We all know the feeling. You’re run down, stuffed up, feverish, and maybe a little chilly with a sore throat and an annoying post nasal drip. Don’t shrug it off as the common cold. You may very well have a sinus infection, or sinusitis. A sinus infection can be tricky to identify, but there are some signs to watch out for. Identifying what is happening with your body when you are ill is the first step to getting better.
You might think it’s just a cold, but before you run to the pharmacy for over-the-counter cold medication, check for these 20 signs of a sinus infection…
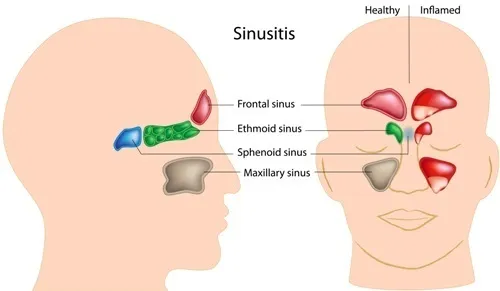
1. Inflamed Sinuses
The inflammation of the sinuses, which is the main sign that you have a sinus infection and not just another cold, will manifest as severe pressure that feels like a dull, throbbing pain behind the eyes or cavities behind the forehead, nasal bones, and cheeks (where your sinuses are located).
Many sinusitis symptoms mimic the common cold, but the 37 million unfortunate Americans who suffer from this painful inflammation of the sinuses each year are on constant high alert when it comes to that cold or allergy, which may lead to another nasty sinus infection.
2. Congestion
Many folks with sinus infections complain that their head feels heavy. This occurs when the sinus pathways (that connect the sinuses to your nasal passages) become so congested with mucus that they’re unable to drain, resulting in pressure on the nerves of the face.
However, before you consider antibiotics, consider these study findings published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, which found that drug resistance was a common occurrence when antibiotics are prescribed for a sinus infection. The study monitored 166 patients with sinus infections–half who were prescribed over-the-counter medications and the other half who were prescribed a 10-day course of antibiotics (i.e., amoxicillin). After day 7 of the treatment, the symptoms of sinus pain, runny nose, post nasal drip, and cough only slightly improved for both those prescribed antibiotics and over-the-counter medications.
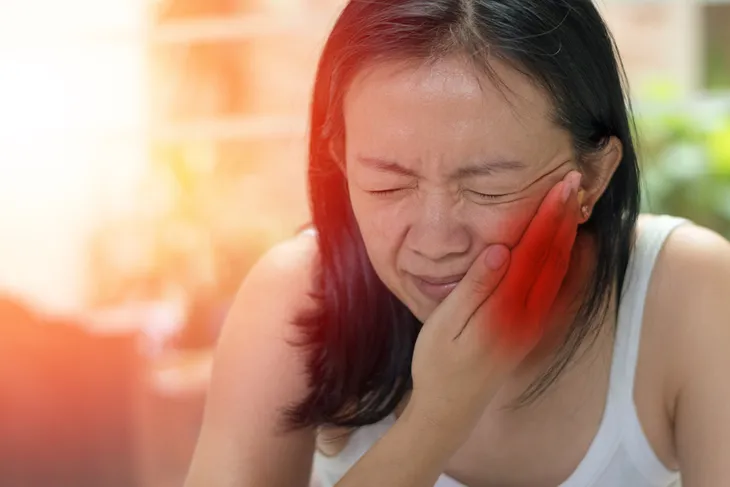
3. Tooth Pain
An achy pain across the top teeth is common in those with a sinus infection. What you’re feeling isn’t actually tooth pain, but pressure in the area due to inflammation of the sinuses, which can feel like a toothache. According to research from Dentistry Today, sinusitis can affect any of the seven sinuses (or air filled cavities) located in the head.
The seven sinuses include the sphenoid, maxillary, frontal, ethmoid, and mastoid sinuses. In fact, chronic sinusitis is one of the more prevalent chronic illnesses in the U.S., due to several causes including sinus infection, allergies, chemical irritation, sinus, obstruction, and tooth infection.
