When sepsis (a condition that results when an infection enters the bloodstream) occurs, the immune system is greatly compromised when the body attempts to put the proper defenses in place. However, if existing health concerns (i.e., cancer, a recent surgery, AIDS, or immune deficiency due to advanced age) are an issue, a blood infection can be life threatening.
That’s why it’s vital to recognize the top 14 signs of blood infection…
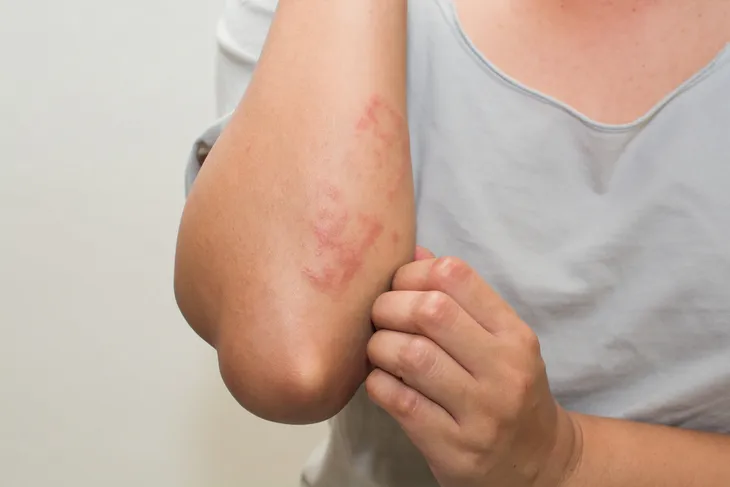
1. Skin Spots
Oftentimes, the first sign of a blood infection will show itself as reddish or spotted patches on the extremities (i.e., hands, legs, arms, and feet), as well as other parts of the body.
2. Abnormal Heart Rate
In advanced cases, blood infection can impact the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the major organs, including the heart. As a result your heart rate, or pulse, may increase or decrease without reason (meaning without cause such as following periods of exertion).
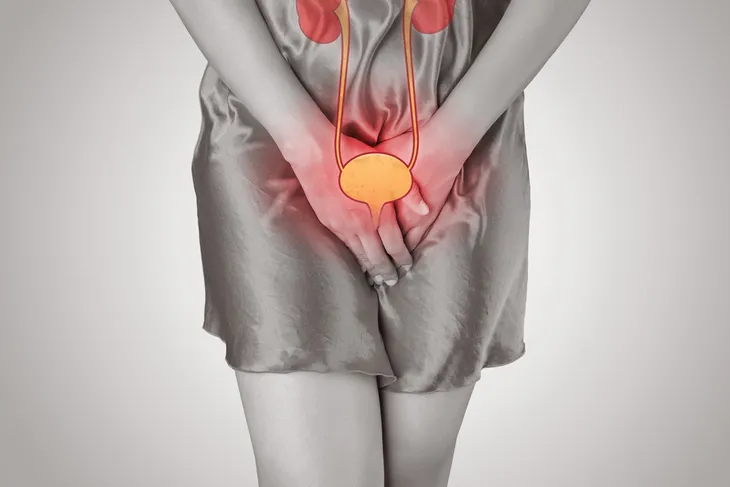
3. Urination Issues
Many times, an advanced blood infection will also impact the kidneys, resulting in reduced urination or urge to urinate, particularly in elderly individuals with existing incontinence issues.
4. Agitation
Agitation on its own is not necessarily a sign of a blood infection. However, in combination with other symptoms, it can be a sign if it comes on suddenly, increases, and lasts for more than a few days.
5. Impaired Focus
If sepsis occurs, your mental state can become affected. Sepsis is basically the immune system’s response to infection, where chemicals are released into the blood to prevent further infection, which can impair blood flow and deprive the brain of nutrients and oxygen.
6. Dizziness
You may become dizzy, confused, disoriented, and unable to focus your thoughts when you have sepsis due to the body reacting to the infection, especially if the infection is left untreated and the blood pressure plummets.
7. Nausea and Vomiting
Sepsis can originate in various parts of the body, making nausea (and eventually vomiting) one of the first signs that infection is present.
