While approximately 59-million people in the US suffer from thyroid issues, the great majority aren’t even aware they have a thyroid problem. However, when the thyroid (the butterfly-shaped gland in the neck) is dysfunctional, it can cause an array of health issues, including weight gain, sexual dysfunction, depression, heart disease, and extreme fatigue. That’s why it’s vital to determine if you have any of the following common symptoms that might indicate a thyroid condition…
1. Fatigue
Feeling exhausted when you wake up, feeling as if 8 or 10-hours of sleep a night is insufficient, or being unable to function all day without a nap can all be signs of a thyroid problem. With an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism), you may also have nighttime insomnia that leaves you exhausted during the day. Fatigue symptoms are usually mild at first before increasing in intensity.
The key identifier of thyroid-related fatigue is that is remains unrelieved, no matter how much you sleep at night or nap during the day. This fatigue inhibits your ability to remain productive in day-to-day life, and it’s often what causes them to see a doctor for a diagnosis.
2. Weight Changes
If you’ve tried every low-fat, low-carb, and low-calorie diet with little weight loss success, you might have an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism). An underactive thyroid gland is like miring your metabolism in quicksand, slowing it down to the point of ineffectualness.
With an overactive thyroid, or hyperthyroidism, patients usually cannot gain weight, no matter how much they eat. This is because an overly active thyroid pushes the metabolisms to warp speed, causing the body to burn calories like rocket fuel. Many patients also experience dramatic and unexplained weight loss.
3. Muscle and Joint Pain
Unexplained aches and pains in the muscles and joints (with little or no physical exertion) can be symptomatic of a thyroid condition. These pains can be intense and unrelenting, interfering with normal activities and inhibiting the patient’s ability to perform movements and actions within their normal range.
These symptoms can also manifest as muscle weaknesses, rendering specific muscle groups suddenly unable to bear normal workloads. Some people experience tremors in their hands, which can become severe. Pain, swelling and stiffness can also occur in the muscles and joints.
4. Swollen Neck
Swelling in the neck or a visibly enlarged thyroid that leads to neck pain and a gravelly voice can indicate thyroid disease. This condition is known as a “goiter,” and it typically presents as a localized enlargement at the base of the neck, affecting the skin and surrounding tissues which that protect the actual thyroid gland.
However, the presence of a goiter does not necessarily signal that there is a problem with the thyroid itself. This type of swelling simply means that there is some underlying condition that is affecting the size of the thyroid and causing it to grow, and if it occurs in isolation without the presence of other symptoms, it may not require aggressive treatment.
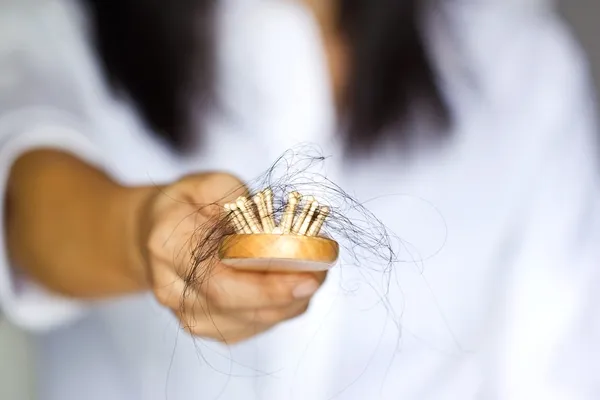
5. Hair and Skin Changes
The hair and skin often show the first signs of thyroid problems, including symptoms such as dry hair, loss of hair, scaly skin, or excessively dry skin. Normal, regulated hair growth is actually dependent on the proper functioning of the thyroid gland and problems with thyroid function can cause balding of the head in both men and women as well as the loss of body hair.
The thyroid gland also regulates the delivery of hormones that play important roles in the maintenance of healthy skin. When the thyroid is underactive or overactive, these hormones aren’t delivered in the proper quantities and noticeable changes in the skin are the end result.
6. Bowel Disturbances
Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can cause changes in bowel habits, as both conditions interfere with the body’s ability to digest food and generate waste. People suffering from hypothyroidism often experience difficulties in passing bowel movements, resulting in chronic constipation. Bowel movements can also be painful and cause additional problems such as hemorrhoids.