4. Dizziness
Because sinus infections cause the sinus membranes to become extremely inflamed and congested with mucus, it makes perfect sense that you may feel off balance, particularly if you tip your head forward or stand up really quickly from a seated position.
According to the University of Maryland Medical Center, sinusitis is characterized as inflamed sinuses, meaning the air filled cavities around your cheeks, nose, and eyes become painfully swollen and blocked due to an accumulation of fluid from infection with a cold virus, fungus, or bacterial. When sinusitis occurs, the sinuses can’t drain, which often impacts balance and coordination causing dizziness.
5. Morning Cough
A nasty morning cough will often be mistaken for the common cold. However, a sinusitis cough will be at its worst first thing in the morning after you’ve been prone all night and the sinuses have drained down the back of your throat. According to medical professionals, sinusitis affects the sinus cavities, which are the mucous-producing air filled cavities behind the cheeks, nose, and eyes. When sinuses become blocked or inflamed, sinus pressure builds up.
Because mucous becomes lodged, it can begin to drain down the back of the throat (called post nasal drip) and cause severe coughing and the need to clear our throats more often. Postnasal drip can be more severe during sleep because of the prone position causing severe cough and disrupted sleep.
6. Postnasal Drip
Postnasal drip results when excessive mucus is expelled by the nasal mucosa. However, if the sinuses are inflamed, the watery, clear mucus accumulates and drains down the back of the throat from the nose. When we are healthy and the sinuses are clean and clear, excess mucus in the sinuses exits via a tiny opening into our noses on a regular basis via sneezes and blowing our nose.
However, when a sinus infection occurs, sinuses become congested and obstructed with sticky mucus, which blocks and builds up pressure in the sinus cavities (i.e., behind the teeth, cheeks, teeth, nose, eyes, and forehead) when mucous can’t be expelled via its normal route. This is how postnasal drip begins, when mucus has no choice but to drain down the back of the throat.
7. Decreased Smell
Difficulty breathing through the nose due to blocked or inflamed sinuses will often lead to a decreased sense of smell. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, smell disorders can occur with any blockage in the sinuses, including a sinus or other upper respiratory infection.
Sinusitis will often cause loss of smell (or hyposmia) when sinuses become congested, swollen, or experience extreme pressure. When odours enter the nose, they enter the nasal vault and dissolve on the thin mucus layer, which stimulates smell receptors. However, while mucus is responsible for dispersing scents to the underlying receptors, excess mucus or blocked and inflamed tissues can impair the smell response.
8. Decreased Taste
Not only can you lose your sense of smell, but you can also lose your sense of taste. The sense of taste is intimately connected to smell. This is because taste is also largely dependent on entering the nasal vault. This doesn’t necessarily mean you lose your sense of taste completely. Instead, things may just taste foul or unpleasant.
 BlurryMe / Shutterstock
BlurryMe / Shutterstock9. Fever
People affected by the common cold usually don’t have a fever. However, those with a serious infection, such as sinusitis, typically experience an increase in body temperature as the immune system attempts to purge the infection. A cold becomes a sinus infection when the sinuses become severely inflamed or swollen. Normally, the sinuses are clear airways; however, when they become blocked and filled with fluid from a viral, fungal, or bacterial infection, it becomes difficult for your body to fight off the infection.
Symptoms of the common cold and sinusitis can often overlap. However, sinus infection includes the symptoms of sinus pain and pressure (i.e., around the eyes, teeth, cheeks, and forehead), thick yellow nasal discharge, smelly nasal discharge, severe headache, fever, and cough due to postnasal drip. You should be suspicious if a cold just gets worse rather than better. If your cold continues for more than 10-days or worsens, you may likely have sinusitis.
