You’ve probably heard of the thyroid, but you may not be as familiar with the condition known as hyperthyroidism, which involves the thyroid gland producing an unnecessary amount of a hormone called thyroxine. The result: your body’s metabolism speeds up to the point where it can be difficult to maintain a healthy body weight. Hyperthyroidism can also result in excessive sweating, anxiety, irritability, and even heart problems.
The good news is that there are a number of ways to help counteract the symptoms associated with hyperthyroidism. Treatment options range from medications to surgery and the removal of the thyroid gland itself; the option for you will depend on your specific health situation.
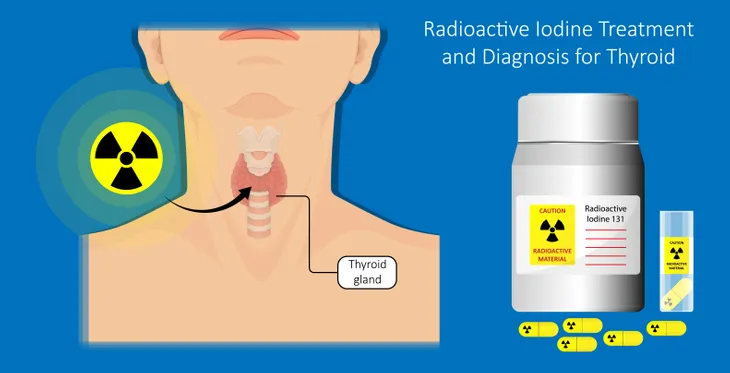
Radioactive Iodine Treatments
It may not sound like the best way to help your body fight hyperthyroidism, but radioactive iodine — taken by mouth — can play a key role in suppressing the problematic symptoms associated with this condition. That’s because, once the radioactive iodine is fully absorbed by the thyroid gland, the gland responds by shrinking in size.
Over time — usually three to six months or so — this will result in the symptoms from hyperthyroidism subsiding to the point where the patient can resume normal lifestyle activities. However, it is possible that a radioactive iodine treatment will make the thyroid go from overproducing to underproducing, which could make it easier to gain weight than before. To limit the side effects of radioactive iodine treatment, doctors may prescribe a medication capable of restoring thyroid activity to acceptable levels.
Anti-Thyroid Drugs
Anti-thyroid drugs can help with hyperthyroidism by restricting the production of hormones that can present health problems when released in excess. As with many medications, however, results take time, with symptoms usually improving after two to three months. Treatment using anti-thyroid drugs can last some time, such as a year or longer.
Of course, not all individuals will see the same results while taking anti-thyroid drugs. Some of these medications can have serious side effects that may actually make life more difficult than hyperthyroidism. For example, the drug propylthiouracil can lead to liver damage in some patients. In any case, if you’re prescribed anti-thyroid drugs, be sure to keep in regular contact with your physician and carefully describe how the medication (or medications) are affecting you.
Beta Blockers
Beta blockers are most often prescribed to patients struggling with high blood pressure. Because this is often a side effect of hyperthyroidism, physicians often prescribe beta blockers to people with serious thyroid problems. However, beta blockers are incapable of doing anything to improve the functionality of the thyroid itself. Should the hyperthyroidism issue subside with the use of other treatments, a physician may cease the use of beta blockers.
There are a number of side effects associated with beta blockers, including feeling tired, upset stomach, difficulty going to the washroom, and headaches. Be sure to talk to your doctor if you experience any of these side effects.
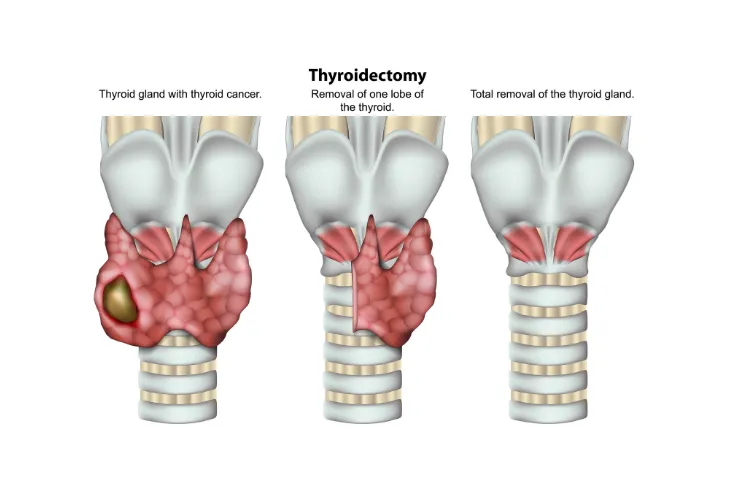
Thyroidectomy
As always, surgery is widely considered a last resort in treating a thyroid condition. However, there are many cases of hyperthyroidism where there is no choice but to go through surgery. For example, many pregnant women cannot be prescribed anti-thyroid drugs because of the impact they could have on the pregnancy.
A thyroidectomy involves the removal of much of the thyroid gland. This is a risky procedure that could result in the vocal cords becoming damaged. Even if this is not the case, anyone who has part of their thyroid removed will need to take medications to regulate their hormones for the remainder of their lives. For this reason, your doctor will be very hesitant to go the surgery route; if they’re not, you may want to seek a second opinion.
Orbital Decompression Surgery
This type of surgery is only necessary if the patient’s hyperthyroidism is the result of Graves’ disease, an autoimmune problem. Graves’ disease often affects the eyes; in mind cases, it can make the eyes dry and uncomfortable. However, in more serious cases it can cause pain and even vision problems that may require orbital decompression surgery.
In this surgery, the surgeon must take out the bone dividing the eye socket and sinuses. If successful, the procedure can significantly improve vision and lessen general discomfort. Potential side effects include double vision which can last for some time following the surgery.
Eye Muscle Surgery
Another surgery related to Graves’ disease and hyperthyroidism involves removing scar tissue from the eye muscles. These scars are often related to the underlying problem with Graves’ disease and can result in double vision or other serious vision problems.
In this type of surgery, the surgeon removes the muscle connecting the eyeball and places it in a position that is less likely to cause double vision or other vision problems. Although end results may take some time to show, a successful surgery can eliminate double vision. Unfortunately, someone with serious vision problems related to Graves’ disease and hyperthyroidism may require several surgeries to complete the transition to improved vision.