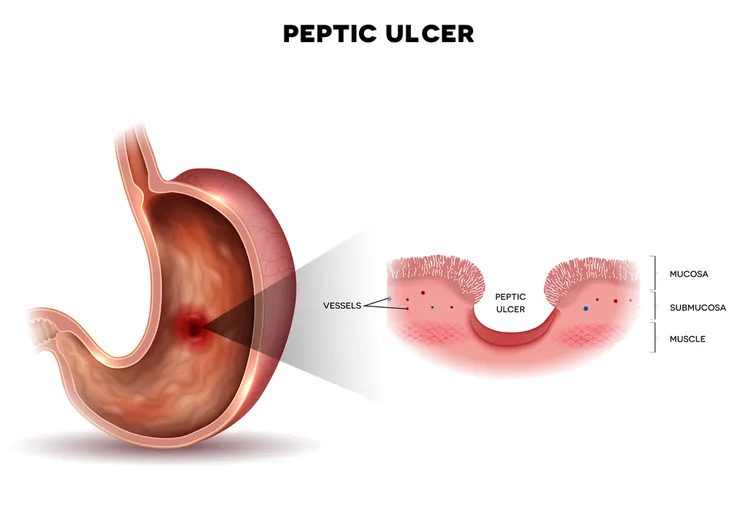
10. Peptic Ulcers
Peptic ulcers are sores that develop in the lining of the stomach or upper part of the small intestine and are typically caused by a bacterial infection (specifically Helicobacter pylori [or H. pylori]), smoking, or as a side effect of excessively taking certain medications such as aspirin, ibuprofen, or naproxen.
They tend to cause symptoms such as stomach pain, nausea, bloating, lack of appetite, and weight loss. If due to a bacterial infection, peptic ulcers are most commonly treated by taking antibiotics and antacids. In severe cases, however, surgery may be necessary.
11. Constipation
Constipation is when it is hard to pass stool, or when bowel movements are infrequent (typically less than three times per week). It is a common condition that affects most everyone at some point or another in his or her life. On a chronic basis, however, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services indicates that approximately 63-million Americans experience it.
It most commonly occurs due to inadequate fiber intake. Because fiber is so essential to digestion and waste elimination, not getting enough of it can cause straining during bowel movements. Fortunately, upping your fiber intake and exercising regularly can relieve most cases of constipation.
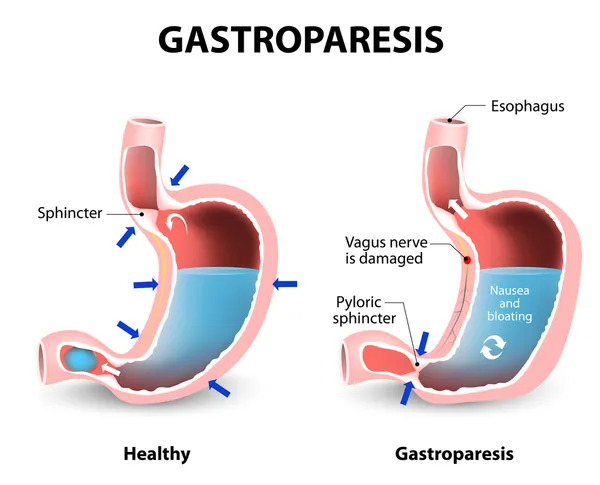
12. Gastroparesis
According to Gastrova.com, gastroparesis is a digestive disorder that “reduces the ability of the stomach to empty its contents, slowing or stopping the movement of food from the stomach to the small intestine.” It is most commonly caused by diabetes, but may also result from intestinal surgery or a nervous system disease.
Symptoms of gastroparesis include stomach pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting, acid reflux, and loss of appetite. Although the disorder tends to be a chronic condition, the source indicates that “a combination of nutritional changes and medication can help manage symptom severity.”