We’re all told things by our parents and friends while growing up that we take as gospel, or hear things from our favorite celebrities that we assume must be true (after all, they’re celebrities).
However, while there are many very real health risks out there to be mindful of, there are some that you can outright ignore – or at least stop worrying about so much, because worrying is not good for your health. Here are 13 health myths to bust…
Eyesight and Proximity to Television
This is one of those classic things we all heard from our parents – “don’t sit so close to the television! You’ll ruin your eyes!” While staring at a television for too long can strain your eyes, modern TVs don’t really pose any danger in terms of causing permanent damage, notes the source.
It explains that the roots of this myth may be due to the fact that prior to the 1950s, some televisions had “radioactive components,” which could indeed lead to eyesight problems (and who knows what else). It assures that modern televisions have “sufficient shielding” to protect the viewer.
Coffee Consumption and Height
Business Insider explains there’s a school of thought out there that drinking too much coffee will stunt your growth. Not true, says the source. “Most research finds no correlation between caffeine consumption and bone growth in kids,” it says – but what kids are drinking several cups of coffee per day?
The site says research about the effects of caffeine on adults has shown it can “slightly limit” calcium absorption, but that impact is so low that “a tablespoon of milk will more than adequately offset the effects of a cup of coffee.” Perhaps you could add a dash of milk to your black coffee for bone health, but chances are you’re fully grown by the time you’re an adult.
Antiperspirant and Breast Cancer
WebMD says some women are apparently of the belief that using antiperspirant to control sweating can lead to breast cancer. However, this belief is apparently perpetuated from some scientists who warn certain chemicals can be absorbed through underarm tissue.
“The idea is they end up in breast tissue and make tumors more likely,” says the source. However, the National Cancer Institute thinks differently, saying there’s no evidence to connect antiperspirants and deodorants to breast cancer, according to WebMD.
Cold Weather and Catching a Cold
This is an easy one to believe – we mean, it’s called a “cold,” so of course people relate being sick to the lowered outdoor temperature. However, EveryDayHealth.com explains there are “many myths about the connection between weather and colds.”
Being outside in the cold on its own won’t give you a cold. However, the source does point out that hypothermia – when your core temperature drops dangerously from exposure to frigid temperatures – can compromise immunity, which can leave you more vulnerable to catching a cold. Cold air can also cause vasoconstriction (narrowing of vessels) in the nose, which can compromise the nose’s job to filter out infections, says the source. So, both sides could be right on this one, depending how you look at it.
Toxins and Cleanses
Cleansing diets and potions to remove “toxins” in the system remain super popular, but detoxing your body is a flat-out myth, notes many sources including The Guardian. “There’s no such thing as ‘detoxing.’ In medical terms, it’s nonsense,” adds the source.
You are in need of detoxing if you’re addicted to a harmful substance, it points out. But the type of detox that is related to diet is apparently bogus. If toxins from what you eat can’t be naturally eliminated from your body, “you’d likely be dead or in need of serious medical intervention,” it says. The liver, kidneys, skin and even lungs do a fine job without a detox diet.
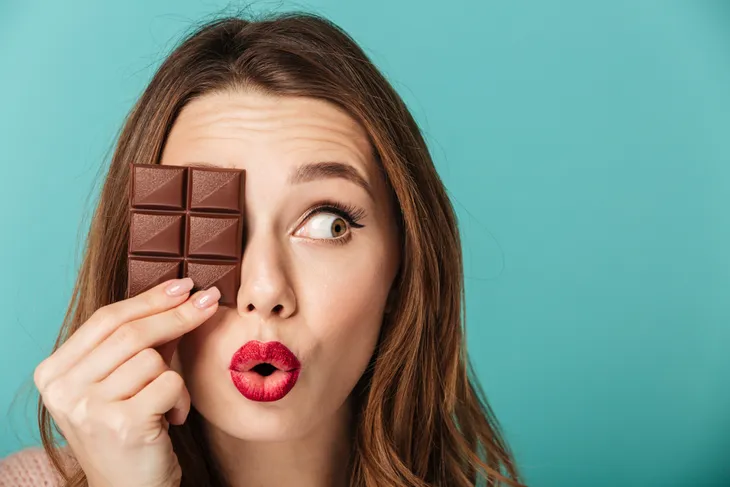
Chocolate and Acne
Are you steering clear of enjoying that chocolate bar stashed in the pantry because you don’t want to ruin your pristine skin? Give it a rest, and eat the chocolate bar. Business Insider says there’s a study that shows chocolate does not mean you’ll break out in acne.