For people with hyperthyroidism, bowel movements can become more frequent and more urgent. Diarrhea can also take place. Stools tend to be loose, with a higher volume of liquid and may occur even if the patient has had little to eat.
7. Menstrual Abnormalities
Both an underactive and overactive thyroid gland can disrupt women’s menstrual cycles, and like other condition-dependent symptoms, the nature of the changes depend on whether the patient is suffering from hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. Women with underactive thyroid glands may experience lighter than normal periods, and they may also miss periods altogether.
On the other hand, overactive thyroid glands can cause heavier than normal periods or periods that last several days longer than normal. The menstrual cycle itself may shorten and spotting can occur.
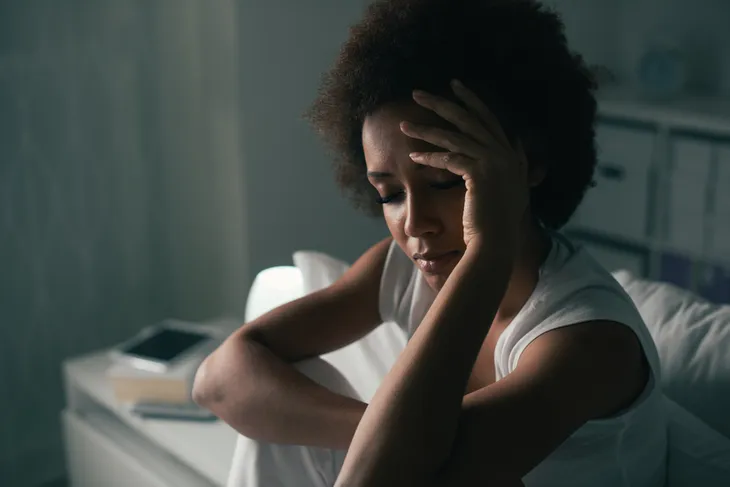
8. Depression
Depression or anxiety disorders can indicate thyroid disease, although these symptoms are typically not enough on their own to warrant a diagnosis. These psychiatric symptoms and mood disturbances may present in a generalized or acute manner. In other words, patients may slowly sink into sustained periods of mild to severe depression, or they could experience unexpected, sudden and intense outbursts of symptoms, such as panic attacks.
Mood imbalances are more often seen with underactive thyroid glands. These symptoms may be accompanied by a general feeling of malaise or lethargy, an inability or lack of desire to concentrate, or a feeling of mental sluggishness.
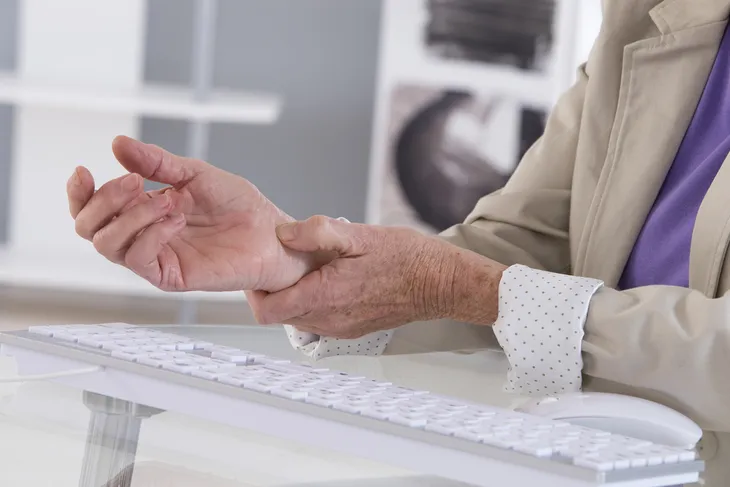
9. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Weakness or tingling in the arms, wrists, or hands may be a sign of carpal tunnel syndrome, which is a common sign of an undiagnosed thyroid condition. While clinically significant numbers of patients experience these symptoms, many doctors and even specialists are not aware of the strong link between thyroid problems and carpal tunnel syndrome. As such, the root cause of the carpal tunnel symptoms is often misdiagnosed.
Treatment for thyroid-related carpal tunnel syndrome is the same as for stress or injury-related carpal tunnel syndrome. Ergonomic improvements, wrist braces, physical therapy, specialized exercise regimens, and anti-inflammatory medications may all be recommended.
