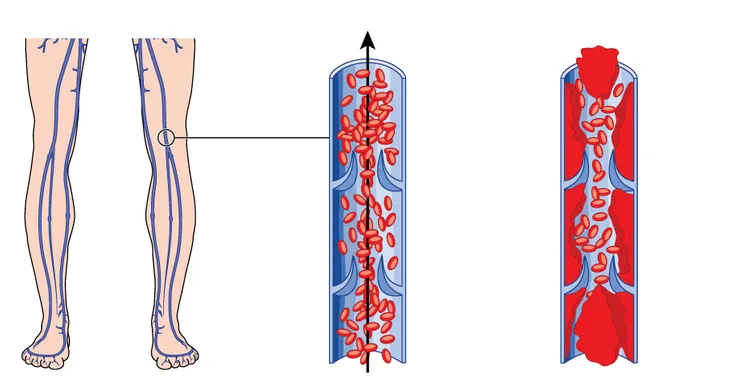
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot forms deep within a vein, typically in regions such as the thigh or calf. Oftentimes, the existence of a DVT causes no pain or symptoms. However, if the DVT blocks blood flow completely (or even partially), pain and swelling may occur in the vicinity of veins close to the surface of the skin and movement may become difficult.
In severe cases, a blood clot will detach from the leg vein and travel through your bloodstream to the heart or lungs, in which case, sudden and severe symptoms and even death can result within a few hours if left untreated.
Let’s take a look at the 10 most common symptoms of DVT…
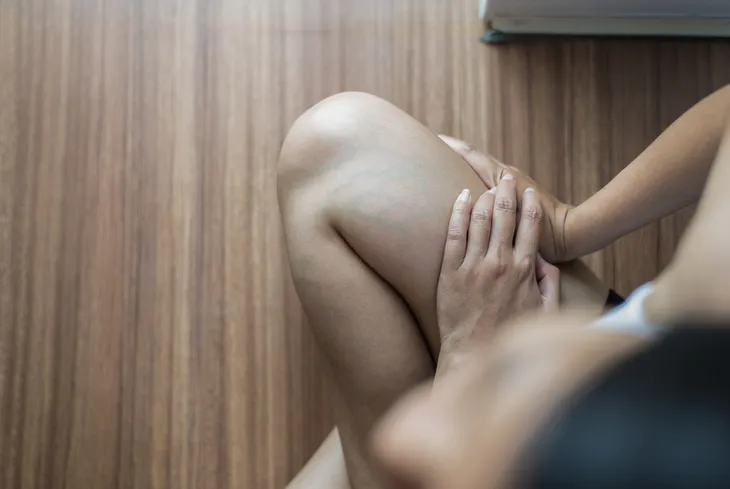
1. Leg Pain or Tenderness
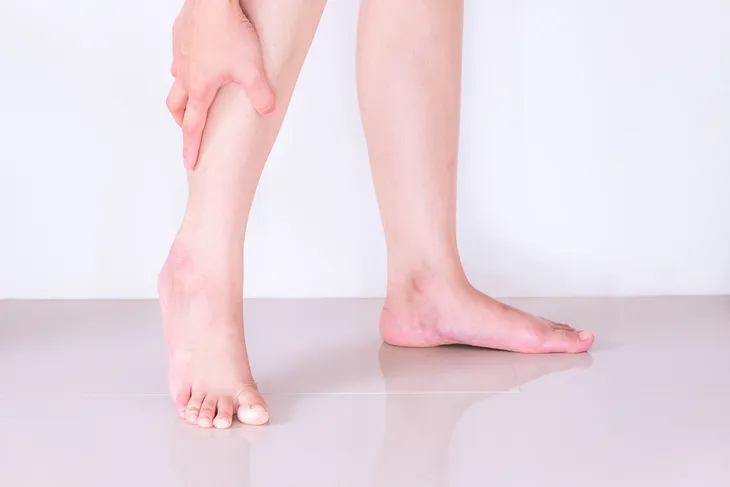
With large blood clots, pain and/or tenderness can occur in the affected leg, particularly when standing, climbing stairs, or walking. In addition to the leg, this symptom may also occur in the ankle, foot, or arm.