10. Yellow Mucus
While you might think it rude to inspect your mucus, it’s hard not to take a peak if you’re producing an overabundance of the thick, sticky stuff. Usually with sinus infection the consistency of your mucous will be different. For instance, it may become thick and yellow. This may be indicative of a sinus infection, as the white blood cells fight off the infection and as they drain (or try to eliminate the infection) from your body.
Also, the texture of mucus may change character with a sinus infection. For instance, mucus may become much thicker when you blow your nose or try to clear your throat. Additionally, mucus may appear yellow or green in color, which according to WebMD, is a clear signal that you may have an infection.
11. Headache
A nasty headache, which is usually caused by increased sinus pressure, can linger for days with sinusitis, as the tissues become inflamed and the muscles tighten around your eyes and forehead. According to the Mayo Clinic, sinus headaches are headaches characterized by sinusitis, an infection that blocks or inflames the membranes lining the sinuses.
A sinus headache may result from increased mucus, fluid, and infection buildup (bacterial, viral, or fungal) that causes extreme pressure and pain. A sinus headache may present as pain and pressure in the sinuses (a feeling of fluid fullness in the areas of the teeth, cheeks, and brow) accompanied by pain and throbbing in the upper teeth and/or decreased taste and smell, and the pain that often worsens when you bend forward or lie down and obstruct (the flow of mucus).
12. Bad Breath
In addition to the unpleasant symptoms already mentioned, sinus infections can also cause you to experience bad breath, or halitosis. The Colgate-Palmolive Company says, “Bad breath is often the first side effect [of a sinus infection] as the sinuses drain into the back of your throat.”
Due to an excess build up of this discolored and smelly mucus in the sinus cavities, air can no longer pass through the nose. As a result, you are forced to breathe through your mouth, and when you exhale, “the odor from the infection transfers to your breath,” says the source.
13. Fatigue
Have you been feeling sluggish and worn out lately? Not getting much sleep at night? It may be a sign of a sinus infection. When your body is battling an infection, the immune system becomes strained, which can lead to exhaustion and lethargy that persist for lengthy periods of time, sometimes months on end.
Fatigue is rarely the sole symptom you’ll experience with a sinus infection. So be mindful of whether you’re suffering from any of the other symptoms already mentioned, particularly sinus inflammation, congestion, and postnasal drip.
14. Sore Throat
With postnasal drip, mucus is forced to drain down the back of the throat because the sinuses are obstructed and it has nowhere else to go. Because this isn’t how mucus is normally expelled from the body, the throat can become irritated.
Healthline explains that “it may start as an annoying tickle,” but can worsen to the point of the throat feeling raw, achy, and inflamed, especially if the infection lasts for several weeks or longer.
15. Hoarse Voice
A sore throat and hoarse voice can often go hand-in-hand. In fact, sinus infections are one of the most common causes of a sinus infection. Your voice becomes hoarse when the vocal cords become swollen due to inflammation or infection. It can make it difficult for you to make sounds when trying to speak.
Your voice may sound weak, breathy, scratchy, or husky while talking. It should go back to normal once the sinus infection clears up, but you should see a doctor if the hoarseness persists.
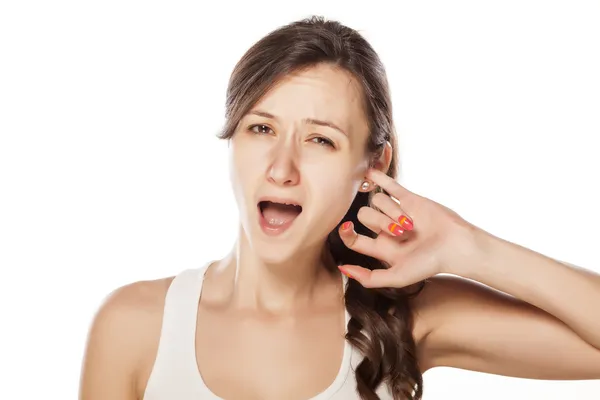
 Ahmet Misirligul / Shutterstock
Ahmet Misirligul / Shutterstock16. Ear Pain
Like tooth pain, ear pain may seem unrelated to a sinus infection, but is in fact a very common symptom. As WebMD explains, “Your sinuses and ears are connected inside your head. So sinus congestion and stuffiness can affect the pressure in your ears.”