It explains researchers gave subjects candy bars containing 10-times the usual amount of chocolate (yum) for one month, and during the same time frame gave other subjects “fake chocolate” bars. When they compared the number of zits before and after the study, there was no difference in either group, says the source.
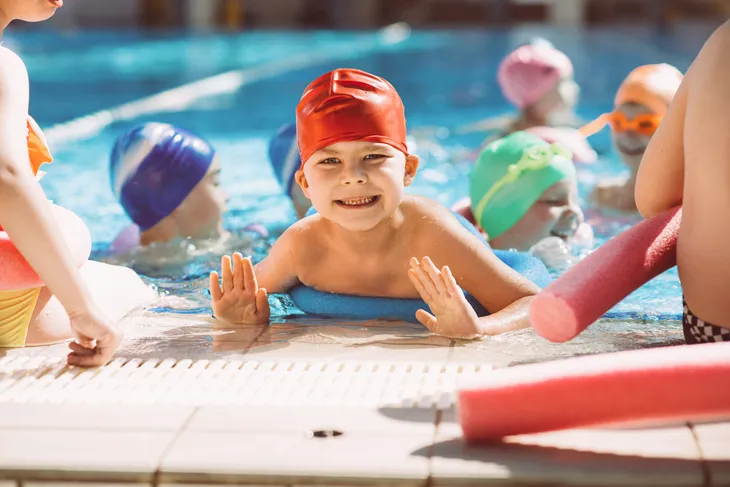
Swimming On a Full Stomach
Think back to how many times you were warned by your parents not to swim right after eating lunch or dinner. The myth points to an impact on your ability to swim and developing potentially life-threatening cramps, notes LiveStrong.
“The simple fact is, however, that swimming on a full stomach does not significantly impact your ability to swim,” it adds. It explains it’s true that blood rushes to the stomach to aid in digestion after eating, but it won’t result in your muscles losing their ability to function from lack of blood. You may get cramps if you swim “vigorously” following eating, but less than 1-percent of drowning deaths in the U.S. are linked to a full stomach, it adds.
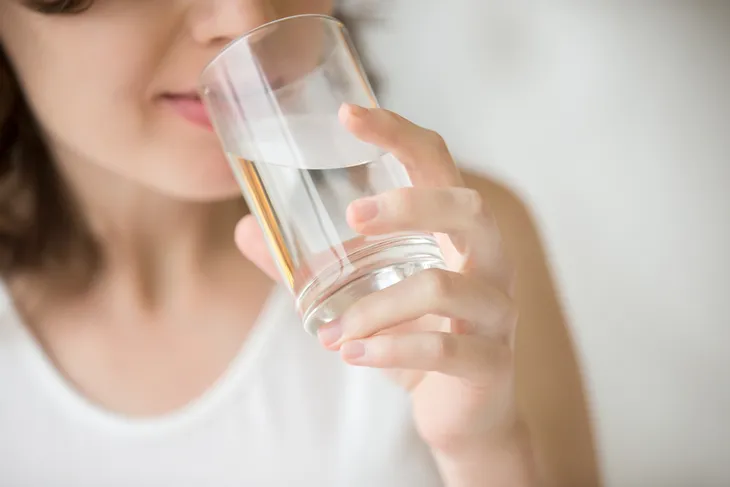
Water Consumption and Proper Hydration
Bustle.com also says many people scramble to meet that imaginary quota of 8-glasses a day of water, so they don’t dry up and blow away. While staying hydrated is very important to overall health, 8-glasses is not a one size fits all approach, says the source.
It adds that you also unknowingly consume a lot of water through the foods you eat, and in some cases, even without eating these foods, 8-glasses may be too much. Remember, there is actually such a thing as hyponatremia, which is a potentially fatal condition caused by drinking too much water too quickly (which dilutes essential sodium in your system to dangerously low levels).