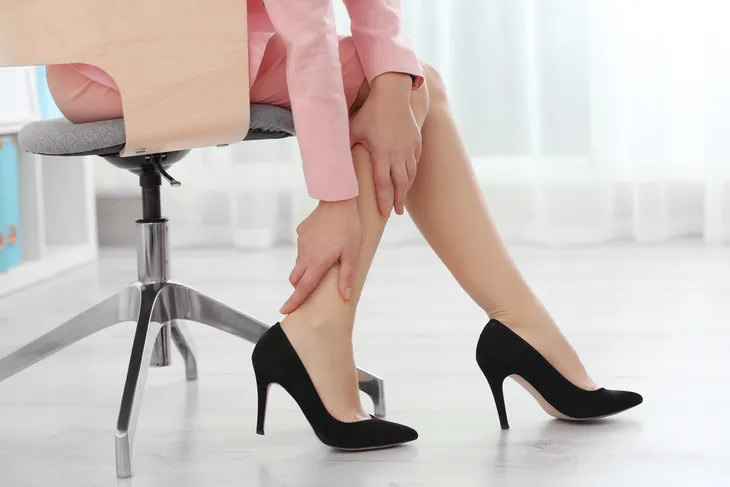
2. Swelling
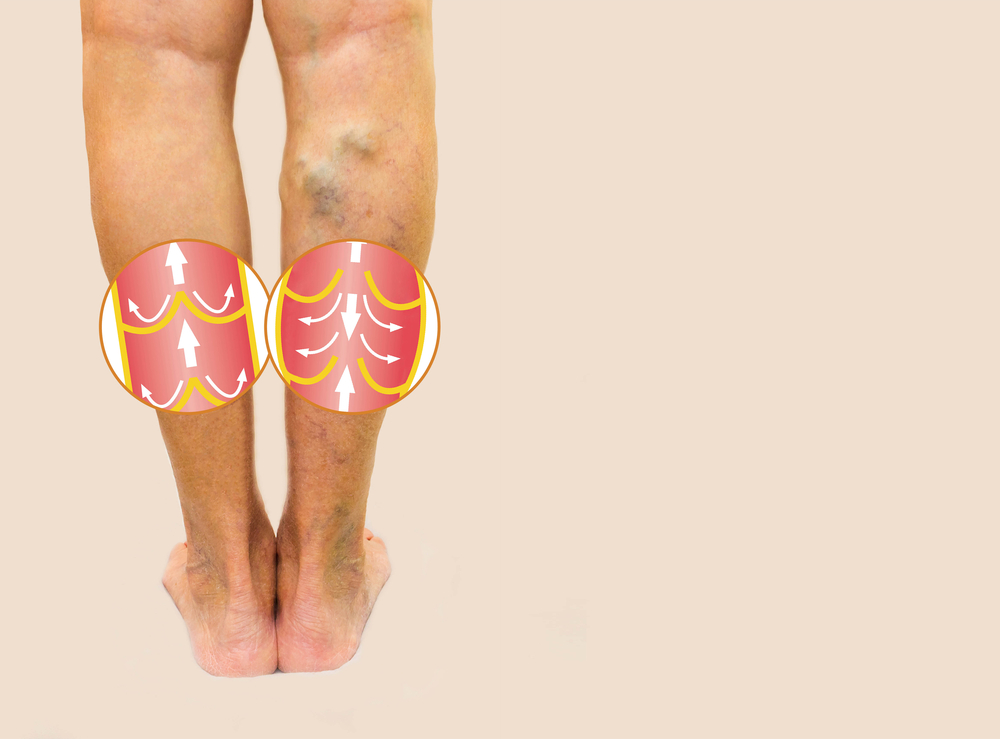
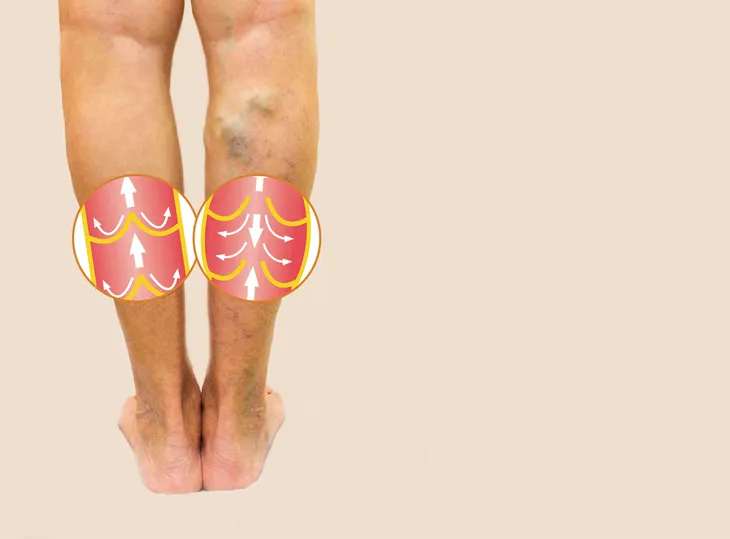
Swelling, particularly around the affected area (i.e., calf or thigh), may occur with a worsening clot. The swelling is typically unilateral (limited to one side of the body), as opposed to bilateral (on both sides of the body). It is unlikely that bilateral swelling is caused by a DVT, as this is more indicative of other illnesses, such as congestive heart failure (CHF) or ingestion of too much salt (sodium).