As a result, you may experience pain in the ear canal, or it may feel as though the ears are blocked, which can cause your hearing to be muffled. Fortunately, Livestrong.com says there a variety of different home remedies that can provide effective relief for ear pain, such as warm compress, elevating the head, and using nasal sprays or rinses. As always, however, be sure to consult with your doctor before trying to treat things on your own.
17. Tenderness of the Face
One of the symptoms doctors will look for when diagnosing a sinus infection is tenderness of the face. When you have this illness, the sinuses become inflamed or infected and fluid can build up in these air-filled spaces. This build up is to blame for many symptoms, such as increased pressure that causes facial pain.
You have sinuses between the eyes, as well as behind the forehead, nose, and cheeks. The pressure can cause pain to occur in any of these areas and is a big reason why you might develop a headache during a sinus infection.
 BlurryMe / Shutterstock
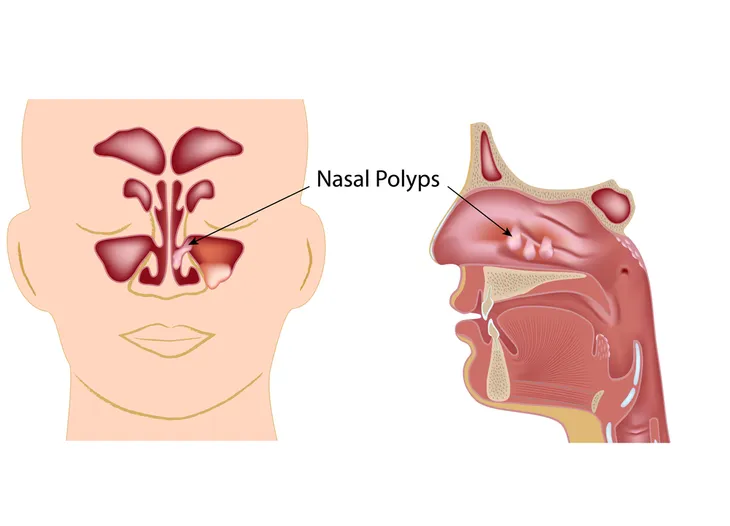
BlurryMe / Shutterstock18. Nasal Polyps
One condition closely related to sinus infections are nasal polyps. These are teardrop-shaped growths that form around the opening to the sinus cavities, which occurs due to inflammation. The polyps can block drainage from the sinuses and lead to a sinus infection. They can also pop up during a sinus infection and become another uncomfortable symptom.
Polyps on the nose are not tumors and don’t necessarily increase your risk of cancer. Nasal polyps may disappear once the sinus infection goes away. Certain medications like corticosteroids can help get rid of polyps, but in some cases, they will need to be removed surgically.
 Alila Medical Media / Shutterstock
Alila Medical Media / Shutterstock
19. Runny Nose
It’s normal to have a runny and stuffy nose when you get a cold. But if it lasts for longer than one week, that could mean your cold is actually a sinus infection. This happens when one or more of your sinuses becomes inflamed, resulting in fluid build up.
 Prostock-studio / Shutterstock
Prostock-studio / Shutterstock20. Symptoms That Last 10 Days
Sinus infections are not fun. While most sinus infections will get better on its own without antibiotics, that’s not always the case. See your doctor if your symptoms don’t go away after 10 days. They can recommend some remedies to get you feeling better. Just make sure to seek medical attention sooner if you have a fever that lasts longer than a few days.
 ANDREI ASKIRKA / Shutterstock
ANDREI ASKIRKA / Shutterstock