Vaccines and Health Conditions
Reader’s Digest takes on the myth about vaccines causing autism in particular (although there are other fears about flu vaccines that can be debunked). The concern is that a preservative called thimerosal, which is mercury, could cause damage – “but the truth is it wasn’t the dangerous kind of mercury, it was the naturally occurring kind,” it notes.
Reader’s Digest says this preservative was “removed from all vaccines” in 2002, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention notes that the Measles, Mumps, and Rubella (MMR) vaccines never contained thimerosal. The CDC does note multi-dose flu vaccines are still available with or without the preservative.
Sunscreen and Skin Cancer
Reader’s Digest also talks about the belief that certain chemicals in sunscreens (some which have been removed due to concerns) can actually cause skin cancer. “However this has never been proven, and the studies linking the two are greatly flawed,” it notes.
The truth is that those who most regularly wear sunscreen are at the greatest risk of sun damage and skin cancer due to their lighter skin type. The source points out there would be a lot more people with skin cancer if they avoided sunscreen altogether. Still, if you have concerns, there are scent-free and chemical-free sunscreens out there on the market.
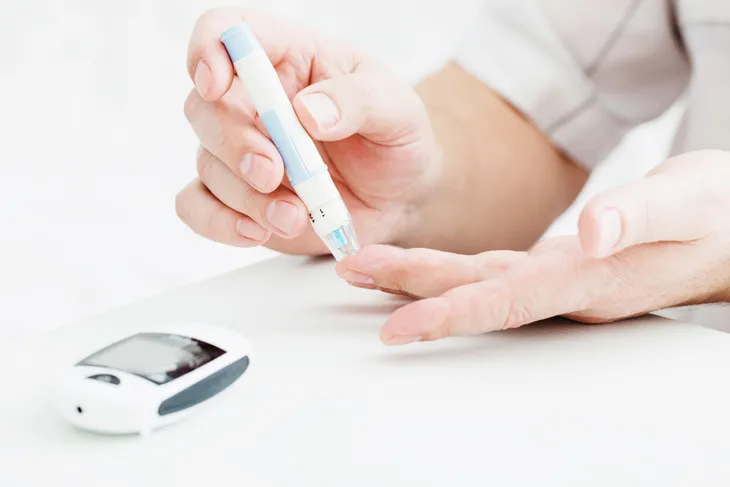
Sugar and Diabetes
Eating too much sugar does not mean you’re going to wake up with diabetes. The American Diabetes Association says the relationship between sugar and diabetes “is not that simple,” and that there are other factors involved.
Type 2 diabetes, the type commonly associated with sugar intake, is actually more about lifestyle factors, says the source. “Being overweight does increase your risk for developing type 2 diabetes, and a diet high in calories from any source contributes to weight gain,” it says. Sugary drinks such as soda and fruit punch can definitely add to this risk as they pack hundreds of calories per serving, it adds.
Sex and Heart Attacks
There’s another (unfortunate) school of thought that dictates lovemaking can raise the risk of having a heart attack. This simply isn’t true; in fact, the opposite is true, according to the CBC in Canada.
“Researchers found that men who had sex at least twice a week were half as likely to die of heart disease,” says the source. It also notes the act helps keep estrogen and testosterone levels in check, and lowers your chance of osteoporosis (leading to brittle bones). Those are good reasons to get busy!
Cancer Isn’t Contagious
Unlike some illnesses that are viral, you can’t catch cancer from another person, assures the American Cancer Society. “There is no evidence that close contact or things like sex, kissing, touching, sharing meals, or breathing the same air can spread cancer from one person to another,” says the source.
This is because unlike viruses and bacteria, cancer cells are generally unable to survive in the body of a healthy person, says the source. A healthy immune system will quickly recognize invaders and destroy them – and that includes cancer cells from another person, it adds. It’s true that some organ transplants from cancer patients have caused cancer in the recipients, but that’s because an organ recipient takes medication to weaken their immune system so their system doesn’t attack the new organ, says the cancer society.