3. Warm Skin
Another common sign in the affected leg is skin that’s warm to the touch, or even “feverish” to some. This is usually accompanied by the next symptom on this list, reddened or discolored skin.
4. Reddened or Discolored Skin
The skin of the leg afflicted with the blood clot may turn red or patches of discoloration (pale or even blue) may develop along the thigh or calf muscle. Although DVT is not the only cause of reddened or discolored skin, it is one of the most common reasons for it to occur suddenly (acutely) as opposed to gradually over time (chronic).
5. Cramping
Severe cramping, or “charley horses,” in the thigh or calf may be an indication that you have a DVT. If this occurs along with one or more visible surface veins becoming red, swollen, and tender to touch, you should seek medical evaluation immediately.
6. Bloody Coughing
Sudden and unexplained bouts of coughing may occur, which may be productive of bloody phlegm (mucus). The clinical term for bloody coughing is hemoptysis. This is more indicative of a blood clot in the lung, also known as a pulmonary embolus (PE), which is a direct result of a DVT and can be life-threatening if not treated immediately.
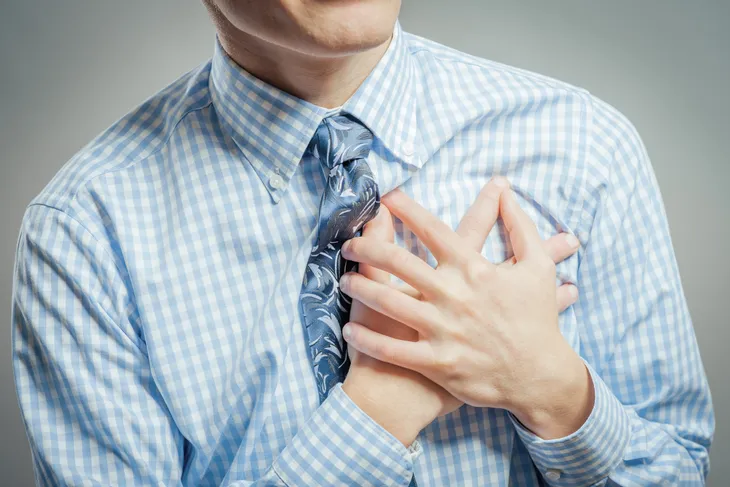
7. Chest Pain or Tightness
Oftentimes, blood clots can cause sharp chest pain or tightness due to restricted breathing, particularly if the clot detaches and reaches the lungs. As you know, a blood clot that enters the lung is referred to clinically as a PE, a potentially life-threatening condition. Chest pain may also be caused by other medical conditions, such as heart attacks or pneumonia, so getting an emergent evaluation is imperative.
8. Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath along with rapid breathing may be another symptom of DVT, especially if a clot breaks off and enters the lung (i.e., PE). If you develop rapid breathing, along with some of the other symptoms on this list, you should see a doctor immediately.
9. Accelerated Heart Rate
An accelerated heart rate (known clinically as tachycardia) may be a sign of DVT. Of course, there are many medical conditions that can cause this symptom. If it occurs along with rapid breathing and shortness of breath, it may indicate that the blood clot has entered the lungs or chest area (i.e., PE).
10. Dizziness or Lightheadedness
As a result of an accelerated heart rate and shortness of breath, you may experience dizziness or lightheadedness, even pass out (clinically referred to as syncope). This usually is the result of the blood clot entering a vital organ, such as the heart or lungs. At this point, the blood clot has the potential to be fatal, and you will need emergency attention immediately.