8. Fever
An infection in the bloodstream is often indicated via a sudden and unexplained high fever (i.e., greater than 38-degrees Celsius or 100.4 Fahrenheit).
9. Chills
In advanced cases of sepsis, your body temperature may plummet and lead to hypothermia (an abnormally low body temperature), causing severe chills and shaking.
10. Rapid Breathing
Pulse isn’t the only thing that can accelerate with sepsis; a person’s breathing can as well. In fact, rapid breathing is considered to be one of the first clues that someone may have a blood infection.
There are a couple of reasons it can occur. The first being that the infection is in the lungs and is causing decreased oxygen levels. The second is that, as the infection worsens, the body needs more and more oxygen, resulting in shortness of breath. Medical guidelines say to be mindful of a respiratory rate that is higher than 22-breaths per minute and to seek immediate medical attention if it occurs.
11. Diarrhea
Because gastrointestinal issues, such as diarrhea, can occur for a wide variety of reasons, from a virus to anxiety, they are not often thought to be a symptom of a blood infection. As the digestive system is sensitive to changes or functional disruptions in the body, diarrhea may be the body’s first attempt to alert you that something is wrong.
Alternatively, you may get diarrhea because the blood infection is being caused by an infection that originated in the gut. Although diarrhea on its own is not necessarily an indication of sepsis, if you are experiencing it alongside other symptoms mentioned on this list, be sure to book an appointment with your doctor to get examined.
12. Pain and Weakness
It’s common for people with sepsis to experience pain, as the body is trying to fight off the infection. This pain may be felt all over, or concentrated in a specific area, such as the joints of the wrists, hips, knees, and ankles.
In addition to pain, weakness is another symptom that affects those with a blood infection. This may be characterized by a lack of strength and muscle wasting, causing individuals to avoid having to move. In some cases, weakness, along with fatigue and low energy levels, may persist even after the sepsis has been treated.
13. Pale and Cold Skin
As mentioned earlier, people with a blood infection oftentimes develop red spots or patches on their skin. But this isn’t the only way the skin can be affected by sepsis; it may also become quite pale in color. This occurs because the body is moving blood to its most vital organs, drawing it away from areas that are considered less important for survival, such as the skin.
In addition to becoming pale due to decreased blood flow, the skin may also feel clammy and cool to the touch. If it occurs in the extremities, such as the hands and feet, it may be indicative of poor blood supply.
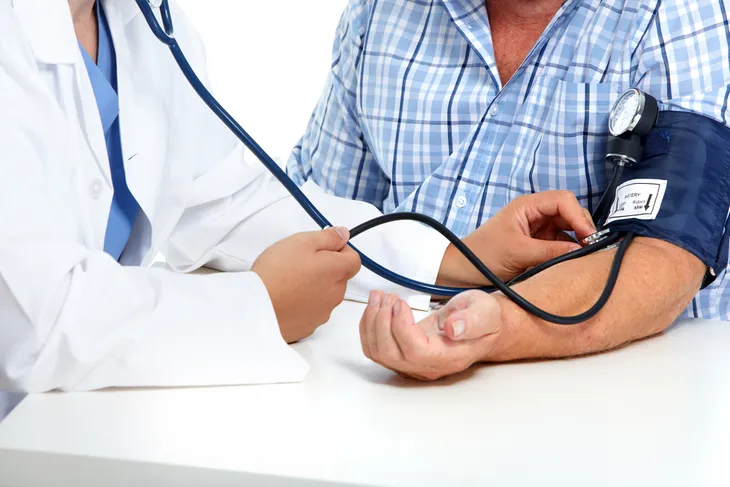
14. Low Blood Pressure
Low blood pressure (known clinically as hypotension) is an especially serious sign of a blood infection, as it can indicate septic shock—the most critical stage of sepsis. It occurs because the body’s blood vessels are losing fluid and the veins and arteries are relaxing, which results in the blood pressure plummeting and blood not circulating through the body as normal.
Due to the severity of this symptom, new medical guidelines for sepsis indicate that doctors should be concerned if systolic blood pressure (the top number in a blood pressure reading) decreases to less than 100-mmHg.