10. Family History
If you have a family history of thyroid disease or “goiter,” you may have thyroid problems down the road. The disease is believed to have a strong genetic component, and you should be particularly vigilant if you have a close female relative who develops an overactive or underactive thyroid condition.
Additional risk factors include a family history of autoimmune disorders, age, and gender. Women have thyroid problems more often than men, and the majority of cases appear in patients who are over 50 years of age. Thyroid disease is yet another reason you should cease to smoke, as research has found that smokers of both genders are at increased risk.
11. Feeling Jittery and Anxious
As mentioned earlier, experiencing anxiety can indicate there may be an issue with your thyroid. However, these symptoms may not necessarily present themselves as a full-blown attack.
Rather, you may feel wired or jittery, as if you’ve drank far too many cups of coffee or experience nervousness and agitation. This generally occurs with hyperthyroidism, because the thyroid gland is producing too much of the thyroid hormone, resulting in the body constantly feeling like it needs to “go go go.” So if you’ve found it hard to relax as of late, an overactive thyroid may be to blame.
12. Heart Palpitations
Oftentimes, the feelings of anxiousness and jitteriness just mentioned are accompanied by heart palpitations, such as feeling like your heart is skipping a beat or beating more rapidly than normal (known medically as tachycardia). These feelings may be felt in the chest or at a pulse point on the body, and are a sign of excess production of thyroid hormone in the body, which is what happens with hyperthyroidism.
With hypothyroidism, however, the opposite can occur. Meaning, the heart rate may slow down. This is because the thyroid hormone regulates heart rate. So, if there’s an insufficient amount of hormone being produced by the thyroid gland, the heart may beat around 10 to 20 beats per minute slower than it typically would.
13. Brain Fog
The brain’s ability to function normally is also impacted by problems with the thyroid—both those that are underactive and those that are overactive. With hypothyroidism, for instance, people often feel like they have “brain fog” and are more sluggish and forgetful than normal.
Conversely, those with hyperthyroidism tend to have difficulty concentrating. This is due to excess thyroid hormone production, which makes it hard for them to relax and focus, and sometimes results in anxiety and panic attacks, as mentioned earlier.
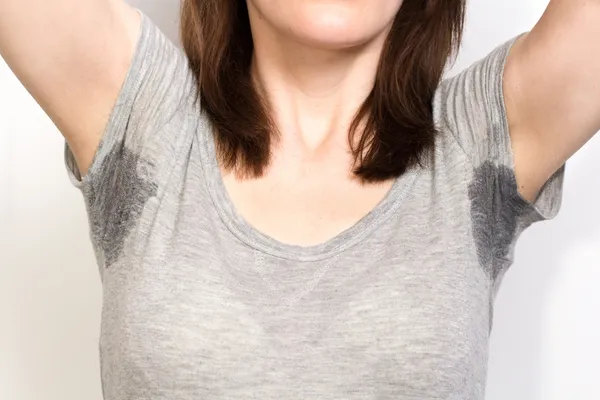
14. Excessive Sweating
If you suddenly find the armpit area of your clothing to be wet for no apparent reason (as in, you’re not physically exerting yourself), it may be a sign of a thyroid problem, more specifically, hyperthyroidism. It occurs because excess thyroid hormone causes the cells to be overactive, resulting in your body temperature being higher than normal and causing excessive perspiration.
In contract, people with hypothyroidism tend to feel the opposite meaning they often feel cold or have the chills. This is due to the fact that, with an underactive thyroid, the body’s cells are burning less energy. And because that energy is what gives the body its heat, less of it means the body’s temperature will be lower than normal.
15. Low Libido and Fertility Issues
A thyroid problem may also be the culprit of a decreased desire to be intimate. With hypothyroidism, low libido is due to there being too little of the thyroid hormone in the body, but symptoms, such as lack of energy and muscle and joint pain, may also contribute.
Along with low libido, women with hypothyroidism may also find it difficult to conceive, or if they do get pregnant, oftentimes they have miscarriages early on. This is also the case for women with hyperthyroidism, as both conditions can interfere with ovulation, impairing fertility and causing complications.